Abstract
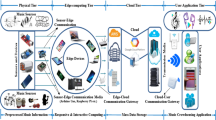
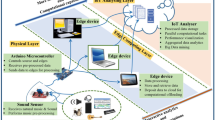
Internet of Things is a promising paradigm that integrates a plethora of heterogeneous computational devices, incorporating the crowd, frameworks, additional system elements, and infrastructure. Information sensing, modeling, retrieval, and distribution perform an emerging role in the Internet of Things network. Dew computing is a challenging research issue, which needs to demonstrate its impact on the sensor data in the domain of parallel and distributed computing. We have presented a dew-cloud computing-based music crowdsourcing framework in this paper, to address the dew computing effectiveness in the context of the Internet of Things. The crowdsourcing paradigms are efficient to collect and analyze billions of information efficiently with a diminutive cost. In this promising paradigm, participated sound sensing devices sense acoustic information from the environment; transmit the sensor data to fog computing devices through dew repository, and eventually, cloud data center stores the processed data for providing aggregated musical information and relevant services to the end-users. This paper presents a Dew-Cloud based music crowdsourcing framework in the ambiance of the Internet of Things. We have illustrated a semantic mathematical background for the proposed crowdsourcing-based Internet of Music Things architecture in the dew-cloud computing framework. We have also discussed the system performance metrics, in terms of information transmission time, service latency, and energy dissipation in this endeavor. We have additionally illustrated a comparative analysis between the proposed paradigm and the conventional cloud computing schema in terms of data transmission time and overall system energy dissipation. The goal of this paper is to conceptualize, how the end-users can be benefitted from data analytics through data sensing, computing, and distributed scenario using a dew-cloud computational framework in the Internet of Things environment.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvaro JL, Barros B (2013) A new cloud computing architecture for music composition. J Netw Comput Appl 36:429–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2012.04.015
Arkian HR, Abolfazl D, Atefe P (2017) MIST: fog-based data analytics scheme with cost-efficient resource provisioning for IoT crowdsensing applications. J Netw Comput Appl 82:152–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2017.01.012
Axak N, Rosinskiy D, Barkovska O, Novoseltsev I (2018) Cloud-fog-dew architecture for personalized service-oriented systems. In: 9th international conference on dependable systems, services and technologies (DESSERT), IEEE, pp 78–82. https://doi.org/10.1109/dessert.2018.8409103
Boyd N, Chang W, Wu J (2017) Crowdsourcing-based musical predictions. In: 2017 IEEE 14th international conference on mobile ad hoc and sensor systems (MASS), IEEE, pp 502–506. https://doi.org/10.1109/mass.2017.79
Dastjerdi AV, Gupta H, Calheiros RN, Ghosh SK, Buyya R (2016) Fog computing: principles, architectures, and applications. Internet Things Principles Paradigms Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-805395-9.00004-6
Eskenazi M, Levow GA, Meng H, Parent G, Suendermann D (2013) Crowdsourcing for speech processing: applications to data collection, transcription and assessment. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118541241
Fensel A, Tomic DK, Koller A (2017) Contributing to appliances’ energy efficiency with Internet of Things, smart data and user engagement. Futur Gen Comput Syst 76:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2016.11.026
Frincu M (2017) Architecting a hybrid cross layer dew-fog-cloud stack for future data-driven cyber-physical systems. In: Information and communication technology, electronics and microelectronics (MIPRO), IEEE pp 399–403. https://doi.org/10.23919/mipro.2017.7973456
Ganti RK, Fan Y, Hui L (2011) Mobile crowdsensing: current state and future challenges. IEEE Commun Mag. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2011.6069707
Geier M, Márquez DG, Mocskos E (2019) SherlockFog: a new tool to support application analysis in Fog and Edge computing. Cluster Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-019-02936-y
Gomes C, Schneider D, Moraes K, Souza JD (2012) Crowdsourcing for music: survey and taxonomy. In: Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), IEEE pp 832–839. https://doi.org/10.1109/icsmc.2012.6377831
Guo K, Tang Y, Zhang P (2017) CSF: crowdsourcing semantic fusion for heterogeneous media big data in the internet of things. Inf Fusion 37:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2017.01.008
Gusev M (2017) A dew computing solution for IoT streaming devices. In: Information and communication technology, electronics and microelectronics (MIPRO), IEEE, pp 387–392. https://doi.org/10.23919/mipro.2017.7973454
Gushev M (2020) Dew computing architecture for cyber-physical systems and IoT. Internet Things Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2020.100186
Haseeb K, Almogren A, Ud Din I, Islam N, Altameem A (2020) SASC: secure and authentication-based sensor cloud architecture for intelligent internet of things. Sensors 20(9):2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092468
Hirsch M, Mateos C, Rodriguez JM, Zunino A (2019) DewSim: a trace-driven toolkit for simulating mobile device clusters in Dew computing environments. Softw Pract Exp Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/spe.2696
Jiang C, Wu J, Li Z (2018) Adaptive thresholds determination for saving cloud energy using three-way decisions. Cluster Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-1879-7
Khan MSH, Roy P, Khanam F, Hera FH, Das AK (2019a) An efficient resource allocation mechanism for time-sensitive data in dew computing. In: 2019 international conference of artificial intelligence and information technology (ICAIIT). IEEE, pp 506–510. https://doi.org/10.1109/icaiit.2019.8834633
Khan FA, Shaheen S, Asif M, Rahman AU, Imran M, Rehman SU (2019b) Towards reliable and trustful personal health record systems: a case of cloud-dew architecture based provenance framework. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 10(10):3795–3808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01292-4
Ko SW, Han K, Huang K (2018) Wireless networks for mobile edge computing: spatial modeling and latency analysis. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2018.2840120
Liu C, Nitschke P, Williams SP, Zowghi D (2019) Data quality and the Internet of Things. Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-019-00746-z
Miao Y, Jianfeng M, Ximeng L, Xinghua L, Zhiquan L, Li H (2017) Practical attribute-based multi-keyword search scheme in mobile crowdsourcing. IEEE Internet Things J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2017.2779124
Mukherjee A, Deb P, De D, Buyya R (2018) C2OF2N: a low power cooperative code offloading method for femtolet-based fog network. J Supercomput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2269-x
Patel H, Suthar K (2017) A novel approach for securely processing information on dew sites (Dew computing) in collaboration with cloud computing: an approach toward latest research trends on Dew computing. In: Engineering (NUiCONE), pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/nuicone.2017.8325622
Ray PP (2018a) An introduction to dew computing: definition, concept and implications. IEEE Access 6:723–737. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2775042
Ray PP (2018b) Minimizing dependency on internetwork: is dew computing a solution? Trans Emerg Telecommun Technol. https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.3496
Ray PP, Dash D, De D (2018) Internet of things-based real-time model study on e-healthcare: device, message service and dew computing. Comput Netw. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2018.12.006
Roman R, Lopez J, Mambo M (2018) Mobile edge computing, fog et al.: a survey and analysis of security threats and challenges. Future Gen Comput Syst 78:680–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2016.11.009
Roy S, Sarkar D, Hati S, De D (2018) Internet of Music Things: an edge computing paradigm for opportunistic crowdsensing. J Supercomput 74:6069–6101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2511-6
Roy S, Sarkar D, De D (2020) Entropy-aware ambient IoT analytics on humanized music information fusion. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 11(1):151–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01261-x
Sharma V, You I, Jayakody DNK, Atiquzzaman M (2017) Cooperative trust relaying and privacy preservation via edge-crowdsourcing in social Internet of Things. Futur Gen Comput Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2017.12.039
Sharma S, Chang V, Tim US, Wong J, Gadia S (2019) Cloud and IoT-based emerging services systems. Cluster Comput 22(1):71–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2821-8
Skala K, Davidovic D, Afgan E, Sovic I, Sojat Z (2015) Scalable distributed computing hierarchy: cloud, fog and dew computing. Open J Cloud Comput 2:16–24
Souri A, Hussien A, Hoseyninezhad M, Norouzi M (2019) A systematic review of IoT communication strategies for an efficient smart environment. Trans Emerg Telecommun Technol Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.3736
Sun Y, Houbing S, Antonio JJ, Rongfang B (2016) Internet of things and big data analytics for smart and connected communities. IEEE Access 4:766–773. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2529723
Trattner C, Jannach D (2020) Learning to recommend similar items from human judgments. User Model User-Adapt Interact Springer 30(1):1–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11257-019-09245-4
Turchet L, Fischione C, Essl G, Keller D, Barthet M (2018) Internet of musical things: vision and challenges. IEEE Access 6:61994–62017. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2872625
Veloso B, Leal F, González-Vélez H, Malheiro B, Burguillo JC (2018) Scalable data analytics using crowdsourced repositories and streams. J Parallel Distrib Comput 122:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2018.06.013
Wang Y (2016) Definition and categorization of dew computing. Open J Cloud Comput 3:1–7. urn:nbn:de:101:1-201705194546
Wang Y, LeBlanc D (2016) Integrating SaaS and SaaP with dew computing. In: IEEE International Conferences on Big Data and Cloud Computing (BDCloud), pp 590–594. https://doi.org/10.1109/bdcloud-socialcom-sustaincom.2016.92
Wang Y, Skala K, Rindos A, Gusev M, Shuhui Y, Yi P (2019) Dew computing and transition of internet computing paradigms. ZTE Commun 15(4):30–37. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5188.2017.04.004
Zhang K, Marchiori A (2017) Crowdsourcing low-power wide-area iot networks. In: Pervasive computing and communications (PerCom), IEEE, pp 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1109/percom.2017.7917849
Zhang B, Liu CH, Lu J, Song Z, Ren Z, Ma J, Wang W (2016) Privacy-preserving QoI-aware participant coordination for mobile crowdsourcing. Comput Netw 101:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2015.12.022
Zhang K, Leng S, He Y, Maharjan S, Zhang Y (2018a) Mobile edge computing and networking for green and low-latency internet of things. IEEE Commun Mag 56:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700882
Zhang P, Chen R, Li Y, Niu X, Wang L, Li M, Pan Y (2018b) A localization database establishment method based on crowdsourcing inertial sensor data and quality assessment criteria. IEEE Internet Things J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2018.2817599
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the University Grants Commission (UGC), Govt. of India, for sanctioning research fellowship under which this article has been completed. Authors are also grateful to the Department of Science and Technology (DST) for sanctioning a research Projects and TEQIP-III, MAKAUT, WB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, S., Sarkar, D. & De, D. DewMusic: crowdsourcing-based internet of music things in dew computing paradigm. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 12, 2103–2119 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02309-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02309-z