Abstract
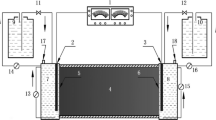
Feasibility of electrolyte conditioning with strong alkaline solution on electrokinetic remediation of fluorine-contaminated field soil was investigated in the laboratory. The initial concentration of fluorine, pH and organic matter content in the soil were 1,058 mg kg−1, 8.17 and 20.51 g kg−1, respectively. Electrokinetic experiments were conducted under two different concentrations of alkaline solution and three different voltage gradients. The removal of fluorine increased with the concentration of the alkaline solution and applied voltage and fluorine removed up to 73% within 10 days. Anolyte enhanced electrokinetic process could promote effectively the migration of fluoride in soil. The electromigration was the main transport mechanism and the electroosmotic flow had an effect on the migration of fluoride in soil. Appropriate anolyte enhanced electrokinetic method could be applied to remediate fluorine from contaminated field soil and has significant potential for removing other anionic pollutants such as arsenate and chromate from soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar YB, Alshawabkeh AN (1993) Principles of electrokinetic remediation. Environ Sci Technol 27:2638–2647
Acar YB, Gale RJ, Alshawabkeh AN, Marks RE, Puppala S, Bricka M, Parker R (1995) Electrokinetic remediation: basics and technology status. J Hazard Mater 55:117–137
Arnesen AKM, Krogstad T (1998) Sorption and desorption of fluoride in soil polluted from the aluminum smelter at Ardal in western Norway. Water Air Soil Pollut 103:357–373
Beak K, Kim DH, Park SW, Ryu BG, Bajargal T, Yang JS (2008) Electrolyte conditioning-enhanced electrokinetic remediation of arsenic-contaminated mine tailing. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.127
Camargo JA (2003) Fluoride toxicity to aquatic organisms: a review. Chemosphere 50:251–264
Chang JH, Liao YC (2006) The effect of critical operational parameters on the circulation-enhanced electrokinetic. J Hazard Mater 129:186–193
Chen XJ, Shen ZM, Lei YM, Ju BX, Wang WH (2006) Enhanced electrokinetic remediation of Cd and Pb spiked soil coupled with cation exchange membrane. Aust J Soil Res 44:523–529
Costarramone N, Tellier S, Astruc M, Grano B, Lecomte D (1998) Application of an electrokinetic technique to the reclamation of fluoride polluted soils: laboratory and pilot scale experiments. Waste Manage Res 16:555–563
Costarramone N, Tellier S, Grano B, Lecomte D, Astruc M (2000) Effect of selected conditions on fluorine recovery from a soil using electrokinetics. Environ Technol 21:789–798
Egli M, Durrenberger S, Fitze P (2004) Spatio-temporal behaviour and mass balance of fluorine in forest soils near an aluminium smelting plant: short- and long-term aspects. Environ Pollut 129:195–207
Islam M, Patel RK (2007) Evaluation of removal efficiency of fluoride from aqueous solution using quick lime. J Hazard Mater 143:303–310
Jha SK, Nayak AK, Sharma YK, Mishra VK, Sharma DK (2008) Fluoride accumulation in soil and vegetation in the vicinity of brick fields. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:369–373
Kim WS, Kim SO, Kim KW (2005) Enhanced electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from soils assisted by ion exchange membranes. J Hazard Mater 118:93–102
Kim DH, Jeon CS, Baek K, Ko SH, Yang JS (2008) Electrokinetic remediation of fluorine-contaminated soil: Conditioning of anolyte. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.084
Lee HH, Yang JW (2000) A new method to control electrolytes pH by circulation system in electrokinetic soil remediation. J Hazard Mater 77:227–240
Li ZM, Yu JW, Neretnieks I (1998) Electroremediation: removal of heavy metals from soils by using cation selective membranes. Environ Sci Technol 32:394–397
Luther SM, Poulsen L, Dudas MJ, Rutherford PM (1996) Fluoride sorption and mineral stability in an Alberta soil interacting with phosphogypsum leachate. Can J Soil Sci 76:83–91
Maini G, Sharman AK, Sunderland G, Knowles CJ, Jackman SA (2000) An integrated method incorporating sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and electrokinetics to enhance of copper from contaminated soil. Environ Sci Technol 34:1081–1087
McQuaker NR, Gurney M (1977) Determination of total fluoride in soil and vegetation using an alkali fusion—selective ion electrode technique. Anal Chem 49:53–56
Ottosen LM, Lepkova K, Kubal M (2006) Comparison of electrodialytic removal of Cu from spiked kaolinite, spiked soil and industrially polluted soil. J Hazard Mater 137:113–120
Park JY, Kim SJ, Lee YJ, Baek K, Yang JW (2005) EK-Fenton process for removal of phenanthrene in a two-dimensional soil system. Eng Geol 77:217–224
Pomes V, Fernandez A, Costarramone N, Grano B, Houi D (1999) Fluorine migration in a soil bed submitted to an electric field: influence of electric potential on fluorine removal. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 159:481–490
Reddy KR, Chinthamreddy S (1999) Electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils under reducing environments. Waste Manage 19:269–282
Reddy KR, Chinthamreddy S (2003) Sequentially enhanced electrokinetic remediation of heavy metals in low buffering clayey soils. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 129:263–277
Sah JG, Chen JY (1998) Study of the electrokinetic process on Cd and Pb spiked soils. J Hazard Mater 58:301–315
Shen ZM, Zhang JD, Qu LY, Dong ZQ, Zheng SS, Wang WH (2008) A modified EK method with an I−/I2 lixiviant assisted and approaching cathodes to remedy mercury contaminated field soils. Environ Geol. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1418-6
Wang LF, Huang JZ (1995) Outline of control practice of endemic fluorosis in China. Soc Sci Med 41:1191–1195
Wang JY, Zhang DS, Stabnikova O, Tay JH (2005) Evaluation of electrokinetic removal of heavy metals from sewage sludge. J Hazard Mater 124:139–146
Weng CH, Yuan C (2001) Removal of Cr(III) from clay soils by electrokinetics. Environ Geochem Health 23:281–285
Yang GCC, Lin SL (1998) Removal of lead from a silt loam soil by electrokinetic remediation. J Hazard Mater 58:285–299
Yuan C, Chiang TS (2008) Enhancement of electrokinetic remediation of arsenic spiked soil by chemical reagents. J Hazard Mater 152:309–315
Zhou DM, Deng CF, Cang L (2004) Electrokinetic remediation of a Cu contaminated red soil by conditioning catholyte pH with different enhancing chemical reagents. Chemosphere 56:265–273
Zhou DM, Deng CF, Cang L, Alshawabkeh AN (2005) Electrokinetic remediation of a Cu–Zn contaminated red soil by controlling the voltage and conditioning catholyte pH. Chemosphere 61:519–527
Acknowledgments
This research has been financially supported by the Scientific Research Foundation of Henan University of Science and Technology for Talents (No. 06-12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Zhang, J. & Dong, T. Removal of fluorine from contaminated field soil by anolyte enhanced electrokinetic remediation. Environ Earth Sci 59, 379–384 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0036-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0036-2