Abstract
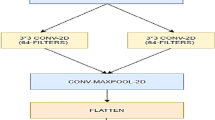
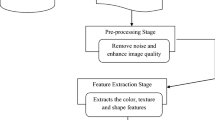
Detection of melanoma in the early stage can provide the patients with more promising treatments. Numerous methods have been proposed for detecting melanoma using computational approaches; however, the application of deep learning in this field is incipient and needs to be assessed further. In this paper, we introduce MDDC, a four-step deep learning-based pipeline for melanoma detection using digital images. MDDC removes image noise using discrete wavelet transform, pre-processes and extends the generalizability using a Gaussian blur filter and image transformation techniques, and finally computes the probability of melanoma in digital images using a convolutional neural network. The model performance is evaluated by considering various CNN architectures and three validation scenarios to find the best CNN architecture. Moreover, we used the transfer learning technique to improve the model performance and generalize it for working on another dataset. MDDC can handle noisy images and is insensitive to image transformations. The validation of MDDC led to 0.96 Accuracy, 0.96 Recall, 0.954 Specificity, 0.99 AUC, and 0.99 AUPR. In addition, further evaluation of the proposed method with state-of-the-art methods verifies that MDDC outperforms other methods. Consequently, MDDC can efficiently and quickly detect melanoma in digital images.





Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
The codes and implementations are available at https://github.com/Omid-Asadi/MelanomaDetection.
References
Adegun AA, Viriri S (2019) Deep learning-based system for automatic melanoma detection. IEEE Access 8:7160–7172
Balaji M, Saravanan S, Chandrasekar M, Rajkumar G, Kamalraj S (2021) Analysis of basic neural network types for automated skin cancer classification using firefly optimization method. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 12(7):7181–7194
Banerjee S, Singh S, Chakraborty A, Das A, Bag R (2020) Melanoma diagnosis using deep learning and fuzzy logic. Diagnostics 10(8):577
Bisla D, Choromanska A, Berman RS, Stein JA, Polsky D (2019) Towards automated melanoma detection with deep learning: Data purification and augmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pages 0–0
Bojarski M, Choromanska A, Choromanski K, Firner B, Jackel L, Muller U, Zieba K (2016) Visualbackprop: visualizing cnns for autonomous driving. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.05418
Chang X, Nie F, Wang S, Yang Y, Zhou X, Zhang C (2015) Compound rank-k projections for bilinear analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(7):1502–1513
Chen K, Yao L, Zhang D, Wang X, Chang X, Nie F (2019) A semisupervised recurrent convolutional attention model for human activity recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(5):1747–1756
Dhivyaa C, Sangeetha K, Balamurugan M, Amaran S, Vetriselvi T, Johnpaul P (2020) Skin lesion classification using decision trees and random forest algorithms. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput, pp 1–13
Dridi S, Morestin F, Dogui A (2012) Use of digital image correlation to analyse the shearing deformation in woven fabric. Exp Tech 36(5):46–52
Glaister JL (2013) Automatic segmentation of skin lesions from dermatological photographs. Master’s thesis, University of Waterloo
Hameed A, Umer M, Hafeez U, Mustafa H, Sohaib A, Siddique MA, Madni HA (2021) Skin lesion classification in dermoscopic images using stacked convolutional neural network. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput pp 1–15
Jayapriya K, Jacob IJ (2020) Hybrid fully convolutional networks-based skin lesion segmentation and melanoma detection using deep feature. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 30(2):348–357
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324
Li Y, Shen L (2018) Skin lesion analysis towards melanoma detection using deep learning network. Sensors 18(2):556
Li Z, Nie F, Chang X, Nie L, Zhang H, Yang Y (2018) Rank-constrained spectral clustering with flexible embedding. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(12):6073–6082
Li Z, Nie F, Chang X, Yang Y, Zhang C, Sebe N (2018) Dynamic affinity graph construction for spectral clustering using multiple features. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(12):6323–6332
Li Z, Yao L, Chang X, Zhan K, Sun J, Zhang H (2019) Zero-shot event detection via event-adaptive concept relevance mining. Pattern Recogn 88:595–603
Luo M, Chang X, Nie L, Yang Y, Hauptmann AG, Zheng Q (2017) An adaptive semisupervised feature analysis for video semantic recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(2):648–660
Mahbod A, Schaefer G, Ellinger I, Ecker R, Pitiot A, Wang C (2019) Fusing fine-tuned deep features for skin lesion classification. Comput Med Imaging Graph 71:19–29
Mahbod A, Schaefer G, Wang C, Ecker R, Ellinge I (2019b) Skin lesion classification using hybrid deep neural networks. In ICASSP 2019 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 1229–1233. IEEE
Majtner T, YildirimYayilgan S, Hardeberg JY (2019) Optimised deep learning features for improved melanoma detection. Multimed Tools Appl 78(9):11883–11903
Marchetti M, Codella NC, Dusza SW, Gutman DA, Helba B, Kalloo A, Mishra N, Carrera C, Celebi M, DeFazio JL et al (2018) Results of the 2016 international skin imaging collaboration international symposium on biomedical imaging challenge: Comparison of the accuracy of computer algorithms to dermatologists for the diagnosis of melanoma from dermoscopic images. J Am Acad Dermatol 78(2):270–277
Miller K, GodingSauer A, Ortiz A, Fedewa S, Pinheiro P, Tortolero-Luna G, Martinez-Tyson D, Jemal A, Siegel R (2018) Cancer statistics for hispanics/latinos, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):425–445
Milton MA (2019) Automated skin lesion classification using ensemble of deep neural networks in isic 2018: Skin lesion analysis towards melanoma detection challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.10802
Naeem A, Farooq MS, Khelifi A, Abid A (2020) Malignant melanoma classification using deep learning: datasets, performance measurements, c.hallenges and opportunities. IEEE Access 8:110575–110597
Nami N, Giannini E, Burroni M, Fimiani M, Rubegni P (2012) Teledermatology: state-of-the-art and future perspectives. Expert Rev Dermatol 7(1):1–3
NasrEsfahani E, Samavi S, Karimi N, Soroushmehr SM, Jafari M, Ward K, Najarian K (2016) Melanoma detection by analysis of clinical images using convolutional neural network. In: 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp 1373–1376, IEEE
Novikov I, Novikov I, Novikov I, Protasov V, Protasov V, Protasov V, Skopina M, Skopina M (2011) Wavelet theory, volume 239. American Mathematical Soc
Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S (2015) Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv:1511.06434
Rotemberg V, Kurtansky N, BetzStablein B, Caffery L, Chousakos E, Codella N, Combalia M, Dusza S, Guitera P, Gutman D et al (2021) A patient-centric dataset of images and metadata for identifying melanomas using clinical context. Sci Data 8(1):1–8
Salido JA, Ruiz C (2018) Using deep learning to detect melanoma in dermoscopy images. Int J Mach Learn Comput 8(1):61–68
SchmidSaugeona P, Guillodb J, Thirana J (2003) Towards a computer-aided diagnosis system for pigmented skin lesions. Comput Med Imaging Graph 27(1):65–78
Soudani A, Barhoumi W (2019) An image-based segmentation recommender using crowdsourcing and transfer learning for skin lesion extraction. Expert Syst Appl 118:400–410
Sreelatha T, Subramanyam, Prasad M (2019) Early detection of skin cancer using melanoma segmentation technique. J Med Syst 43(7):1–7
Yan C, Chang X, Luo M, Zheng Q, Zhang X, Li Z, Nie F (2020) Self-weighted robust lda for multiclass classification with edge classes. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 12(1):1–19
Zhang D, Yao L, Chen K, Wang S, Chang X, Liu Y (2019) Making sense of spatio-temporal preserving representations for eeg-based human intention recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(7):3033–3044
Zhou R, Chang X, Shi L, Shen Y, Yang Y, Nie F (2019) Person reidentification via multi-feature fusion with adaptive graph learning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(5):1592–1601
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Asadi, O., Yekkalam, A. & Manthouri, M. MDDC: melanoma detection using discrete wavelet transform and convolutional neural network. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 12959–12966 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-04381-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-04381-z