Abstract
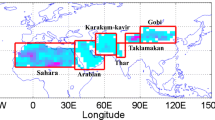
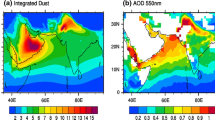
Windblown mineral aerosol dust derived from the crustal surface is an important atmospheric component affecting the earth’s radiation budget. Deposition of atmospheric dust was measured in the fresh snow on glacier no. 1 at the headwater of the Urumqi River in eastern Tian Shan, central Asia. An analysis of seasonal variation of concentrations of dust particles in the snow suggests that the number concentration of dust particle is significantly high from April to June, which may be caused by Asian dust storms in the spring. The comparison of mass-size distribution of dust particles from April to August shows an obvious seasonal change trend. The distribution of particles changes from single model (3–21 μm) in the non-dust period before dust events in April, to bi-model (3–21 and 20–80 μm) during the Asian dust period, and to single model (3–21 μm) after July in the non-dust period again. The Ca2+ concentration in the fresh snow is also very high from April to June, while NH4 + and SO4 2−, as water-soluble constituents, have concentration changes that are different from each other. Backward trajectory was also employed to examine the transport process of air mass in this region.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreae MO (1995) Climatic effects of changing atmospheric aerosol levels. In: Henderson-Sellers) A (ed) Future climates of the world: a modeling perspective world survey of climatology, vol 16. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 347–398
Buck CF, Mayewski PA, Spencer MJ et al (1992) Determination of major ions in snow and ice cores by ion chromatography. J Chrom A 594:225–228
Chun Y, Kim J, Choi JC et al (2001) Characteristic number size distribution of aerosol during Asian dust period in Korea. Atmos Environ 35:2715–2721
Gao Y, Arimoto RM, Zhou Y et al (1992) Relationships between the dust concentrations over eastern Asia and the remote North Pacific. J Geophys Res 97(D9):9867–9872
In HJ, Park SU (2003) The soil particle size dependent emission parameterization for an Asian dust (Yellow Sand) observed in Korea in April 2002. Atmos Environ 37:4625–4636
Junge CE (1963) Air chemistry and radioactivity. Academic Publishers, New York, p 382
Li ZQ, Edwards R, Thompson EM et al (2006) Seasonal variability of ionic concentrations in surface snow and elution processes in snow-firn packs at the PGPI site on Urumqi glacier No.1, eastern Tien Shan, China. Ann Glaciol 43:250–256
Merrill JT, Uematsu M, Bleck R (1989) Meteorological analysis of long range transport of mineral aerosols over the north Pacific. J Geophys Res 94:8584–8598
Nakajima T (1989) Aerosol optical characteristics in the yellow sand events observed in May, 1982 at Nagasaki—Part II Models. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 67:279–291
Niimura N, Okada K, Fan XB et al (1998) Formation of Asian dust-storm particles mixed internally with sea salt in the atmosphere. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 76(2):275–288
Osada K, Hajime I, Mizuka KM (2004) Mineral dust layers in snow at Mount Tateyama, Central Japan: formation processes and characteristics. Tellus 56B:382–392
Prospero JM, Ginoux P, Torres O et al (2002) Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soli dust identified with the nimbus 7 total ozone mapping spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev Geophys 40 (1): 2–1–2–31. doi: 10.1029/2000RG000095
Seinfeld JH, Pandis SN (1998) Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change. Wiley, New York, p 1326
Steffensen JP (1997) The size distributions of microparticle from selected segments of the Greenland Ice Core Project ice core representing different climatic periods. J Geophys Res 102(C12):26755–26763
Tegen I, Lacis A (1996) Modeling of particle size distribution and its influence on the radiative properties of mineral dust aerosol. J Geophys Res 101:19237–19244
Uematsu M, Duce R, Prospero JM (1983) Transport of mineral aerosol from Asia over the North Pacific Ocean. J Geophys Res 88:5343–5352
Wake CP, Mayewski PA, Li ZQ et al (1994) Modern eolian dust deposition in central Asia. Tellus 46B:220–223
Watanabe K, Kasuga H, Yamada Y et al (2006) Size distributions of aerosol number concentrations and water-soluble constituents in Toyama, Japan: a comparison of the measurements during Asian dust period with non-dust period. Atmos Res 82:719–727
You X, Li Z, Wang F, Wang F et al (2006) Seasonal evolution of insoluble micropartical stratigraphy in glacier No.1 percolation zone, Eastern Tianshan, China. Adv Earth Sci 21(11):1164–1170 (in Chinese)
Zdanowicz CM, Zielinski GA, Wake CP et al (1998) Characteristics of modern atmospheric dust deposition in snow on the Penny Ice Cap, Baffin Island, Arctic Canada. Tellus 50B:506–520
Zhu Y, Li Z, You X (2006) Application and technique in glacier by Accusizer 780A optical particle sizer. Mod Sci Apparatus 3:81–84 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate suggestions from the two anonymous referees and especially Dr. James LaMoreaux (editor-in-chief) improving our paper. This work was jointly supported by the National Key Project for Basic Research of China (2007CB411501), the Knowledge Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Science (KZCXZ-YW-127), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40631001, 40571033, 40701034, 40371028, J0630966), and the Project for Outstanding Young Scientists of National Natural Science Foundation of China (40121101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Z., Li, Z., Xiao, C. et al. Characteristics of aerosol dust in fresh snow in the Asian dust and non-dust periods at Urumqi glacier no. 1 of eastern Tian Shan, China. Environ Earth Sci 60, 1361–1368 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0271-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0271-6