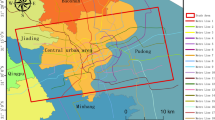
Abstract
Land subsidence in Semarang is a severe hazard threatening people and urban infrastructure. The evolution of land subsidence has been monitored between 1996 and 2000 with few leveling stations. Hence, maps show an overall distribution of land subsidence, but are inaccurate in detail. Stable points network (SPN) technique has been applied to improve land-subsidence mapping. SPN measures ground motion using Synthetic Aperture Radar satellite images. For the SPN processing, 35 radar satellite images acquired between 2002 and 2006 have been selected. Derived land-subsidence rates vary from fractions of 1 mm/year to values of 10 cm/year and even beyond. Classification and visualization of the ground motion data illustrate the boundary between mainly stable ground in the south of Semarang and increasingly land-subsidence-affected land toward the coast. Final result is a map featuring the land subsidence with much higher accuracy as had been possible before. This article presents a brief description of the land subsidence in Semarang and introduces briefly the concept of SPN technique. Results of SPN-based ground motion detection in Semarang are presented and discussed from a user’s point of view.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin HZ, Djaja R, Andreas H, Gamal M, Hirose K, Maryama Y (2004) Capabilities and constraints of geodetic techniques for monitoring land subsidence in the urban areas of Indonesia. In: Third FIG regional conference for Asia and the Pacific, Jakarta, Indonesia, 3–7 October
Arnaud A, Adam N, Hanssen R, Inglada J, Duro J, Closa J, Eineder M (2003) ASAR ERS interferometric phase continuity. IGARSS 2003, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July, 2003
Bontenbal M (2001) Land subsidence in Bangkok—an overview of changes in land subsidence over the last 25 years. MSc Thesis, Free University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Crosetto M, Monserrat O, Adam N, Parizzi A, Bremmer C, Dortland S, Hanssen RF, van Leijen FJ (2008) Validation of existing processing chains in Terrafirma stage 2. GMES TERRAFIRMA, ESRIN/Contract no. 19366/05/I-E, Final report 30th June 2008
Dolan R, Grant Goodell H (1986) Sinking cities. Am Sci 74:38–47
Duro J, Inglada J, Closa J, Adam N, Arnaud A (2005) High resolution differential interferometry using time series of ERS and ENVISAT SAR data. In: FRINGE 2003, Frascati, Italy, 1–5 December
Ferretti A, Prati C, Rocca F (2001) Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39:8–20. doi:10.1109/36.898661
Harnandi D (2007) Groundwater condition at Semarang—Demak Area. Unpublished report, Geological Agenmcy, Center for Geological Environment, Bandung, Indonesia
Kampes BM (2006) Radar interferometry—Persistent Scatterer Technique. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Kuehn F, Margane A, Tatong T, Wever T (2004) InSAR-based land subsidence map for Bangkok, Thailand. Z Angew Geol 1:74–81
Marfai MA (2003) GIS modelling of river and tidal flood hazards in a Waterfront City—case study: Semarang City, Central Java, Indonesia. Thesis submitted to the International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation (ITC), Enschede, The Netherlands
Marfai MA, King L (2007a) Monitoring land subsidence in Semarang, Indonesia. Environ Geol 53:651–659. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0680-3
Marfai MA, King L (2007b) Coastal flood management in Semarang, Indonesia. Environ Geol. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-1101-3
Marfai MA, King L (2008a) Tidal inundation mapping under enhanced land subsidence in Semarang Central Java Indonesia. Nat Hazard 44:93–109. doi:10.1007/s11069-007-9144-z
Marfai MA, King L (2008b) Potential vulnerability implications of coastal inundation due to sea level rise for the coastal zone of Semarang City, Indonesia. Environ Geol 54:1235–1245. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0906-4
Marfai MA, King L, Sartohadi J, Sudrajat S, Budiani SR, Yulianto F (2008) The impact of tidal flooding on a coastal community in Semarang, Indonesia. Environmentalist 28:237–248. doi:10.1007/s10669-007-9134-4
Murdohardono D, Tobing (2001) Engineering geology evaluation of landsubsidence in Semarang. Unpublished report, Geological Agency, Directorate of Environment of Geology and Mining, Bandung, Indonesia
Prokopovich NP (1979) Genetic classification of land subsidence. In: Proceedings of the American society of civil engineers, engineering foundation conference, international conference on evaluation and prediction of subsidence, Pensacola Beach, Florida; published in New York, NY, pp 389–399
Said HD, Sukrisno (1988) Hydrogeological map of Indonesia, 1:250,000, Semarang sheet. Directorate of Environmental Geology, Bandung, Indonesia
Schmidt G (2002) Groundwater quantification—validation of groundwater models, vol 2 (case studies). Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe (BGR) (File 5164/02)
Sutanta H (2002) Spatial modeling of the impact of land subsidence and sea level rise in a coastal urban setting. ITC, The Netherlands
Thanden RE, Sumadirdja H, Richards PW, Sutisna K, Amin TC (1996) Geological map of the Magelang and Semarang sheets. Java. Geological Research and Development Centre, Bandung, Indonesia
Tobing, Panggabean J, Murdohardono D (2001) Land subsidence map of Semarang. Geological Agency, Center for Environmental Geology, Bandung, Indonesia
Acknowledgments
This SPN-based land-subsidence mapping for Semarang is a technical component of the project “Good Local Governance-Mitigation of Georisks,” financed by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ). We would like to thank Mr. Gunawan and the Local Mining Agency of Central Java Province, (Semarang), for supporting the verification of SPN results during field campaigns in May and November 2007. We are further indebted to Gerhard Schmidt (BGR Hannover) for numerous technical discussions and advice on hydrogeological aspects of the Semarang land subsidence. Mrs. Erika Purwaningsih and Mr. Arief Daryanto (Geological Agency, Bandung) greatly supported land subsidence study through GIS-treatment of the SPN data and final composition of updated land-subsidence map for Semarang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuehn, F., Albiol, D., Cooksley, G. et al. Detection of land subsidence in Semarang, Indonesia, using stable points network (SPN) technique. Environ Earth Sci 60, 909–921 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0227-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0227-x