Abstract
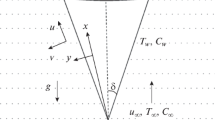
A mathematical model is presented for laminar, steady natural convection mass transfer in boundary layer flow from a rotating porous vertical cone in anisotropic high-permeability porous media. The transformed boundary value problem is solved subject to prescribed surface and free stream boundary conditions with a Maple 17 shooting method. Validation with a Chebyshev spectral collocation method is included. The influence of tangential Darcy number, swirl Darcy number, Schmidt number, rotational parameter, momentum (velocity slip), mass slip and wall mass flux (transpiration) on the velocity and concentration distributions is evaluated in detail. The computations show that tangential and swirl velocities are enhanced generally with increasing permeability functions (i.e., Darcy parameters). Increasing spin velocity of the cone accelerates the tangential flow, whereas it retards the swirl flow. An elevation in wall suction depresses both tangential and swirl flow. However, increasing injection generates acceleration in the tangential and swirl flow. With greater momentum (hydrodynamic) slip, both tangential and swirl flows are accelerated. Concentration values and Sherwood number function values are also enhanced with momentum slip, although this is only achieved for the case of wall injection. A substantial suppression in tangential velocity is induced with higher mass (solutal) slip effect for any value of injection parameter. Concentration is also depressed at the wall (cone surface) with an increase in mass slip parameter, irrespective of whether injection or suction is present. The model is relevant to spin coating operations in filtration media (in which swirling boundary layers can be controlled with porous media to deposit thin films on industrial components), flow control of mixing devices in distillation processes and also chromatographical analysis systems.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
L Bennamoun and A Belhamri Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process.4 221 (2008)
A S Altevogt, D E Rolston and S Whitaker Adv. Water Resour.26 717 (2003)
O Anwar Beg and O D Makinde, Petroleum Sci. Eng.76 93 (2011)
C Nicholson Rep. Prog. Phys.64(7) 815 (2001)
M A G Ulson de Souza and S Whitaker, Braz. J. Chem. Eng.20(2) 191 (2003)
K G Helmer, J D Bernard and H S Christopher NMR Biomed.8 297 (1995)
R M Cotta, C Baohua and P F L Heilbron Filho Convective Heat and Mass Transfer in Porous Media. NATO ASI Series. (Berlin: Springer) Volume 525 (1991)
J Piquemal, F A Kulacki and F Arinç Transp. Porous Media10 271 (1993)
K Vafai and C L Tien Int. J. Heat Mass Transf.25 1183 (1982)
H Marcus J. Geophys. Res.67 5215 (1962)
X Wang, F Thauvin and K K Mohanty Chem. Eng. Sci.54 1859 (1999)
K L Adams, W B Russel and E Rebenfeld Int. J. Multiph. Flow.14 203 (1988)
G Mishra and A Reddy ASCE J. Hydraul. Eng.109(6) 897 (1983)
G Chiogna, O A Cirpka, M Rolle and A Bellin J. Chem. Phys.51 261 (2015)
A Nakayama and F Kuwahara, Hand Book of Porous Media, Editor (K. Vafai), CRC Press, 235 (2005)
F Salzberg and S P Kezios ASME J. Heat Transf.87(4) 469 (1965)
J Newman J. Electrochem. Soc.119 69 (1972)
K A Smith and C K Colton AIChemE J.18 949 (1972)
B T Ellison and I Cornet, J. Electrochem. Soc.118(68) (1971)
C M Mohr and J Newman J. Electrochem. Soc.123 1687 (1976)
M Toren, M Ungarish, G Pinchuk and A Solan ASME J. Appl. Mech.58(2) 566 (1991)
A A Rashaida, D J Bergstrom and R J Sumner ASME J. Appl. Mech.73(1) 108 (2005)
Y Taamneh and R Omari J. Fluids2013 60483 (2013)
A F Miguel Thermal Sci.16(1) 167 (2012)
W A Khan, M J Uddin and A I M Ismail PloS One8(3) e54024 (2013)
O Anwar Bég, M J Uddin, M M Rashidi and N Kavyani, J. Eng. Thermophysics.23(2) 79 (2014)
C Y Wang Chem. Eng. Sci.57 3745 (2002)
V R Prasad, A Subba Rao, N B Reddy, B Vasu and O Anwar Beg Proc. IMechE-PART E J. Proc. Mech. Eng.227(4) 309 (2013)
K Bhattacharya Front. Heat Mass Transf.3 043006 (2012)
T Fang and W Jing Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul.19 3086 (2014)
M C Ece Appl. Math. Comput.179 231 (2006)
MAPLE from Waterloo Maple Software Inc., Canada (www.maplesoft.com) (2015)
M J Uddin, O Anwar Beg and N S Amin J. Magn. Magn. Mat.368 252 (2014)
O Anwar Beg, M Ferdows, S Islam and M N Islam J. Mech. Med. Biol.14 1450039-1 (2014)
M J Uddin, N H M Yusoff, O Anwar Beg and A I M Ismail Phys. Scr.87 1 (2013)
M J Uddin, W A Khan and A I M Ismail Transp. Porous Media92 867 (2012)
J P Boyd Chebyshev & Fourier Spectral Methods, 2nd edn. (Dover, New York) (2001)
G J Li, J Ma and B W Li ASME J. Heat Transf. 137(3) 032701 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4029237
A F Elsayed and O Anwar Beg J. Mech. Med. Biol.14(3) 1450043-1 (2014)
O Anwar Beg, M Hameed and T A Beg Int. J. Comput. Meth. Eng. Sci. Mech.14 104 (2013)
M M Hoque, M M Alam, M Ferdows and O Anwar Beg Proc. IMechE-Part H J. Eng. Med.227(11) 1155 (2013)
O Anwar Beg Numerical methods for multi-physical magnetohydrodynamics, New Developments in Hydrodynamics Research, Chapter 1 (New York: Nova Science) (2012)
Z Hussain PhD Thesis (Applied Mathematics, University of Birmingham, UK) (2010)
B Gebhert Heat Conduction and Mass Diffusion (New York: MacGraw Hill) (1993)
L Storelsetten and D A S Rees, Transp. Porous Media19 79 (1995)
B Gebhart, Y Jaluria, R L Mahajan and B Sammakia Buoyancy-Induced Flows and Transport (Washington: Hemisphere) (1988)
D Tripathi and O Anwar Beg, Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng.18(15) 1648 (2015)
Z Mehmood, R Mehmood and Z Iqbal Commun. Theor. Phys. 67(4) 443 (2017)
R Mehmood, S Nadeem, S Saleem and N S Akbar J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng.74 49 (2017)
R Tabasum, R Mehmood and O Pourmehran Part E J. Proc. Mech. Eng.232(5) 622 (2018)
G Makanda, O D Makinde and P Sibanda Math. Prob. Eng.2013 934712 (2013)
O D Makinde, N Sandeep, I L Animasaun and M S Tshehla Defect and Diffus. Forum. 374 67 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bég, O.A., Uddin, M.J., Bég, T.A. et al. Numerical study of self-similar natural convection mass transfer from a rotating cone in anisotropic porous media with Stefan blowing and Navier slip. Indian J Phys 94, 863–877 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01520-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01520-9