Abstract
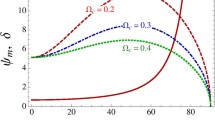
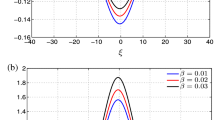
By employing quantum hydrodynamic formulation, oblique propagation of electrostatic ion waves and nonlinear structures are investigated in a magnetized dense Fermi plasma. Constituents are quantum (degenerate) electrons and non-degenerate mobile ions in presence of stationary massive ions (either positive or negative) in background. To reveal features of low frequency ion waves, where effects of Fermi degeneracy and quantum diffraction are significant, linear dispersion equation is derived by Fourier analysis of model equations. Nonlinear solitary pulse solution in low-amplitude limit is obtained via Korteweg de Vries equation. It is shown that wave dispersion due to electron Fermi pressure is important at very short wavelength regime. Effects of concentration of heavy ions and angle of propagation on wave are also studied. Results are discussed numerically with relevance of superdense plasmas mainly found in astrophysical regimes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Bonitz, A Filinov, J Boning and J W Dufty Introduction to Complex Plasmas (Berlin: Springer) (eds.) M Bonitz, N J Horing and P Ludwig p 41 (2010)
S A Khan and M Bonitz Quantum hydrodynamics Complex Plasmas: Scientific Challenges and Technological Opportunities (Berlin: Springer) (eds.) M Bonitz, K Becker, J Lopez and H Thomsen (2013)
F Haas Quantum Plasmas-An Hydrodynamic Approach (New York: Springer) (2011)
P K Shukla and B Eliasson Rev. Mod. Phys. 83 885 (2011)
D Kremp, M Schlanges and W D Kraeft Quantum Statistics of Nonideal Plasmas (Berlin: Springer) (2005)
A Markowich, C Ringhofer and C Schmeiser Semiconductor Equations (Vienna: Springer) (1990)
G Manfredi, P-A Hervieux, Y Yin and N Crouseilles Atomic-Scale Modeling of Nanosystems and NanostructuredMaterials, (Berlin: Springer) (eds.) C Massobrio, H Bulou and C Goyhenex p 1 (2010)
S H Glenzer and R Redmer Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 1625 (2009)
A Serbeto, L Monteiro, K Tsui and J T Mendonca Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 51 124024 (2009)
G Chabrier, D Saumon and A Y Potekhin J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 39 4411 (2006)
A Y Potekhin, G Chabrier, D Lai, W C G Ho and M van Adelsberg J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 39 4453 (2006)
A K Harding and D Lai Rep. Prog. Phys. 69 2631 (2006)
C Deutsch Phys. Lett. A 60 317 (1977)
C Deutsch, M M Gombert and H Minoo Phys. Lett. A 66 381 (1978)
V S Belyaev and V N Mikhaelov Laser Phys. 11 957 (2001)
F Haas, L G Garcia, J Goedert and G Manfredi Phys. Plasmas 10 3858 (2003)
F Haas Phys. Plasmas 12 062117 (2005)
P K Shukla and B Eliasson Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 245001 (2006)
S Chndrasekhar An Introduction to study of Stellar Structure (Chicago: University of Chicago Press) (1939)
G Manfredi and F Haas Phys. Rev. B 64 075316 (2001)
G Manfredi Fields Inst. Commun. 46 263 (2005)
P K Shukla and B Eliasson Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 096401 (2007)
S A Khan Phys. Plasmas 19 014506 (2012)
I Zeba, W M Moslem and P K Shukla Astrophys J. 750 72 (2012)
R Sabry, W M Moslem and P K Shukla Eur. Phys. J. D 51 233 (2009)
W F El-Taibany and A A Mamun Phys. Rev. E 85 026406 (2012)
S A Khan and W Masood Phys. Plasmas 15 062301 (2008)
S A Khan Astrophys. Space Sci. Phys. 343 683 (2011)
S A Khan, S Mahmood and M Mirza Arshad Phys. Lett. A 372 148 (2008)
L Stenflo, P K Shukla and M Marklund Europhys. Lett. 74 844 (2005)
W M Moslem, S Ali, P K Shukla, X Y Yang and G Rowlands Phys. Plasmas 14 082308 (2007)
S A Khan, A Mushtaq and W Masood Phys. Plasmas 15 013701 (2008)
B Sahu and R Roychoudhury Indian J. Phys. 86 401 (2012)
A H Bhrawy, M A Abdelkawy, S Kumar, S Johnson and A Biswas Indian J. Phys. 87 455 (2013)
A A Mamun, M N Alam, A K Das, Z Ahmed and T K Datta Phys. Scr. 28 72 (1998)
H Washimi and T Taniuti Phys. Rev. Lett. 17 996 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S.A. Obliquely propagating solitary structures in a heavier ion Fermi plasma. Indian J Phys 88, 433–438 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-013-0427-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-013-0427-9