Abstract
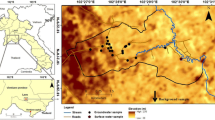
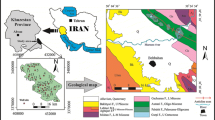
This manuscript presents major, minor and trace elements data for groundwater samples collected from wells, tube wells, springs and karezes from Quetta Valley. Quetta Valley in Pakistan has frequently experienced shortage of groundwater. In recent years, the water quality has had a sharp decline at many locations. The study of groundwater resources in this valley is an attempt to understand the causes of and sources of contamination. At several locations, nitrate, sulfate, arsenic, selenium, chromium and nickel contamination has been determined. The preliminary results indicate that these contaminations apparently result from a combination of rock alteration and mining activity in the area. Different water sources could have also contributed to the deterioration of the water quality of Quetta Valley. This research provides the basis for future work, which will involve detailed hydrological modeling and water quality studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchard DC, Williams MK, Surampalli RY (1992) Nitrate contamination of groundwater: sources and potential health effects. J Am Water Works Assoc 84(9):85–90
Bright KS (2006) Ultramafic bedrock source of arsenic in private wells of Stowe, Vermont. Unpublished senior thesis, Middlebury College, Middlebury, VT
Chen CJ, Chuang YC, Lin TM, Wu HY (1985) Malignant neoplasms among residents of a Blackfoot disease-endemic area in Taiwan: high-arsenic artesian well water and cancers. Cancer Res 45:5895–5899
Chowdhury UK, Biswas BK, Chowdhury TR, Samanta G, Mandal BK, Basu GC, Chanda CR, Lodh D, Saha KS, Mukherjee SK, Roy S, Kabir S, Quamruzzaman Q, Chakraborti D (2000) Groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh and West Bengal, India. Environ Health Perspect 108(5):393–397. doi:10.2307/3454378
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Rice EW, Greenberg AE, Franson MAH (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, centennial edn.
Feder GL (1985) Environmental influence of selenium in waters of the western United States. US Geological Survey, 1985 annual report, pp 5–8
Heizer WD, Sandler RS, Seal E, Murray SC, Busby MG, Schliebe BG, Pusek SN (1997) Intestinal effects of sulfate in drinking water on normal human subjects. J Digest Disease Sci 42(5):1055–1061. doi:10.1023/A:1018801522760
Hopenhayn-Rich C, Biggs ML, Fuchs A, Bergoglio R, Tello EE, Nicolli H, Smith AH (1996) Bladder cancer mortality associated with arsenic in drinking water in Argentina. Epidemiology 7:117–124. doi:10.1097/00001648-199603000-00003
Kazmi AH, Abbas SG, and Younas M (2005) Water resources and hydrogeology of Quetta baisn. Geological Survey of Pakistan, special publication
Khan SD, Mahmood K (2008) The application of remote sensing techniques to the study of ophiolites. Earth Sci Rev 89:135–143. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2008.04.004
Khan AS, Mian BA (2000) Groundwater development issues of Baluchistan. In: Proceedings of the global water partnership seminar on regional groundwater management, Islamabad
Khan SD, Mahmood K, Casey JF (2007) Mapping of Muslim Bagh ophiolite complex (Pakistan) using new remote sensing and field data. J Asian Earth Sci 30:333–343. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2006.11.001
Knobeloch L, Salna B, Hogan A, Postle J, Anderson H (2000) Blue babies and nitrate-contaminated well water. Environ Health Perspect 108(7):675–678. doi:10.2307/3434890
Morales KH, Ryan L, Kuo T, Wu M, Chen C (2000) Risk of internal cancers from arsenic in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 108(7):655–661. doi:10.2307/3434887
National Research Council (1999) Arsenic in drinking water. National Academy Press, Washington DC
Smith AH, Hopenhayn-Rich C, Bates MN, Goeden HM, Hertz-Picciotto I, Duggan HM, Wood R, Kosnett MJ, Smith MT (1992) Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Health Perspect 97:259–267. doi:10.2307/3431362
Smith AH, Goycolea M, Haque R, Biggs ML (1998) Marked increase in bladder and lung cancer mortality in a region of northern Chile due to arsenic in drinking water. Am J Epidemiol 147:660–669
Stetzenbach KJ, Amano M, Kreamer DK, Hodge VF (1994) Testing the limits of ICP-MS: determination of trace elements in groundwater at the part-per-trillion level. Ground Water 32(6):976–985
World Health Organization (2003) Nitrate and nitrite in drinking water: background document for preparation of WHO guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organization (WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/56), Geneva
World Health Organization (2006) Guidelines for drinking water quality (electronic resource): incorporating first addendum, vol 1. Recommendations, 3rd edn
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the USAID grant through the US Academy of Sciences and Higher Education Commission of Pakistan. The authors thank Khawar Sohail and Ishaq Kakar, Center of Excellence of Mineralogy, University of Balochistan for their help in the field. LienTh Nguyen and Dr. Yongjun Gao are thanked for their help in chemical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S.D., Mahmood, K., Sultan, M.I. et al. Trace element geochemistry of groundwater from Quetta Valley, western Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 60, 573–582 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0197-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0197-z