Abstract
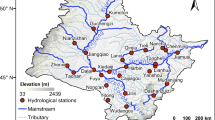
The Songhua River plays a key role in the national development of China, owing to its unique natural condition and resources. Recent changes in the streamflow in the Songhua River are important with regard to local sustainable development and management under the background of global warming and aggravating soil erosion. In order to detect changes in the streamflow, two streamflow series from 1955 to 2004 (observed at the Harbin and Jiamusi stations) in the mainstream of Songhua River basin were obtained, and methods of statistical analysis, wavelet transform, and double mass analysis were employed to analyze the data. Reasons for the changes to the streamflow are discussed with respect to natural and man-made drivers. The results show the following: (1) From 1955 to 2004, the streamflow series present obvious declining trends. (2) The streamflow series followed the pattern of a wet–dry–wet–dry cycle pattern over the past 50 years. In the mainstream of Songhua River, wet years mainly occurred during the periods of 1955–1966 and 1984–1993, while dry years mainly occurred in the 1970s and after 2000. (3) Within the 50-year scale, the streamflow series appeared in the main periods of circa 33-, 13- and 4-year, in which the 33-year periodicity is the strongest. (4) Precipitation and temperature directly influenced the streamflow in the mainstream of the basin. The discharge was positively correlated with the precipitation and negatively correlated with the temperature. In addition, human activity was another important driving factor for streamflow change. (5) In the mainstream of Songhua River basin, the influences on streamflow can be divided into three periods: 1955–1976, 1977–1997, and 1998–2004. In the first period climate change played a dominant role, and during the latter two periods human influences were enhanced significantly.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
An G, Sun L, Lian Y, Shen BZ (2002) The climatic changes analysis of Qian’an in the last 40 years. Clim Environ Res 7(3):370–376
Burn DH, Elnur MAH (2002) Detection of hydrologic trends and variability. J Hydrol 255:107–122
Chatfield C (2004) The analysis of time series, an introduction, 6th edn. Chapman & Hall/CRC, New York
Chen JS, Xia XH, Zhang LT, Li HB (1999) Relationship between water quality changes in the Yangtze, Yellow and Songhua Rivers and the economic development in the river basins. Acta Sci Circumstant 19(5):500–506
Chen XQ, Zong YQ, Zhang EF, Xu JG, Li SJ (2001) Human impacts on the Changjiang (Yangtze) River basin, China, with special reference to the impacts on the dry season water discharge into the sea. Geomorphology 41:111–123
Dai SB, Yang SL, Gao A, Liu Z, Li P, Li M (2007) Trend of sediment flux of main rivers in China in the past 50 years. J Sediment Res 2:49–59
Ding YH, Ren GY, Shi GY (2006) National assessment report of climate change (I): climate change in China and its future trend. Adv Clim Change Res 2(1):3–8
Fu BJ, Wang YF, Lu YH, He CS, Chen LD, Song CJ (2009) The effects of land-use combinations on soil erosion: a case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Prog Phys Geogr 33(6):793–804
Guo JL, Jing XY, Zhang J, Wang YB, Zhang XM, Ji JZ, Fang LJ, Wang YQ (2004) Prediction, assessment and countermeasures against flood in master stream of Songhua River. J Nat Disasters 13(4):37–44
Hu D, Saito Y, Kempe S (1998) Sediment and nutrient transport to the coastal zone. In: Galloway JN, Mellilo JM (eds) Asian change in the context of global climate change: impact of natural and anthropogenic changes in Asia on global biogeochemical cycles. IGBP Publ. Series, vol. 3. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hu W, Shao MA, Wang QJ (2005) Scale-dependency of spatial variability of soil moisture on a degrade slope-land on the Loess Plateau. T CSAE 21(8):11–17
Hu G, Wu YQ, Liu BY, Yu ZT, You ZM, Zhang YG (2007) Short-term gully retreat rates over rolling hill areas in black soil of Northeast China. Catena 71:321–329
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. In: Solomon S et al (eds) Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Jiang JM, Zhang D, Fraedrich K (1997) Historical climate variability of wetness in East China (1960–1992): a wavelet analysis. Int J Climatol 17:968–981
Jin HJ, Li SX, Wang SL, Zhao L (2000) Impacts of climatic change on permafrost and cold regions environments in China. Acta Geogr Sin 55(2):161–174
Jing XY, Guo JL, Zhang J, Wang YB, Zhang XM, Ji JZ, Fang LJ, Wang YQ (2006) Prediction method of lowest water level of Songhua River mainstream in Spring. Meteorol Sci Technol 34(2):147–151
Kahya E, Kalayci S (2004) Trend analysis of streamflow in Turkey. J Hydrol 289:128–144
Labat D, Goddéris Y, Probst JL, Guyot JL (2004) Evidence for global runoff increase related to climate warming. Adv Water Resour 27:631–642
Lettenmaier DP, Wood EF, Wallis JR (1994) Hydroclimatological trends in the continental United States 1948–1988. J Clim 7:586–607
Li X, Li WJ, Zhao ZG (2005) Long-term variation pattern and future trend of precipitation in the valleys of Songhuajiang and Liaohe Rivers. J Appl Meteorol Sci 16(5):593–600
Li CH, Yang ZF, Huang GH, Li YP (2009) Identification of relationship between sunspots and natural runoff in the Yellow River based on discrete wavelet analysis. Expert Syst Appl 36:3309–3318
Liu JR, Pang YX, Tang XL, Dong HW, Chen BQ, Sun CH (2007) Genotoxic activity of organic contamination of the Songhua River in the north-eastern region of the People’s Republic of China. Mutat Res 634:81–92
Miao CY, Wei X, Sun L, Xu X (2007) Characteristics of precipitation in summer seasons in Nenjiang and Haerbin over the past 48 years. Res Sci 29(6):25–31
Miao CY, Ni JR, Borthwick AGL (2010) Recent changes of water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow River basin, China. Prog Phys Geogr 34(4):541–561
Morgan RPC (2006) Soil erosion and conservation. Blackwell Publishing Ltd., Oxford
National Bureau of Statistics (2005) China compendium of statistics, 1949–2004. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Ozaki N, Fukushima T, Kojiri T (2008) Simulation of the effects of the alteration of the river basin land use on river water temperature using the multi-layer mesh-typed runoff model. J Hydrol 215:159–169
Peel MC (2009) Hydrology: catchment vegetation and runoff. Prog Phys GeogR 33(6):837–844
Shi HL, Hu CH, Wang YG, Zhang YQ (2007) Evolution of the stem channel of Songhua River and water demand for maintaining channel stability. Shuili Xuebao 38(4):473–480
Shiau J, Feng S, Nadarajah S (2007) Assessment of hydrological droughts for the Yellow River China, using copulas. Hydrol Process 21:2157–2163
Sun YG, Bai RH (2005) Meteorological disaster in the Nenjiang and Songhua River. Meteorological Press, Beijing
Wang HJ, Yang ZS, Saito Y, Liu JP, Sun XX, Wang Y (2007) Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950–2005): Impacts of climate change and human activities. Glob Planet Change 57:331–354
Xu JX (1996) Wandering braided river channel pattern developed under quasi-equilibrium: an example from the Hanjiang River, China. J Hydrol 181:85–103
Xu JX (2005) The water fluxes of the Yellow River to the Sea in the Past 50 years, in response to climate change and human activity. Environ Manage 35(5):620–631
Xu NP, Zhang GH, Yuan MY, Pan HS (2005) Analysis of floods in main stream of Songhua River and Song-Nen Valley flood in 1998: cause and regularity of occurrence. J Nat Disasters 14(5):14–20
Xu JJ, Yang DW, Yi YH, Lei ZD, Chen J, Yang WJ (2008) Spatial and temporal variation of runoff in the Yangtze River basin during the past 40 years. Quat Int 186:32–42
Yang FS (2001) Analysis and application of the wavelet transform. Science Press, Beijing
Yue S, Pilon P, Phinney B, Cavadias G (2002) The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol Process 16:1807–1829
Zhang GS, Li L, Shi XH, Xu WX, Dong LX, Wang QC (2000) Climatic changes over the upper Yellow River and its effects on water resources. Adv Water Sci 11(3):277–284
Zhang Q, Liu C, Xu C, Xu Y, Jiang T (2006a) Observed trends of annual maximum water level and streamflow during past 130 years in the Yangtze River basin, China. J Hydrol 324:255–265
Zhang Q, Xu C, Becker S, Jiang T (2006b) Sediment and runoff changes in the Yangtze River basin during past 50 years. J Hydrol 331:511–523
Zhang JY, Zhang SL, Wang JX, Li Y (2007a) Study on runoff trends of the six larger basins in China over the past 50 years. Adv Water Sci 18(2):230–234
Zhang YG, Wu YQ, Liu BY, Zheng QH, Yin JY (2007b) Characteristics and factors controlling the development of ephemeral gullies in cultivated catchments of black soil region, Northeast China. Soil Till Res 96:28–40
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the research funding supported by the National Key Basic Special Foundation Project of China (No. 2007CB407204) and State Key Laboratory of Earth Surface Processes and Resource Ecology (No. 2009-KF-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, C., Yang, L., Liu, B. et al. Streamflow changes and its influencing factors in the mainstream of the Songhua River basin, Northeast China over the past 50 years. Environ Earth Sci 63, 489–499 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0717-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0717-x