Abstract
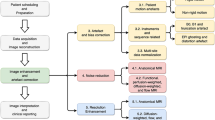
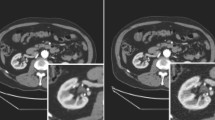
We propose a novel method for brain MR image completion in the case of unknown deformation in MR images. An efficient technique for MR image completion can keep patients from requiring a secondary shot, thus limiting radiation exposure. To address this challenge, we propose an MR image completion method guided by multimodal registration and simultaneously propose a new multimodal registration method, i.e., synthetic-CT-based multimodal registration (IC-G-MR). The majority of existing multimodal registration methods cannot perform well under the conditions mentioned above. The significance of our method can be summarized as follows: (1) Through a combination of transfer learning and indirect multimodal registration, the proposed IC-G-MR method can be used to solve the problem of brain MR image completion based on corresponding normal CT images. (2) Due to the transfer learning technique, our method can generate synthetic brain CT images of good quality. (3) Due to the novel multimodal registration method, the proposed IC-G-MR method performs effectively in registration for large-scale elastically deformed MR images. The experimental results indicate that our proposed IC-G-MR method can effectively complete MR images of the brain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Khan MF (2018) Multimodal non-rigid image registration based on elastodynamics. Vis Comput 34(1):21–27
Alafeef M, Fraiwan M (2019) On the diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease using continuous wavelet transform complex plot. J Ambient Intell Humanized Comput 10(7):2805–2815
Alvén J, Norlén A, Enqvist O, Kahl F (2016) Überatlas: fast and robust registration for multi-atlas segmentation. Pattern Recogn Lett 80:249–255
Akhbardeh A, Parekth VS, Jacobs MA (2015) TU-CD-BRA-01: A novel 3D registration method for multiparametric radiological. Images Medical physics 42(6Part32):3605–3606
Chen Q, Li G, Xie L, Xiao Q, Xiao M (2019) Structure guided image completion using texture synthesis and region segmentation. Optik 185:896–909
Farjam R, Tyagi N, Deasy JO, Hunt MA (2019) Dosimetric evaluation of an atlas-based synthetic CT generation approach for MR-only radiotherapy of pelvis anatomy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 20(1):101–109
Fernandez-de-Manuel L, Wollny G, Kybic J, Jimenez-Carretero D, Tellado JM, Ramon E, Ledesma-Carbayo MJ (2014) Organ-focused mutual information for nonrigid multimodal registration of liver CT and Gd–EOB–DTPA-enhanced MRI. Med Image Anal 18(1):22–35
Guo K, Cao R, Kui X, Ma J, Kang J, Chi T (2019) LCC: towards efficient label completion and correction for supervised medical image learning in smart diagnosis. J Netw Comput Appl 133:51–59
Han B, Han Y, Gao X, Zhang L (2018) Boundary constraint factor embedded localizing active contour model for medical image segmentation. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0978-x
Hofmann M, Steinke F, Scheel V, Charpiat G, Farquhar J, Aschoff P, Pichler BJ (2008) MRI-based attenuation correction for PET/MRI: a novel approach combining pattern recognition and atlas registration. J Nucl Med 49(11):1875–1883
Iizuka S, Simo-Serra E, Ishikawa H (2017) Globally and locally consistent image completion. ACM Trans Graph (ToG) 36(4):107
Janssens G, Jacques L, de Xivry JO, Geets X, Macq B (2011) Diffeomorphic registration of images with variable contrast enhancement. J Biomed Imaging 2011:3
Keereman V, Fierens Y, Broux T, De Deene Y, Lonneux M, Vandenberghe S (2010) MRI-based attenuation correction for PET/MRI using ultrashort echo time sequences. J Nucl Med 51(5):812–818
Kops ER, Herzog H (2008) Template based attenuation correction for PET in MR-PET scanners. In: 2008 IEEE nuclear science symposium conference record pp 3786–3789
Lee D, Nam WH, Lee JY, Ra JB (2010) Non-rigid registration between 3D ultrasound and CT images of the liver based on intensity and gradient information. Phys Med Biol 56(1):117
Manchanda M, Sharma R (2018) An improved multimodal medical image fusion algorithm based on fuzzy transform. J Vis Commun Image Represent 51:76–94
Qian P, Sun S, Jiang Y, Su KH, Ni T, Wang S, JrRF Muzic (2016) Cross-domain, soft-partition clustering with diversity measure and knowledge reference. Pattern Recogn 50:155–177
Raja NSM, Fernandes SL, Dey N, Satapathy SC, Rajinikanth V (2018) Contrast enhanced medical MRI evaluation using Tsallis entropy and region growing segmentation. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0854-8
Schneider W, Bortfeld T, Schlegel W (2000) Correlation between CT numbers and tissue parameters needed for Monte Carlo simulations of clinical dose distributions. Phys Med Biol 45(2):459
Sharif M, Tanvir U, Munir EU, Khan MA, Yasmin M (2018) Brain tumor segmentation and classification by improved binomial thresholding and multi-features selection. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1075-x
Tao X, Wang R, Chang R, Li C (2019) Density-sensitive fuzzy kernel maximum entropy clustering algorithm. Knowl-Based Syst 166:42–57
Wen J, Tian Y, Yehang SHOU, Yongchuan T, Weiwei HU (2018) Improved evidential fuzzy c-means method. J Syst Eng Electron 29(1):187–195
Xue C, Tang FH (2014) An adaptive patient specific deformable registration for breast images of positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging using finite element approach. In: Medical imaging 2014: image processing, Vol. 90343H, International Society for Optics and Photonics, 21 March 2014, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2043252
Yang L, Guo BL, Ni W (2008) Multimodality medical image fusion based on multiscale geometric analysis of contourlet transform. Neurocomputing 72(1–3):203–211
Yoo JC, Han TH (2009) Fast normalized cross-correlation. Circuits Syst Signal Processing 28(6):819
Zaidi H, Montandon ML, Slosman DO (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging-guided attenuation and scatter corrections in three-dimensional brain positron emission tomography. Med Phys 30(5):937–948
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61702225 and 61772241, by the 2018 Six Talent Peaks Project of Jiangsu Province under Grant XYDXX-127, by a Science and Technology Demonstration Project for the Social Development of Wuxi under Grant WX18IVJN002, and by the Jiangsu Committee of Health under Grant H2018071.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, J., Xia, K., Zheng, Q. et al. A smart brain MR image completion method guided by synthetic-CT-based multimodal registration. J Ambient Intell Human Comput (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01416-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01416-w