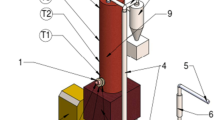
Abstract
Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) can be used to produce a large volume of non-thermal plasma at atmospheric pressure. Such plasmas are sources of highly reactive species (radicals, ozone, atoms, ions and excited molecules). Due to its characteristics, the DBD plasma can be applied for the pretreatment of lignocellulosic materials, in order to extract lignin that prevents the access to remained fermentable sugars in the biomass. In this context, an alternative method for pretreatment of lignocellulosic material in an in-liquid DBD plasma reactor using non-contact electrodes, working with atmospheric air, has been proposed. After the pretreatment, the solids were washed and submitted to enzymatic hydrolysis with a commercial enzyme complex, at 10 FPU/g of pretreated biomass and 50 g/L solids concentration (dry basis), for 72 h. The release of fermentable sugars was measured, comparing the samples obtained with and without plasma treatment. The highest sugar release was achieved using the plasma-in-liquid pretreatment in a single step, with glucose and xylose yields of 51.3 and 38.5%, respectively, after enzymatic hydrolysis. Thus, an effective pretreatment was developed to be applied to biomass such as: corn cob, sugarcane bagasse, bamboo, eucalyptus, etc., in order to reduce the environmental impact and, at the same time, produce biofuels.
Graphic Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alex Marvin, W., Schmidt, L.D., Benjaafar, S., Tiffany, D.G., Daoutidis, P.: Economic optimization of a lignocellulosic biomass-to-ethanol supply chain. Chem. Eng. Sci. 67, 68–79 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2011.05.055
Maas, R.H.W., Bakker, R.R., Boersma, A.R., Bisschops, I., Pels, J.R., de Jong, E., Weusthuis, R.A., Reith, H.: Pilot-scale conversion of lime-treated wheat straw into bioethanol: quality assessment of bioethanol and valorization of side streams by anaerobic digestion and combustion. Biotechnol. Biofuels 1, 1 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-1-14
Arantes, V., Saddler, J.N.: Access to cellulose limits the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis: the role of amorphogenesis. Biotechnol. Biofuels 3, 1–11 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-3-1
Lopes, M.L., Cristina, S., Paulillo, D.L., Godoy, A., Cherubin, R.A., Lorenzi, M.S., Henrique, F., Giometti, C., Bernardino, C.D., Berbert, H., Neto, D.A., Amorim, H.V.De: Biotechnology and industry microbiology ethanol production in Brazil : a bridge between science and industry. Brazilian J. Microbiol. 47, 64–76 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2016.10.003
De Guilherme, A.A., Dantas, P.V.F., Soares, J.C.J., Dos Santos, E.S., Fernandes, F.A.N., De Macedo, G.R.: Pretreatments and enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse aiming at the enhancement of the yield of glucose and xylose. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 34, 937–947 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-6632.20170344s20160225
Aditiya, H.B., Mahlia, T.M.I., Chong, W.T., Nur, H., Sebayang, A.H.: Second generation bioethanol production : a critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 66, 631–653 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.07.015
Jönsson, L.J., Alriksson, B., Nilvebrant, N., Wear, S., Paper, C., Effects, S.: Bioconversion of lignocellulose: inhibitors and detoxification. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 6, 16 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-6-16
Taherzadeh, M.J., Karimi, K.: Pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes to improve ethanol and biogas production: a review. (2008)
Kumar, P., Kumar, P., Barrett, D.M., Barrett, D.M., Delwiche, M.J., Delwiche, M.J., Stroeve, P., Stroeve, P.: Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for ef cient hydrolysis and biofuel production. Ind. Eng. Chem. 48, 3713–3729 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie801542g
Kriegseis, J., Möller, B., Grundmann, S., Tropea, C.: Capacitance and power consumption quantification of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma actuators. J. Electrostat. 69, 302–312 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elstat.2011.04.007
Kogelschatz, U., Eliasson, B., Egli, W., Kogelschatz, U., Eliasson, B., Principle, W.E.D.D.: Dielectric-barrier discharges. Principle and Applications. HAL Id : jpa-00255561. (1997)
Bruggeman, P., Leys, C.: Non-thermal plasmas in and in contact with liquids. J. Phys. D 42, 053001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/42/5/053001
Žigon, J., Petrič, M., Dahle, S.: Dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma pretreatment of lignocellulosic materials in air at atmospheric pressure for their improved wettability: a literature review. Holzforschung 72, 979–991 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2017-0207
Fiebrandt, M., Lackmann, J.W., Stapelmann, K.: From patent to product? 50 years of low-pressure plasma sterilization. Plasma Process. Polym. 15(12), 1800139 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.201800139
Miranda, F.S., Maciel, H.S., Skane, K.K., Santos, L.V., Santos, P.M., Silva, J.S., Pessoa, R.S.: Reator de plasma de descarga por barreira dielétrica, processo e sistema de pré-tratamento de biomassa lignocelulósica—BR1O2012 031364–2 A2, (2014)
Lucas, J., Lucas, P., Mercier, T.Le, Rollat, A., Davenport, W.: Rare earths science, technology, production and use. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2015)
Zhu, Y., Malten, M., Torry-Smith, M., McMillan, J.D., Stickel, J.J.: Calculating sugar yields in high solids hydrolysis of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 2897–2903 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.134
Sluiter, J.B., Chum, H., Gomes, A.C., Tavares, R.P.A., Azevedo, V., Pimenta, M.T.B., Rabelo, S.C., Marabezi, K., Curvelo, A.A.S., Alves, A.R., Garcia, W.T., Carvalho, W., Esteves, P.J., Mendonça, S., Oliveira, P.A., Ribeiro, J.A.A., Mendes, T.D., Vicentin, M.P., Duarte, C.L., Mori, M.N.: Evaluation of Brazilian sugarcane bagasse characterization: an interlaboratory comparison study. J. AOAC Int. 99, 579–585 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.15-0063
Mok, W.S.L., Antal, M.J.: Uncatalyzed solvolysis of whole biomass hemicellulose by hot compressed liquid water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 31, 1157–1161 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00004a026
Laroussi, M.: Low temperature plasma-based sterilization: overview and state-of-the-art. Plasma Process. Polym. 2, 391–400 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.200400078
Rutala, W.A., Weber, D.J.: Disinfection, sterilization, and antisepsis: an overview. Am. J. Infect. Control. 47, A3–A9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2019.01.018
Wright, A., Bandulasena, H., Ibenegbu, C., Leak, D., Holmes, T., Zimmerman, W., Shaw, A., Iza, F.: Dielectric barrier discharge plasma microbubble reactor for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. AIChE J. 64, 3803–3816 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.16212
Grous, W.R., Converse, A.O., Grethlein, H.E.: Effect of steam explosion pretreatment on pore size and enzymatic hydrolysis of poplar. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 8, 274–280 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(86)90021-9
Li, J., Henriksson, G., Gellerstedt, G.: Lignin depolymerization/repolymerization and its critical role for delignification of aspen wood by steam explosion. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 3061–3068 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.10.018
Vanholme, R., Demedts, B., Morreel, K., Ralph, J., Boerjan, W.: Lignin biosynthesis and structure. Plant Physiol. 153, 895–905 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.155119
Singh, R., Shukla, A., Tiwari, S., Srivastava, M.: A review on delignification of lignocellulosic biomass for enhancement of ethanol production potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 32, 713–728 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.01.051
Reid, J.S.G.: Carbohydrate metabolism structural carbohydrates. Academic Press, London (1997)
Kataria, R., Ghosh, S.: NaOH pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of saccharum spontaneum for reducing sugars production. Energy Sources A 36, 1028–1035 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2010.551268
Zheng, Y., Lin, H.M., Tsao, G.T.: Pretreatment for cellulose hydrolysis by carbon dioxide explosion. Biotechnol. Prog. 14, 890–896 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1021/bp980087g
Vidal, P.F., Molinier, J.: Ozonolysis of lignin - Improvement of in vitro digestibility of poplar sawdust. Biomass. 16, 1–17 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-4565(88)90012-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miranda, F.S., Rabelo, S.C., Pradella, J.G.C. et al. Plasma in-Liquid Using Non-contact Electrodes: A Method of Pretreatment to Enhance the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Biomass. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 4921–4931 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00824-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00824-5