Abstract
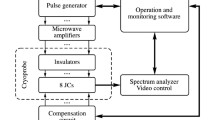
We have developed a digitally operated addressing and control module (DACM) for addressing and controlling of equipment from a remote computer using a communication protocol developed in-house. This is useful for automation of an experiment that uses multiple equipment in a pre-decided synchronized manner. We also report design of a multipurpose high voltage direct current (DC) source that provides output of 0–100 V with an average stability of 1.90 (36) mV and has minimum step size of 3 mV. Operation of the DACM is examined by selecting the desired equipment, which in this case is the dc source, and remotely controlling its output from a computer. We also show that this can generate voltage with different waveforms within a 0–10 Hz frequency bandwidth. Such computer controlled ultra-stable high voltage sources tuneable to any arbitrary waveforms at low frequencies have many applications such as, driving a piezo for smooth scanning of laser frequencies, tuning length of a Fabry–Perot cavity, biasing of the electrodes in an ion trap and so on.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Throughout in this article quantities within {} defines a digital BUS.
References
S. De, N. Batra, S. Chakraborty, S. Panja and A. Sen Gupta, Design of an ion trap for trapping single 171Yb+, Curr. Sci. 106 (2014) 1348.
N. Batra, B.K. Sahoo and S. De., An optimized ion trap geometry to measure quadrupole shifts of 171Yb+ clocks, Chin. Phys. B, 25 (2016) 113703.
A. Acharya, V. Bharath, P. Arora, et al., Systematic uncertainty evaluation of cesium fountain primary frequency standard at NPL India, MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc India, 32 (2017) 67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-016-0190-4.
K. Pant, P. Arora, S. Yadav. et al., Generation of quadrupole magnetic field for trapping atoms in Cs fountain being developed at NPL India, MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc India, 26 (2011) 285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-011-0026-1.
A. Rastogi, N. Batra, A. Roy, J. Thangjam, V.P.S. Kalsi, S. Panja and S. De, Design of the ion trap and vacuum system for 171Yb –ion optical frequency standard, MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc India, 30 (2015) 169.
N. Batra, S. Panja, S. De, A. Roy, S. Majhi, S. Yadav and A. Sen Gupta, Design and construction of a helical resonator for delivering radio frequency to an ion trap, MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc India, 32 (2017) 193.
S. Yadav, A. Acharya, P. Arora, and A. Sen Gupta, An electronic sequence controller for the Cs fountain frequency standard developed at CSIR-NPL India, Measurement, 75 (2015) 192.
A. Agarwal and A. Sen Gupta, Frequency and intensity control of lasers to cool and control caesium atoms. MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc India, 27 (2012) 169.
P. Arora, S.B. Purnapatra, A. Acharya, R. Kumar and A. Sen Gupta, Measurement of temperature of atomic cloud using timeof-flight technique. MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc India, 27 (2012) 31.
A. Acharya, S. De, P. Arora, and A. Sen Gupta., A universal driver for vibration free operation of mechanical shutter, Measurement, 61 (2014) 16.
H.J. Lewandowski, D.M. Harber, D.L. Whitaker and E.A. Cornell (2003) url - http://jila.colorado.edu/bec/CornellGroup/JLTP Lewandowski2003.pdf.
S.F. Owen and D.S. Hal, Fast line based timming system for lab view, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 75 (2004) 259.
D.S. Hall, Triggerable general-purpose interface bus controller, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 75 (2004) 562.
P.E. Gaskell, J.J. Thorn, S. Alba and D.A. Steck, An open source, extensible system for laboratory timing and control, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 80 (2009) 115103.
A. Keshet and W. Ketterle, A distributed, graphical user interface based, computer control system for atomic physics experiments, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 84 (2013) 015105.
E.E. Eyler, A single-chip event sequencer and related microcontroller instrumentation for Atomic physics research, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 82 (2011) 013105.
E. E. Eyler, Instrumentation for laser physics and spectroscopy using 32-bit microcontrollers with an Android tablet interface, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 84 (2013) 103101.
Acknowledgements
SD thanks Florian Schreck, U. Amsterdam, Netherlands for useful discussions.
Funding
This work was supported by CSIR-National Physical Laboratory, Department of Science and Technology (Grant No. SB/S2/LOP/033/2013) and Board of Researchin Nuclear Science (Grant No. 34/14/19/2014-BRNS/0309).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, A., Batra, N., Majhi, S. et al. Design of a Stable DC Voltage Source and Computer Controlling of It Using an Indigenously Developed All-Digital Addressing-Cum-Control Hardware. MAPAN 33, 139–145 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-017-0241-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-017-0241-5