Abstract
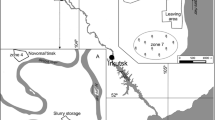
Mercury, zinc and copper contamination was evaluated in soils and fluvial sediments from an abandoned gold mining site at Descoberto Municipality (southern Minas Gerais State, Brazil). Metals bioavailability and potential mobility were studied through physical, chemical and mineralogical characterization, geoaccumulation indexes calculations, mercury speciation and determination of potentially bioavailable contents of zinc and copper. Values of pH were in the neutral range, while organic matter concentrations were very low. Mineralogical characterization, in the total samples, indicated the presence of quartz, kaolinite and gibbsite for all samples. Total mercury, zinc and cooper concentrations were higher than the limits recommended by Brazilian documents. Geoaccumulations indexes revealed that most of the sediment samples were low to moderately polluted by zinc and copper, while just one sample was very strongly polluted by mercury. Mercury speciation revealed the predominance of the elementary form for all samples, and low concentrations for exchangeable, strongly bound and residual fractions. Zinc and copper behavior was strongly controlled by iron and aluminum concentrations, while their bioavailable contents were very low in comparison with the total concentrations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino O, Giacomino A, Malandrino M, Mentasi E (2007) The efficiency of vermiculite as natural sorbent for heavy metals: application to a contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 181:149–160
Branco OEA, Carvalho-Filho CA, Trindade MC (2005) Evaluation of mercury contamination in soils: the case of the rural area of the municipality of Descoberto, State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. In: International conference on heavy metals in the environment, 8, Rio de Janeiro, Book of Abstracts, p 35
Carvalho-Filho CA, Trindade MC, Branco OEA (2005) Contamination by mercury from past gold mining activities at Descoberto, State of Minas Gerais, Brazil: historical reconstitution. In: International conference on heavy metals in the environment, 8, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Book of Abstracts. p 74
Castilhos ZC, Bidone ED, Hartz SM (2001) Bioaccumulation of mercury by Tucunaré (Cichla ocellaris) from Tapajós River region, Brazilian Amazon: a field dose-response approach. Bull Environ Contaminat Toxicol 66:631–637
Caussy D, Gochfeld M, Gurzau E, Neagu C, Ruedel H (2003) Lessons from case studies of metals: investigating exposure, bioavailability and risk. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 56:45–51
Cesar RG, Egler SG, Polivanov H, Castilhos ZC, Rodrigues APC, Araujo PC (2008) In: Biodisponibilidade de metilmercúrio, zinco e cobre em distintas frações granulométricas de solo contaminado utilizando oligoquetas da espécie Eisenia andrei. Anuário do Instituto de Geociências (UFRJ). Available via <http://www.anuario.igeo.ufrj.br/anuario_2008_2/2008_2_33_41.pdf>. Accessed 12 Feb 2010
CETESB (Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental) (2005) In: Valores Orientadores para Solos e Águas Subterrâneas no Estado de São Paulo. Available via <http://www.cetesb.sp.gov.br/Solo/relatorios/tabela_valores_2005.pdf>. Accessed 20 Mar 2008
CONAMA (Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente) (2004) In: Resolução 344. Available via <http://www.ibrapam.com.br/leis/344%202004%20Dragagem.pdf>. Accessed 20 Mar 2008
DePaula FCF, Mozeto AA (2001) Biogeochemical evolution of trace elements in a pristine watershed in the Brazilian southeastern coastal region. Appl Geochem 16:1139–1151
Drasch G, Bose-O’Reilly S, Beinhoff C, Roider G, Maydll S (2001) The Mt. Diwata study on the Philippines (1999)—assessing mercury intoxication of the population by small scale mining. Sci Total Environ 267:151–168
Egler SG, Rodrigues-Filho S, Villas-Boas R, Beinhoff C (2006) Evaluation of mercury pollution in cultivated and wild plants from two small communities of the Tapajós gold mining reserve, Pará State, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 368:424–433
Egler SG, Ramos AS, Cesar RG (2008) Transposição de mercúrio para plantas e minhocas em um antigo garimpo de ouro em Descoberto, Brasil. In: Brazilian congress of ecotoxicology, 5, Bento Gonçalves, RS, Book of abstracts, p 89
EMBRAPA (EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUÁRIA) (1997) Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos. In: Manual de métodos de análises de solo. Rio de Janeiro, RJ, p 212
Gimeno-García E, Andreu V, Boluda R (1996) Heavy metals incidence in the application of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides to rice farming soils. Environ Pollut 92:19–25
Hylander LD, Meili M, Oliveira LJ, Silva ED, Guimarães JR, Araujo DM, Neves RP, Stachiw R, Barros AJP, Silva GD (2000) Relationship of mercury with alumnium, iron and manganese oxi-hydroxides in sediments from the Alto Pantanal, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 260:97–107
Katz SA, Salem H (1993) The toxicology of chromium with respect to its chemical speciation: a review. J Appl Toxicol 13:217–224
Lechler P, Miller J, Hsu L, Desilets M (1997) Mercury mobility at the Carson River Superfund Site West-Central Nevada, USA: interpretation of mercury speciation data in mill tailings, soils and sediments. J Geochem Explor 58:259–267
Lechler PJ, Miller JR, Lacerda LD, Vinson D, Bonzongo JC, Lyons WB, Warwick JJ (2000) Elevated mercury concentrations in soils, sediments, water and fish of the Madeira River basin, Brazilian Amazon: a function of natural enrichments? Sci Total Environ 260:87–96
Lukkari T, Astsinki M, Väisänen A, Haimi J (2005) Toxicity of copper and zinc assessed with three different earthworms tests. Appl Soil Ecol 30:133–146
Martin CW (2004) Heavy metal storage in near channel sediments of the Lahn River, Germany. Geomorphology 61:275–285
Matschullat J (2000) Arsenic in the geosphere—a review. Sci Total Environ 249:297–312
Matschullat J, Borba RP, Deschamps E, Figueiredo BR, Gabrio T, Schwenk M (2000) Human and environmental contamination in the Iron Quadrangle, Brazil. Appl Geochem 15:181–190
Mello JWV, Roy WR, Talbott JL, Stucki JW (2006) Mineralogy and arsenic mobility in arsenic-rich Brazilian soils and sediments. J Soils Sediments 6:9–19
Müller G (1979) Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins–Veränderungen seit. Umschau 79:778–783
Ohriel DM, Paterson MJ, Blanchfield PJ, Bodaly RA, Gilmour CC, Hintelmann H (2008) Temporal changes in the distribution, methylation, and bioaccumulation of newly deposited mercury in an aquatic ecosystem. Environ Pollut 154:77–88
Palmieri HE, Nalini HA, Leonel LV, Windmöller CC, Santos RC, de Brito W (2005) Quantification and speciation of mercury in soils from the Tripuí Ecological Station, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 368:69–78
Peakall D, Burger J (2003) Methodologies for assessing exposure to metals: speciation, bioavailability of metals, and ecological host factors. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 56:110–121
Peijnenburg WJGM, Jager T (2003) Monitoring approaches to assess bioaccessibility and bioavailability of metals: matrix issues. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 56:63–77
Rea AW, Lindberg SE, Keeler GJ (2001) Dry deposition and foliar leaching of mercury and selected trace elements in deciduous forest thoughfall. Atmos Env 35:3453–3462
Reimann C, Garret RG (2005) Geochemical background—concept and reality. Sci Total Environ 350:12–27
Rodrigues-Filho S, Maddock JEL (1997) Mercury pollution in two gold mining areas of the Brazilian Amazon. J Geochem Explor 58:231–240
Rodrigues-Filho S, Behling H, Müller G (2002) Evidence for lake formation as response to an inferred Holocene climatic transition in Brazil. Quat Res 57:131–137
Rodrigues-Filho S, Castilhos ZC, Santos RLC, Yallouz AV, Egler SG, Nascimento FMF, Pedrozo LR, Villas-boas RC, Veiga MM (2004) Biogeochemical assessment of mercury pollution in two Indonesian gold mining sites. In: International symposium on environmental geochemistry in tropical countries, 4, Búzios, RJ, Book of abstracts, pp 235–237
Roulet M, Lucotte M (1995) Geochemistry of mercury in pristine and flooded ferralitic soils of a tropical rain forest in French Guiana, South America. Water Air Soil Pollut 80:1079–1085
Ruilian YU, Xing YUAN, Yuanhui ZHAO, Gongren HU, Xianglin TU (2008) Heavy metal pollution in intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay, China. J Environ Quality 664:669
Shandro JA, Veiga MM, Chouinard R (2009) Reducing Mercury pollution from artisanal gold mining in Munhena, Mozambique. J Clean Prod 17:525–532
Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall F (2007) Heavy metal contamination of soil and vegetables in suburban areas of Varanasi, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 66:258–266
Solomons W, Förstner U (1984) Metals in the hydrocycle. Springer-Verlag, Berlim, p 349
Veiga MM, Bermudez D, Pacheco-Ferreira H, Pedrozo LR, Gunson A, Berrios G, Vos L, Huidobro P, Roeser M (2005) Mercury pollution from artisanal gold mining in Block B, El Callao, Bolívar State, Venezuela. In: Pirrone N, Mahaffey K (eds) Dynamics of mercury pollution on regional and global scales: atmospheric processes, human exposure around the world. Springer Publisher, Norwell, pp 421–450
Wasserman JC, Hacon S, Wassermann MA (2003) Biogeochemistry of mercury in the Amazonian environment. Ambio 32(5):336–342
Wasserman JC, Calixto RC, Hacon SS, Farias RA, Caires SM (2007) Mercury in soils and sediments from gold mining liabilities in southern Amazon. Quim Nova 30(4):768–773
Weerasooriya R, Tobschall HJ, Wijesekara HKDK, Arachchige EKIAUK, Pathirathne KAS (2003) On the mechanistic modeling of As(III) adsorption on gibbsite. Chemosphere 51:1001–1013
WHO (World Health Organization) (1990) Methylmercury. IPCS environmental health criteria document 101. World Health Organization, Geneva
Windmöller CC, Santos R, Athayde M, Palmieri H (2007) Distribuição e Especiação de Mercúrio em Sedimentos de Áreas de Garimpo de Ouro no Quadrilátero Ferrífero. Quim Nova 30(5):1088–1094
Yallouz AV, Cesar RG, Egler SG (2008) Potential application of a semiquantitative method for mercury determination in soils, sediments and gold mining residues. Environ Pollut 121:429–433
Yin Y, Allem HE, Li Y, Huang CP, Sanders P (1996) Adsorption of mercury by soil: effects of pH, chloride and organic matter. J Environ Quality 25:837–844
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Environmental Foundation of Minas Gerais State (FEAM) and the Centre for Nuclear Technology Development (CDTN), especially Dr. Peter Fleming and Dr. Otávio Branco, for their help during the sampling campaigns. We also thank the geographers Ricardo Sierpe Silva and Nilo Teixeira for confectioning the sampling points map. Ricardo Cesar was supported by a scholarship program for graduate students from the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq). Without such financial help, this work could not be executed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cesar, R., Egler, S., Polivanov, H. et al. Mercury, copper and zinc contamination in soils and fluvial sediments from an abandoned gold mining area in southern Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 64, 211–222 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0840-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0840-8