Abstract
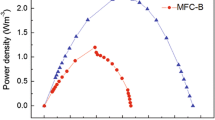
Alternative glycerol treatment and valorization, could be a promising solution, contributing to the biodiesel production economy. Thus, the potential of electricity generation from pure glycerol, using a two-chamber microbial fuel cell (MFC), was evaluated. The effect of glycerol concentration in a range of 0.5–5.2 g COD L−1 on MFC performance was examined. In order to achieve a stable MFC performance and a high power density, special attention was paid during the acclimation phase of the anaerobic consortium, which was performed using glucose, instead of glycerol, as substrate. The best performance of the cell was observed at a glycerol concentration of 3.2 g COD L−1. At this concentration, the Coulombic efficiency (CE) was 34.1 %, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency was approximately 99 % and the maximum power density was 65.4 mW m−2. Further increase of glycerol concentration to 5.2 g COD L−1 did not enhance the MFC performance, since the power density remained at 63.4 mW m−2, while the CE and the COD removal efficiency decreased to 22.1 and 81 %, respectively. The experimental results showed that glycerol is a suitable and promising substrate for power generation, using a simple two-chamber MFC and that acclimation of anaerobic sludge using glucose as substrate, is a suitable procedure for securing a stable MFC performance, even at high glycerol concentrations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yazdani, S.S., Gonzalez, R.: Anaerobic fermentation of glycerol: a path to economic viability for the biofuels industry. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 18, 213–219 (2007)
Rashid, U., Anwar, F.: Production of biodiesel through optimized alkaline-catalyzed transesterification of rapeseed oil. Fuel 87, 265–273 (2008)
Asad, R., Saman, W.R.G., Nomura, N., Sato, S., Matsumura, M.: Pretreatment and utilization of raw glycerol from sunflower oil biodiesel for growth and 1, 3- propanediol production by Clostridium butyricum. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 83, 1072–1080 (2008)
Claude, S.: Research of new outlets for glycerol recent developments in France. Lipid Fett 101, 101–104 (1999)
Ciriminna, R., Della Pina, C., Rossi, M., Pagliaro, M.: Understanding the glycerol market. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 116, 1432–1439 (2014)
Robra, S., Cruz, R.S., Oliveira, A.M., Neto, J.A.A., Santos, J.V.: Generation of biogas using crude glycerin from biodiesel production as a supplement to cattle slurry. Biomass Bioenergy 34, 1330–1335 (2010)
Vlassis, T., Stamatelatou, A., Antonopoulou, G., Lyberatos, G.: Methane production via anaerobic digestion of glycerol: a comparison of conventional (CSTR) and high-rate digesters (PABR). J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 88, 2000–2006 (2013)
Akutsu, Y., Lee, D.Y., Li, Y.Y., Noike, T.: Hydrogen production potentials and fermentative characteristics of various substrates with different heat-pretreated natural microflora. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 34, 5365–5373 (2009)
Seifert, K., Waligorska, M., Wojtowski, M., Laniecki, M.: Hydrogen generation from glycerol in batch fermentation process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 34, 3671–3678 (2009)
Ito, T., Nakashimada, Y., Senba, K., Matsui, T., Nishio, N.: Hydrogen and ethanol production from glycerol-containing wastes discharged after biodiesel manufacturing process. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 100(3), 260–265 (2005)
Vlassis, T., Stamatelatou, A., Antonopoulou, G., Lyberatos, G.: Anaerobic treatment of glycerol for methane and hydrogen production. Glob. Nest J. 14(2), 149–156 (2012)
Bond, D.R., Holmes, D.E., Tender, L.M., Lovley, D.R.: Electrode-reducing microorganisms that harvest energy from marine sediments. Science 295, 483–485 (2002)
Rabaey, K., Rodríguez, J., Blackall, L.L., Keller, J., Gross, P., Batstone, D., Verstraete, W., Nealson, K.H.: Microbial ecology meets electrochemistry: electricity-driven and driving communities. ISME J. 1, 9–18 (2007)
Rabaey, K., Butzer, S., Brown, S., Keller, J., Rozendal, R.A.: High current generation coupled to caustic production using a lamellar bioelectrochemical system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(11), 4315–4321 (2010)
Clauwaert, P., Ha, D., Verstraete, W.: Energy recovery from energy rich vegetable products with microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 30, 1947–1951 (2008)
Feng, Y., Yang, Q., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Lee, H., Ren, N.: Treatment of biodiesel production wastes with simultaneous electricity generation using a single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 411–415 (2011)
Chookaew, T., Prasertsan, P., Ren, Z.J.: Two stage conversion of crude glycerol to energy using dark fermentation linked with microbial fuel cell or microbial electrolysis cell. New Biotechnol. 31(2), 179–184 (2014)
Sharma, Y., Parnas, R., Li, B.: Bioenergy production from glycerol in hydrogen producing bioreactors (HPBs) and microbial fuel cells (MFCs). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 36, 3853–3861 (2011)
Guimaraes, A.Q., Linares, J.J.: Glycerol utilization in microbial fuel cells: conditioning stage and influence of the glycerol concentration. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161(1), F125–F132 (2014)
Nimje, V.R., Chen, C.Y., Chen, C.C., Chen, H.R., Tseng, M.J., Jean, J.S., Chang, Y.F.: Glycerol degradation in single-chamber microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 2629–2634 (2011)
Reiche, A., Kirkwood, K.M.: Comparison of Escherichia coli and anaerobic consortia derived from compost as anodic biocatalysts in a glycerol-oxidizing microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 123, 318–323 (2012)
Bond, D.R., Lovely, D.R.: Electricity production by Geobacter sulfurreducens attached to electrodes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 1548–1555 (2003)
Aelterman, P., Freguia, S., Keller, J., Verstraete, W., Rabaey, K.: The anode potential regulates bacterial activity in microbial fuel cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 78, 409–418 (2008)
Logan, B.E., Cheng, S., Watson, V., Estadt, G.: Graphite fiber brush anodes for increased power production in air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 3341–3346 (2007)
Skiadas, I.V., Lyberatos, G.: The periodic anaerobic baffled reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 38, 401–408 (1998)
Antonopoulou, G., Stamatelatou, K., Bebelis, S., Lyberatos, G.: Electricity generation from synthetic substrates and cheese whey using a two chamber microbial fuel cell. Biochem. Eng. J. 50(1–2), 10–15 (2010)
Logan, B.E., Hamelers, B., Rozendal, R., Schroeder, U., Keller, J., Freguia, S., Aelterman, P., Verstraete, W., Rabaey, K.: Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 5181–5192 (2006)
APHA, AWWA, WPCF, American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC (1995)
Oh, S.E., Min, B., Logan, B.E.: Cathode performance as a factor in electricity generation in microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 4900–4904 (2004)
Sharma, Y., Li, B.: The variation of power generation with organic substrates in single-chamber microbial fuel cells (SCMFCs). Bioresour. Technol. 101, 1844–1850 (2010)
Zhang, Y., Min, B., Huang, L., Angelidaki, I.: Electricity generation and microbial community response to substrate changes in microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 102(2), 1166–1173 (2011)
Liu, H., Logan, B.E.: Electricity generation using an air–cathode single chamber microbial fuel cell in the presence and absence of a proton exchange membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 4040–4046 (2004)
Min, B., Cheng, S., Logan, B.E.: Electricity generation using membrane and salt bridge microbial fuel cells. Water Res. 39, 1675–1686 (2005)
Lefebvre, O., Tan, Z., Kharkwal, S., Ng, H.Y.: Effect of increasing anodic NaCl concentration on microbial fuel cell performance. Bioresour. Technol. 112, 336–340 (2012)
Logan, B.E., Murano, C., Scott, K., Gray, N.D., Head, I.M.: Electricity generation from cysteine in a microbial fuel cell. Water Res. 39, 942–952 (2005)
Chaudhuri, S.K., Lovley, D.R.: Electricity generation by direct oxidation of glucose in mediatorless microbial fuel cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1229–1232 (2003)
Tremouli, A., Antonopoulou, G., Bebelis, S., Lyberatos, G.: Operation and characterization of a microbial fuel cell fed with pretreated cheese whey at different organic loads. Bioresour. Technol. 131, 380–389 (2013)
Huang, L., Zeng, R.J., Angelidaki, I.: Electricity production from xylose using a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 99(10), 4178–4184 (2008)
Park, D.H., Zeikus, J.G.: Improved fuel cell and electrode designs for producing electricity from microbial degradation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 81, 348–355 (2003)
Ghangrekar, M.M., Shinde, V.B.: Performance of membrane-less microbial fuel cell treating wastewater and effect of electrode distance and area on electricity production. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 2879–2885 (2007)
Behera, M., Ghangrekar, M.M.: Performance of microbial fuel cell in response to change in sludge loading rate at different anodic feed pH. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 5114–5121 (2009)
Min, B., Kim, J.R., Oh, S.E., Regan, J.M., Logan, B.E.: Electricity generation from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cells. Water Res. 39, 4961–4968 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tremouli, A., Vlassis, T., Antonopoulou, G. et al. Anaerobic Degradation of Pure Glycerol for Electricity Generation using a MFC: The Effect of Substrate Concentration. Waste Biomass Valor 7, 1339–1347 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9498-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9498-0