Abstract
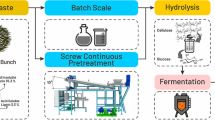
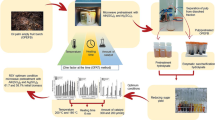
Pretreatment is an important step in the conversion of biomass to bioethanol. In this study microwave-assisted oxalic acid (MOA) pretreatment was chosen to pretreat oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB) to enhance enzymatic saccharification of the biomass. The objective of this study was to determine an optimum pretreatment condition for reducing sugar production, which could be further fermented by yeast to produce ethanol. Preliminary study was conducted to determine the range of duration of heating and temperature that will be used in the optimization by using response surface methodology (RSM). Central composite design (CCD) was used with three independent variables (duration of heating, temperature and acid concentration). Reducing sugar yield per initial biomass was used as a response variable. Preliminary study, that was conducted at 160, 170, 180, 190, and 200 °C for 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5, and 15 min, shows that pretreatment at temperature of 170–190 °C for 5–10 min produced higher reducing sugars than other conditions. Optimization using RSM shows that the optimum condition of MOA pretreatment of OPEFB was at 190 °C for 3 min with 1.1% oxalic acid, which resulted in as much as 34.60% reducing sugars after enzymatic saccharification. The pretreated OPEFB was then characterized and compared with untreated OPEFB. MOA pretreatment successfully removed 50.57% of lignin and 76.56% of hemicellulose from the OPEFB that were confirmed by a decrease or disappearance of the absorption bands of functional groups at 1339–1650 cm−1 and 1735 cm−1, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kementerian Sekretariat Negara Republik Indonesia.: Peraturan Presiden Republik Indonesia Nomor 5 Tahun 2006 Tentang Kebijakan Energi Nasional. http://www.setneg.go.id/cindex.php?Option=com_perundangan&id=44&task=detail&catid=6&Itemid=42&tahun=2006/ (2016). Accessed 26 Nov 2016
Dewan Energi Nasional Republik Indonesia.: Outlook Energi Indonesia 2014. http://www.den.go.id/index.php/publikasi/index/EnergyOutlook/ (2016). Accessed 26 Nov 2016
Banco Nacional de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Social, Centro de Gestão e Estudos Estratégicos.: Sugar-cane Based Bioethanol Energy for Sustainable Development, 1st edn. BNDES, Rio de Janeiro (2008)
Chaudhary, N., Qazi, J.I.: Lignocellulose for ethanol production: a review of issue relating to bagasse as source material. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 1(8), 1270–1274 (2011)
Mariam, I., Manzoor, K., Ali, S., Ul-haq, I.: Enhanced production of ethanol from free and immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae under stationary culture. Pak. J. Bot. 41(2), 821–833 (2009)
Ishola, M.M., Taherzadeh, M.J.: Effect of fungal and phosphoric acid pretreatment on ethanol production from oil palm empty fruit bunches (OPEFB). Bioresour. Technol. 165, 9–12 (2014)
Kristiani, A., Nurdin, E., Yosi, A., Fauzan, A., Sudiyani, Y.: Effect of combining chemical and irradiation pretreatment process to characteristic of oil palm’s empty fruit bunches as raw material for second generation bioethanol. Energy Procedia 68, 195–204 (2015)
Statistics Indonesia: Indonesian Oil Palm Statistics 2016. Statistics Indonesia, Jakarta (2017)
Wong, E.D., Razali, A.K., Kawai, S.: Zero emission in palm oil industry: case study of East Oil Mill, Golden Hope Plantation Bhd., Malaysia. In: Proceedings of the Third International Wood Science Symposium, pp. 153–156 (2000)
Joshi, B., Bhatt, M.R., Sharma, D., Joshi, J., Malla, R., Srerrama, L.: Review lignocellulosic ethanol production: current practise and recent developments. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 6(8), 172–182 (2011)
Zheng, Y., Pan, Z., Zhang, R.: Overview of biomass pretreatment for cellulosic ethanol production. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2(3), 51–68 (2009)
Hermiati, E., Mangunwidjaja, D., Sunarti, T.C., Suparno, O., Prasetya, B.: Pemanfaatan biomassa lignoselulosa ampas tebu untuk produksi bioetanol. J. Litbang Pertan. 29(4), 121–130 (2010)
Idi, A., Mohamad, S.E.: Bioethanol from second generation feedstock (lignocellulose biomass). Interdiscip. J. Contemp. Res. Bus. 3(8), 919–935 (2011)
Dawson, L., Boopathy, R.: Cellulosic ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse without enzymatic saccharification. BioResources 3(2), 452–460 (2008)
Patel, S.J., Onkarappa, R., Sobha, K.S.: Fungal pretreatment studies on rice husk and bagasse for ethanol production. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 6(4), 1921–1926 (2007)
Naik, S.N., Goud, V.V., Rout, P.K., Dalay, A.K.: Production of first and second generation biofuels: a comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14, 578–597 (2010)
Chandel, A.K., Kapoor, R.K., Singh, A.K., Kuhad, R.C.: Detoxification of sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 1947–1950 (2007)
Mohamad, N.L., Kamal, S.M.M., Abdullah, N., Ismail, I.: Evaluation of fermentation conditions by Candida tropicalis for xylitol production from sago trunk cortex. BioResources 8(2), 2499–2509 (2013)
Li, Z., Guo, X., Feng, X., Li, C.: An environment friendly and efficient process for xylitol bioconversion from enzymatic corncob hydrolysate by adapted Candida tropicalis. Chem. Eng. J. 263, 249–256 (2015)
Saracoglu-Eken, N., Arslan, Y.: Comparison of different pretreatment in ethanol fermentation using corn cob hemicellulosic hydrolysate with Pichia stipitis and Candida shehatae. Biotechnol. Lett. 22, 855–858 (2000)
Puligundla, P., Oh, S.-E., Mok, C.: Microwave-assisted pretreatment technologies for the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to sugars and ethanol: a review. Carbon Lett. 17(1), 1–10 (2016)
Aguilar-Reynosa, A., Romani, A., Rodriguez-Jasso, R.M., Aguilar, C.N., Garrote, G., Ruiz, H.A.: Microwave heating processing as alternative of pretreatment in second generation biorefinery: an overview. Energy Convers. Manag. 136, 50–65 (2017)
Fatriasari, W.: Reducing Sugar Production Through Pretreatment Process Engineering of Betung Bamboo (Dendrocalamus asper (Schult. f)). Doctoral thesis, Graduate School, Bogor Agricultural University, Bogor (2014)
Fatriasari, W., Syafii, W., Wistara, N., Syamsu, K., Prasetya, B.: Lignin and cellulose changes of betung bamboo (Dendrocalamus asper) pretreated microwave heating. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 6(2), 187–196 (2016)
Tsubaki, S., Oono, K., Onda, A., Yanagisawa, K., Azuma, J.: Comparative decomposition kinetics of neutral monosaccharides by microwave and induction treatments. Carbohydr. Res. 375, 1–4 (2013)
Lanigan, B.A.: Microwave Processing of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Production of Fuels. Thesis, Department of Chemistry, University of York, York (2010)
Mood, S.H., Golfeshan, A.H., Tabatabei, M., Jouzani, G.S., Najafi, G.H., Gholami, M., Ardjmand, M.: Lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol, a comprehensive review with a focus on pretreatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 27, 77–93 (2013)
Ethaib, S., Omar, R., Kamal, S.M.M., Biak, D.R.A.: Microwave-assisted pretreatment of lignocellulossic biomass: a review. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2:97–109 (2015)
Lee, J.-W., Rodrigues, R.C.L.B., Kim, H.J., Choi, I.G., Jeffries, T.W.: The roles of xylan and lignin in oxalic acid pretreated corncob during separate enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 4379–4385 (2010)
Yan, Y., Zhang, C., Lin, Q., Wang, X., Cheng, B., Li, H., Ren, J.: Microwave-assisted oxalic acid pretreatment for the enhancing of enzyme hydrolysis in the production of xylose and arabinose from bagasse. Molecules 23, 862 (2018)
Lee, J.-W., Rodrigues, R.C.L.B., Kim, H.J., Choi, I.-G., Jeffries, T.W.: The role of xylan and lignin in oxalic acid pretreatment corncob during separate enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 4379–4385 (2010)
Nomanbhay, S.M., Hussain, R., Palanisamy, K.: Microwave-assisted alkaline pretreatment and microwave-assisted enzymatic saccharification of oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber for enhanced fermentable sugar yield. J. Sustain. Energy Syst. 3, 7–17 (2013)
Akhtar, J., Teo, C.L., Lai, L.W., Hassan, N., Idris, A., Aziz, R.A.: Factors affecting delignification of oil palm empty fruit bunch by microwave-assisted dilute acid/alkali pretreatment. BioResources 10(1), 588–596 (2015)
Laghari, S.M., Isa, M.H., Laghari, A.J.: Delignification of OPEFB by microwave-assisted chemical pretreatment. Malays. J. Sci. 35(1), 8–14 (2016)
Risanto, L., Anita, S.H., Hermiati, E., Falah, F.: Microwave irradiation and enzymatic hydrolysis of sengon (Paraserianthes falcatarina). Proc. Indones. Wood Res. Soc. 355–361 (2011)
Hermiati, E.: Process Engineering of Cassava Pulp Hydrolysis Using Microwave Heating for Ethanol Production. Doctoral thesis, Graduate School, Bogor Agricultural University, Bogor (2012)
Fatriasari, W., Syafii, W., Wistara, N., Syamsu, K., Prasetya, B.: Digestibility of betung bamboo fiber following fungal pretreatment. Makara J. Technol. 18(22), 51–58 (2014)
Anita, S.H., Risanto, L., Hermiati, E., Fatriasari, W.: Pretreatment of oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB) using microwave irradiation. Proc. Indones. Wood Res. Soc. 348–354 (2011)
Solihat, N.N., Sari, F.P., Risanto, L., Anita, S.H., Fitria, Fatriasari, W., Hermiati, E.: Disruption of oil palm empty fruit bunches by microwave assisted-oxalic acid pretreatment. J. Math. Fundam. Sci. 49(3), 244–257 (2017)
Fatriasari, W., Raniya, R., Oktaviani, M., Hermiati, E.: The improvement of sugar and bioethanol production of oil palm empty fruit bunches (Elaeis guineensis Jacq) through microwave-assisted maleic acid pretreatment. BioResources 13(2), 4378–4403 (2018)
Amenaghawon, A.N., Balogun, A.A., Agbonghac, E.E., Ogbeide, S.E., Okieimen, C.O.: Statistical optimisation of dilute acid pretreatment of corn stover using response surface methodology. J. Environ. 2(2), 34–40 (2013)
Risanto, L., Fitria, Fajriutami, T., Hermiati, E.: Enzymatic Saccharification of Liquid Hot Water and Dilute Sulfuric Acid Pretreated Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch and Sugarcane Bagasse. IOP, Bristol (2018)
Warrand, J., Janssen, H.-G.: Controlled production of oligosaccharides from amylose by acid-hydrolysis under microwave treatment: comparison with conventional heating. Carbohydr. Polym. 69(2), 353–362 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.10.021
Whistler, R.L., Daniel, J.R.: Carbohydrates. In: Fennema, O.R. (ed.) Food Chemistry, pp. 69–137. Marcel Dekker, New York (1985)
Adney, B., Baker, J.: Measurement of Cellulase Activities: Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP). Issue Date: 08/12/1996. Technical Report NREL/TP-510-42628. January 2008. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Colorado (2008)
TAPPI. TAPPI T264 cm-97.: Preparation of Wood for Chemical Analysis. TAPPI Press, Atlanta (1997)
TAPPI. TAPPI Test Method T 211 om-02.: Ash in Wood, Pulp, Paper, and Paperboard: Combustion at 525 °C (2002)
TAPPI. TAPPI Test Method T 204 cm-97.: Solvent Extractives of Wood and Pulp (1997)
Punyamurthy, R., Sampathkumar, D., Bennehalli, B., Srinivasa, C.V.: Influence of esterification on the water absorption property of single abaca fiber. Chem. Sci. Trans. 2(2), 413–422 (2013). https://doi.org/10.7598/cst2013.371
Sluiter, A., Hames, B., Ruiz, R., Scarlata, C., Sluiter, J., Templeton, D., Crocker, D.: Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass—Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP). In: National Renewable Energy Laboratory Technical Report NREL/TP-510-42618 (2012)
Wise, L.E., Murphy, M., Addieco: Chlorite holocellulose, its fractionation and bearing on summative wood analysis and on studies on the hemicelluloses. Pap. Trade J. 122(2), 35–43 (1946)
Rowell, R.M., Pettersen, R., Han, J.S., Rowell, J.S., Tshabalala, M.A.: Cell wall chemistry. In: Rowell, R.M. (ed.) Handbook Wood Chemistry and Wood Composites, 1st edn., pp. 71–72. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005)
Focher, B., Palma, M.T., Canetti, M., Torri, G., Cosentino, C., Gastaldi, G.: Structural differences between non-wood plant celluloses: evidence from solid state NMR, vibrational spectroscopy and X-ray diffractometry. Ind. Crops Prod. 13, 193–208 (2001)
Tan, L., Yu, Y., Li, X., Zhao, J., Qu, Y., Choo, Y.M., Loh, S.K.: Pretreatment of empty fruit bunch from oil palm for fuel ethanol production and proposed biorefinery process. Bioresour. Technol. 135, 275–282 (2013)
Um, B.-H., van Walsum, G.P.: Effect of pretreatment severity on accumulation of major degradation products from dilute acid pretreated corn stover and subsequent inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 168, 406–420 (2012)
Behera, S., Arora, R., Nandhagopai, N., Kumar, S.: Importance of chemical pretreatment for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 36, 91–106 (2014)
Scordia, D., Cosentino, S.L., Jeffries, T.W.: Second generation bioethanol production from Saccharum spontaneum L. spp. aegyptiacum (Willd.) Hack. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 5358–5365 (2010)
Scordia, D., Cosentino, S.L., Lee, J.W., Jeffries, T.W.: Dilute oxalic acid pretreatment for biorefining giant reed (Arundo donux L.). Biomass Bioenergy 35, 3018–3024 (2011)
de Carvalho, D.M., Sevastyanova, O., Penna, L.S., da Silva, B.P., Lindstrom, M.E., Colodette, J.L.: Assessment of chemical transformations in eucalyptus, sugarcane bagasse, and straw during hydrothermal, dilute acid, and alkaline pretreatments. Ind. Crops Prod. 73, 118–126 (2015)
Xu, F., Yu, J., Tesso, T., Dowell, F., Wang, D.: Qualitative and quantitative analysis of lignocellulosic biomass using infrared techniques: a mini-review. Appl. Energy 104, 801–809 (2013)
Lee, J.W., Kim, J.Y., Jang, H.M., Lee, M.W., Park, J.M.: Sequential dilute acid and alkali pretreatment of corn stover: sugar recovery efficiency and structural characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 182, 296–301 (2015)
Sim, S.F., Mohamed, M., Lu, N.A., Lu, M.I., Sarman, N.S.P., Samsudin, S.N.S.: Computer-assisted analysis of fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra for characterization of various treated and untreated agriculture biomass. BioResources 7(4), 5367–5380 (2012)
Dong, S.J., Zhang, B.X., Gao, Y.F., Hu, X.M.: An efficient process for pretreatment of lignocelluloses in functional ionic liquids. Int. J. Polym. Sci. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/978983
Ishola, M.M., Millati, R., Syamsiah, S., Cahyanto, M.N., Niklasson, C., Taherzadeh, M.J.: Structural changes of oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB) after fungal and phosphoric acid pretreatment. Molecules 17, 14995–15012 (2012)
Koutsianitis, D., Mitani, C., Giagli, K., Tsalagkas, D., Halász, K., Kolonics, O., Gallis, C., Csóka, L.: Properties of ultrasound extracted bicomponent lignocellulose thin films. Ultrason. Sonochem. 23, 148–155 (2015)
O’Dowyer, J.P., Zhu, L., Granda, C.B., Holzapple, M.T.: Enzymatic hydrolysis of lime-pretreated corn stover and investigation of the HCH-1 model:inhibition pattern, degree of inhibition, validity of simplified HCH-1 model. Bioresour. Technol. 98(16), 2969–2977 (2007)
Pramasari, D.A., Haditjaroko, L., Sunarti, T.C., Hermiati, E., Syamsu, K.: The effectiveness of physical and alkali hydrothermal pretreatment in improving enzyme susceptibility of sweet sorghum bagasse. Jurnal Bahan Alam Terbarukan 6(2), 117–131 (2017)
Kim, D.S., Myint, A.A., Lee, H.W., Yoon, J., Lee, Y.W.: Evaluation of hot compressed water pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification of tulip tree sawdust using severity factors. Bioresour. Technol. 144, 460–466 (2013)
Harmsen, P.F.H., Hujigen, W.J.J., Bermudez Lopez, L.M., Bakker, R.R.C.: Literature Review of Physical and Chemical Pretreatment Processes for Lignocellulosic Biomass, pp. 1–49. Food & Biobased Research, Wageningen (2010)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by JST (Japan Science and Technology Agency)—JICA (Japan International Collaboration Agency)—SATREPS (Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development) Project: Innovative Bio-production in Indonesia: Integrated Bio-refinery Strategy to Promote Biomass Utilization using Super-microbes for Fuels and Chemicals Production (2013–2018) and DIPA of Research Center for Biomaterials LIPI (Indonesian Institute of Sciences) in the Fiscal Year of 2015–2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anita, S.H., Fitria, Solihat, N.N. et al. Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Oxalic Acid Pretreatment of Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch for Production of Fermentable Sugars. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 2673–2687 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-00566-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-00566-w