Abstract
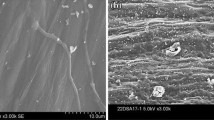
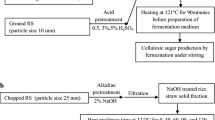
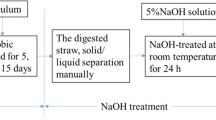
Chemical and biological pretreatments (with NaOH, HCl, CO(NH2)2 and cellulase) were used to pretreat rice straw at ambient temperature (about 20 °C) to improve its biodegradability and increase anaerobic biogas production. The NaOH and CO(NH2)2 pretreatments reduced the percentage contents of hemicellulose and lignin. The HCl pretreatment mainly dissolved the hemicellulose and resulted in decreases of 12.5–7.1% of the hemicellulose. The percentage content of cellulose showed a dramatic decrease, from 38.3 to 10.9%, after the cellulase pretreatment. Compared with untreated rice straw substrate, the total biogas yield ratios were 3.38–5.91, 1.63–2.99, 1.93–5.22 and 3.62–6.45, with a hydraulic retention time of 30 days, under NaOH, HCl, CO(NH2)2 and cellulose pretreatments, respectively. The highest yields of biogas and methane were obtained from 40 U/g total solids (TS) cellulase-pretreated rice straw (20.433 and 9.918 L respectively). Biogas production yields of volatile solids (VS) were 123.7, 273.8, 318.5, 353.5 mL/g for control, 6% CO(NH2)2-, NaOH- and 40 U/g TS cellulase-pretreated rice straw substrate, respectively. Compared to untreated rice straw substreates, cumulative biogas production yields increased 16–103, 25–122% for NaoH- and cellulase-pretreated rice straw substrate, respectively. The results suggested that the highest removal efficiencies of TS and VS were obtained from 6% NaOH-pretreated (53.80 and 36.80%), 6% CO(NH2)2-pretreated (54.90 and 36.10%) and 40 U/g TS cellulase-pretreated (51.30 and 37.30%) rice straw substrate. In short, NaOH, HCl, CO(NH2)2 and cellulase pretreatment was suitable to enhance the biogas production. However, to choose the optimal treatment, the energy requirements relative to the energy gain as extra biogas production have to be taken into account, as well as the costs of chemicals or enzymes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandra, R., Takeuchi, H., Hasegawa, T., Kumar, R.: Improving biodegradability and biogas production of wheat straw substrates using sodium hydroxide and hydrothermal pretreatments. Energy. 43(1), 273–282 (2012)
Mussgnug, J.H., Klassen, V., Schluter, A., Kruse, O.: Microalgae as substrate for fermentative biogas production in a combined biorefinery concept. J. Biotechnol. 150(1), 51–56 (2010)
Ziemiński, K., Romanowska, I., Kowalska, M.: Enzymatic pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes to improve biogas production. Waste Manage. 32(6), 1131–1137 (2012)
Cavinato, C., Bolzonella, D., Pavan, P., Fatone, F., Cecchi, F.: Mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of waste activated sludge and source sorted biowaste in pilot- and full-scale reactors. Renew. Energy 55, 260–265 (2013)
Scano, E.A., Asquer, C., Pistis, A., Ortu, L., Demontis, V., Cocco, D.: Biogas from anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable wastes: experimental results on pilot-scale and preliminary performance evaluation of a full-scale power plant. Energy Convers. Manage. 77, 22–30 (2014)
Grimberg, S.J., Hilderbrandt, D., Kinnunen, M., Rogers, S.: Anaerobic digestion of food waste through the operation of a mesophilic two-phase pilot scale digester—Assessment of variable loadings on system performance. Bioresour. Technol. 178, 226–229 (2015)
Monlau, F., Sambusiti, C., Antoniou, N., Barakat, A., Zabaniotou, A.: A new concept for enhancing energy recovery from agricultural residues by coupling anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis process. Appl. Energy 148, 32–38 (2015)
Bi, Y., Gao, C., Wang, Y., Li, B. Estimation of straw resources in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 25, 211–217 (2009)
Amiri, H., Karimi, K., Zilouei, H.: Ogranosolv pretreatment of rice straw for efficient acetone, butanol, and ethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 152, 450–456 (2014)
Lei, Z., Chen, J., Zhang, Z., Sugiura, N.: Methane production from rice straw with acclimated anaerobic sludge: effect of phosphate supplementation. Bioresour. Technol. 101(12), 4343–4348 (2010)
Zheng, M.X., Li, X.J., Li, L.Q., Yang, X.J., He, Y.F.: Enhancing anaerobic biogasification of corn stover through wet state NaOH pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 100(21), 5140–5145 (2009)
Mussoline, W., Esposito, G., Giordano, A., Lens, P.: The anaerobic digestion of rice straw: a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(9), 895–915 (2013)
Shafiei, M., Kabir, M.M., Zilouei, H., Horváth, I.S., Karimi, K.: Techno-economical study of biogas production improved by steam explosion pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 148, 53–60 (2013)
Kumar, P., Barrett, D.M., Delwiche, M.J., Stroeve, P.: Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient hydrolysis and biofuel production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 48(8), 3713–3729 (2009)
Alvira, P., Tomás-Pejó, E., Ballesteros, M., Negro, M.J.: Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: areview. Bioresour. Technol. 101(13), 4851–4861 (2010)
Sawatdeenarunat, C., Surendra, K.C., Takara, D., Oechsner, H., Khanal, S.K.: Anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic biomass: challenges and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 178, 178–186 (2015)
Taherzadeh, M., Karimi, K.: Pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes to improve ethanol and biogas production: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 9(9), 1621–1651 (2008)
Bruni, E., Jensen, A.P., Angelidaki, I.: Comparative study of mechanical, hydrothermal, chemical and enzymatic treatments of digested biofibers to improve biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 101(22), 8713–8717 (2010)
Teghammar, A., Karimi, K., Horváth, I.S., Taherzadeh, M.J.: Enhanced biogas production from rice straw, triticale straw and softwood spruce by NMMO pretreatment. Biomass Bioenerg. 36, 116–120 (2012)
Taherdanak, M., Zilouei, H.: Improving biogas production from wheat plant using alkaline pretreatment. Fuel. 115, 714–719 (2014)
Kabir, M.M., Niklasson, C., Taherzadeh, M.J., Horváth, I.S.: Biogas production from lignocelluloses by N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) pretreatment: effects of recovery and reuse of NMMO. Bioresour. Technol. 161, 446–450 (2014)
Yuan, X., Wen, B., Ma, X., Zhu, W., Wang, X., Chen, S., Cui, Z.: Enhancing the anaerobic digestion of lignocellulose of municipal solid waste using a microbial pretreatment method. Bioresour. Technol. 154, 1–9 (2014)
Gabhane, J., William, S.P.M.P., Vaidya, A.N., Das, S., Wate, S.R.: Solar assisted alkali pretreatment of garden biomass: effects on lignocellulose degradation, enzymatic hydrolysis, crystallinity and ultra-structural changes in lignocellulose. Waste Manage. 40, 92–99 (2015)
Motte, J.C., Sambusiti, C., Dumas, C., Barakat, A.: Combination of dry dark fermentation and mechanical pretreatment for lignocellulosic deconstruction: an innovative strategy for biofuels and volatile fatty acids recovery. Appl. Energy 147, 67–73 (2015)
Geddes, C.C., Peterson, J.J., Roslander, C., Zacchi, G., Mullinnix, M.T., Shanmugam, K.T., Ingram, L.O.: Optimizing the saccharification of sugar cane bagasse using dilute phosphoric acid followed by fungal cellulases. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 1851–1857 (2010)
Xi, B.D., He, X.S., Dang, Q.L., Yang, T.X., Li, M.X., Wang, X.W., Li, D., Tang, J: Effect of multi-stage inoculation on the bacterial and fungal community structure during organic municipal solid wastes composting. Bioresour. Technol. 196, 399–405 (2015)
Hansen, T.L., Schmidt, J.E., Angelidaki, I., Marca, E.J.C., Mosbaek, H., Christensen, T.H.: Method for determination of methane potentials of solid organic waste. Waste Manage. 24(4), 393–400 (2004)
APHA: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 21st ed. American Public health association, Washington (2005)
Van Soest, P.J., Robertson, J.B., Lewis, B.A.: Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 74(10), 3583–3597 (1991)
Eveleigh, D.E., Mandels, M., Andreotti, R., Roche, C.: Measurement of saccharifying cellulase. Biotechnol. Biofuel 2, 21 (2009)
Xiao, B., Sun, X.F., Sun, R.: Chemical, structural, and thermal characterizations of alkali-soluble lignins and hemicelluloses, and cellulose from maize stems, rye straw, and rice straw. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 74(2), 307–319 (2001)
Hu, Z., Wen, Z.: Enhancing enzymatic digestibility of switch grass by microwave-assisted alkali pretreatment. Biochem. Eng. J. 38(3), 369–378 (2008)
Chen, H.: Chemical composition and structure of natural lignocellulose. In: Chen H (ed) Biotechnology of Lignocellulose, pp. 25–71. Springer, Dordrecht (2014)
Fan, L.T., Gharpuray, M.M., Lee, Y.H.: Cellulose hydrolysis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1987)
Ramos, L.P.: The chemistry involved in the steam treatment of lignocellulosic materials. Qumica Nova 26(6), 863–871 (2003)
Luo, L., Ding, Q., Gong, W., Wang, Z., Li, W., Qin, L.: Urea ammoniated pretreatment improving dry anaerobic fermentation characteristics of rice straw. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 31, 234–239 (2015)
Li, X., Dang, F., Zhang, Y., Zou, D., Yuan, H.: Anaerobic digestion performance and mechnaism of ammoniation pertreatment of corn stover. Bioresources 10, 5777–5790 (2015)
Pang, Y.Z., Liu, Y.P., Li, X.J., Wang, K.S., Yuan, H.R.: Improving biodegradability and biogas production of corn stover through NaOH solid state pretreatment. Energy Fuel 22(4), 2761–2766 (2008)
Zhong, W., Zhang, Z., Luo, Y., Sun, S., Qiao, W., Xiao, M.: Effect of biological pretreatments in enhancing corn straw biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 102(24), 11177–11182 (2011)
Kryvoruchko, V., Machmuller, A., Bodiroza, V., Amon, B., Amon, T.: Anaerobic digestion of by-products of sugar beet and starch potato processing. Biomass Bioenerg. 33(4), 620–627 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41503110), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20160430), the Project Funded by China Post doctoral Science Foundation (2016M591757), and the Natural Science Foundation for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province of China (15KJD480001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Bl., Guo, Xj., Yuan, Dh. et al. Comparison of Different Pretreatments of Rice Straw Substrate to Improve Biogas Production. Waste Biomass Valor 9, 1503–1512 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9950-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9950-9