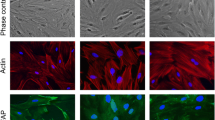
Abstract
Astrocytes are dynamic glial cells that maintain brain homeostasis, particularly metabolic functions, inflammatory response, and antioxidant defense. Since menopause may be associated with brain dysfunction, in the present study, we evaluated anti- and proinflammatory cytokine release in cortical and hippocampal astrocyte cultures obtained from adult female Wistar rats subjected to ovariectomy, a known experimental model of menopause. We also tested some parameters of metabolic functionality (Na+, K+-ATPase activity) and cellular redox status, such as antioxidant enzyme defenses (superoxide dismutase and catalase) and the intracellular production of reactive oxygen species in this experimental model. Female adult Wistar rats (180 days-age) were assigned to one of the following groups: sham (submitted to surgery without removal of the ovaries) and ovariectomy (submitted to surgery to removal of the ovaries). Thirty days after ovariectomy or sham surgery, we prepared astrocyte cultures from control and ovariectomy surgery animals. Ovariectomized rats presented an increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor α, interleukins 1β, 6, and 18) and a decrease in interleukin 10 release, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, in cortical and hippocampal astrocytes, when compared to those obtained from sham group (control). In addition, Na+,K+-ATPase activity decreased in hippocampal astrocytes, but not in cortical astrocyte cultures. In contrast, antioxidant enzymes did not alter in cortical astrocyte cultures, but increased in hippocampal astrocytes. In summary, our findings suggest that ovariectomy is able to induce an inflammatory response in vivo, which could be detected in in vitro astrocytes after approximately 4 weeks.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures (2018) Alzheimers Dement 14:367–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.001
Araújo GW, Beyer C, Arnold S (2008) Oestrogen influences on mitochondrial gene expression and respiratory chain activity in cortical and mesencephalic astrocytes. J Neuroendocrinol 20:930–941. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01747.x
Arnold S, de Araújo GW, Beyer C (2008) Gender-specific regulation of mitochondrial fusion and fission gene transcription and viability of cortical astrocytes by steroid hormones. J Mol Endocrinol 41:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1677/JME-08-0085
Avila-Rodriguez M, Garcia-Segura LM, Hidalgo-Lanussa O et al (2016) Tibolone protects astrocytic cells from glucose deprivation through a mechanism involving estrogen receptor beta and the upregulation of neuroglobin expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol 433:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.05.024
Bartsch T, Wulff P (2015) The hippocampus in aging and disease: from plasticity to vulnerability. Neuroscience 309:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.084
Bean LA, Ianov L, Foster TC (2014) Estrogen receptors, the hippocampus, and memory. Neuroscientist 20:534–545. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858413519865
Bélanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ (2011) Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab 14:724–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.016
Bellaver B, Souza DG, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A (2017) Hippocampal astrocyte cultures from adult and aged rats reproduce changes in glial functionality observed in the aging brain. Mol Neurobiol 54:2969–2985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9880-8
Ben J, Soares FMS, Cechetti F, Vuaden FC, Bonan CD, Netto CA, Wyse AT (2009) Exercise effects on activities of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase, acetylcholinesterase and adenine nucleotides hydrolysis in ovariectomized rats. Brain Res 1302:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.09.013
Bolaños JP (2016) Bioenergetics and redox adaptations of astrocytes to neuronal activity. J Neurochem 139(Suppl 2):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13486
Bossù P, Ciaramella A, Salani F, Vanni D, Palladino I, Caltagirone C, Scapigliati G (2010) Interleukin-18, from neuroinflammation to Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 16:4213–4224
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chan KM, Delfert D, Junger KD (1986) A direct colorimetric assay for Ca2+ -stimulated ATPase activity. Anal Biochem 157:375–380
Colombo E, Farina C (2016) Astrocytes: key regulators of neuroinflammation. Trends Immunol 37:608–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2016.06.006
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-0082(00)00067-8
de Souza Wyse AT, Streck EL, Worm P, Wajner A, Ritter F, Netto CA (2000) Preconditioning prevents the inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity after brain ischemia. Neurochem Res 25:971–975
Deckx N, Lee W-P, Berneman ZN (2013) Cools N (2013) Neuroendocrine immunoregulation in multiple sclerosis. Clin Dev Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/705232
Dresselhaus EC, Meffert MK (2019) Cellular Specificity of NF-κB function in the nervous system. Front Immunol 10:1043. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01043
Dringen R, Brandmann M, Hohnholt MC, Blumrich E-M (2015) Glutathione-dependent detoxification processes in astrocytes. Neurochem Res 40:2570–2582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1481-1
Dubal DB, Wise PM (2002) Estrogen and neuroprotection: from clinical observations to molecular mechanisms. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 4:149–161
Edwards BJ, Li J (2013) Endocrinology of menopause: endocrinology of menopause. Periodontology 2000 61:177–194. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2011.00407.x
Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL et al (1997) Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA 278:1349–1356
Ferreira AGK, Stefanello FM, Cunha AA, da Cunha MJ, Pereira TC, Bonan CD, Bogo MR, Netto CA, Wyse AT (2011) Role of antioxidants on Na+,K+-ATPase activity and gene expression in cerebral cortex of hyperprolinemic rats. Metab Brain Dis 26:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-011-9243-0
Garcia JM, Stillings SA, Leclerc JL, Phillips H, Edwards NJ, Robicsek SA, Hoh BL, Blackburn S, Doré S (2017) Role of interleukin-10 in acute brain injuries. Front Neurol 8:244. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00244
Guo J, Duckles SP, Weiss JH, Li X, Krause DN (2012) 17β-Estradiol prevents cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction by an estrogen receptor-dependent mechanism in astrocytes after oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion. Free Radic Biol Med 52:2151–2160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.03.005
Hwang D-S, Kim N, Choi JG, Kim HG, Kim H, Oh MS (2017) Dangguijakyak-san ameliorates memory deficits in ovariectomized mice by upregulating hippocampal estrogen synthesis. BMC Complement Altern Med 17:501. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-017-2015-6
Illarionova NB, Illarionava NB, Brismar H et al (2014) Role of Na,K-ATPase α1 and α2 isoforms in the support of astrocyte glutamate uptake. PLoS ONE 9:e98469. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098469
Jamme I, Petit E, Divoux D, Gerbi A, Maixent JM, Nouvelot A (1995) Modulation of mouse cerebral Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity by oxygen free radicals. Neuroreport 7:333–337
Jellinger KA, Attems J (2013) Neuropathological approaches to cerebral aging and neuroplasticity. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 15:29–43
Jensen CJ, Massie A, De Keyser J (2013) Immune players in the CNS: the astrocyte. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 8:824–839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-013-9480-6
Kawas C, Resnick S, Morrison A, Brookmeyer R, Corrada M, Zonderman A, Bacal C, Lingle DD, Metter E (1997) A prospective study of estrogen replacement therapy and the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Neurology 48:1517–1521. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.48.6.1517
Kesner RP, Churchwell JC (2011) An analysis of rat prefrontal cortex in mediating executive function. Neurobiol Learn Mem 96:417–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2011.07.002
Khan D, Ansar Ahmed S (2015) The immune system is a natural target for estrogen action: opposing effects of estrogen in two prototypical autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 6:635. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00635
Kim SK, Nabekura J, Koizumi S (2017) Astrocyte-mediated synapse remodeling in the pathological brain. Glia 65:1719–1727. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23169
Kubben N, Zhang W, Wang L, Voss TC, Yang J, Qu J, Liu GH, Misteli T (2016) Repression of the antioxidant NRF2 pathway in premature aging. Cell 165:1361–1374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.017
Kurella E, Kukley M, Tyulina O, Dobrota D, Matejovicova M, Mezesova V, Boldyrev A (1997) Kinetic parameters of Na/K-ATPase modified by free radicals in vitro and in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci 834:661–665
Lau A, Tymianski M (2010) Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Pflugers Arch 460:525–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-010-0809-1
Lebel CP, Bondy SC (1990) Sensitive and rapid quantitation of oxygen reactive species formation in rat synaptosomes. Neurochem Int 17:435–440
Longoni A, Bellaver B, Bobermin LD, Santos CL, Nonose Y, Kolling J, Dos Santos TM, de Assis AM, Quincozes-Santos A, Wyse ATS (2018) Homocysteine induces glial reactivity in adult rat astrocyte cultures. Mol Neurobiol 55:1966–1976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0463-0
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mackedanz V, Mattos CB, Feksa LR, Wannmacher CM, Wyse AT (2011) Ovariectomy alters energy metabolism in rat striatum: effect of supplementation with soy diet rich in isoflavones. Metab Brain Dis 26:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9216-8
Marklund S (1985) Pyrogalol autoxidation. In: Greenwald RA (ed) Handbook for Oxygen Radical Research. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 243–247
Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ (2002) Cellular response to oxidative stress: signaling for suicide and survival. J Cell Physiol 192:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.10119
Mehta A, Prabhakar M, Kumar P, Deshmukh R, Sharma PL (2013) Excitotoxicity: bridge to various triggers in neurodegenerative disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 698:6–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.10.032
Melcangi RC, Magnaghi V, Galbiati M, Martini L (2001) Glial cells: a target for steroid hormones. In: Progress in Brain Research. Elsevier, pp 31–40
Miller AH, Haroon E, Raison CL, Felger JC (2013) Cytokine targets in the brain: impact on neurotransmitters and neurocircuits. Depress Anxiety 30:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22084
Monteiro SC, Matté C, Delwing D, Wyse ATS (2005) Ovariectomy increases Na+, K+-ATPase, acetylcholinesterase and catalase in rat hippocampus. Mol Cell Endocrinol 236:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2005.03.006
Mosconi L, Rahman A, Diaz I, Wu X, Scheyer O, Hristov HW, Vallabhajosula S, Isaacson RS, de Leon MJ, Brinton RD (2018) Increased Alzheimer’s risk during the menopause transition: a 3-year longitudinal brain imaging study. PLoS ONE 13:e0207885. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0207885
Müller N, Weidinger E, Leitner B, Schwarz MJ (2015) The role of inflammation in schizophrenia. Front Neurosci 9:372. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00372
Nebel RA, Aggarwal NT, Barnes LL, Gallagher A, Goldstein JM, Kantarci K, Mallampalli MP, Mormino EC, Scott L, Yu WH, Maki PM, Mielke MM (2018) Understanding the impact of sex and gender in Alzheimer’s disease: a call to action. Alzheimers Dement 14:1171–1183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.04.008
Newcombe EA, Camats-Perna J, Silva ML, Valmas N, Huat TJ, Medeiros R (2018) Inflammation: the link between comorbidities, genetics, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 15:276. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1313-3
Parpura V, Heneka MT, Montana V et al (2012) Glial cells in (patho)physiology. J Neurochem 121:4–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07664.x
Pinto JV, Passos IC, Librenza-Garcia D et al (2017) Neuron-glia interaction as a possible pathophysiological mechanism of bipolar disorder. Curr Neuropharmacol. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X15666170828170921
Prince M, Ali G-C, Guerchet M, Prina AM, Albanese E, Wu YT (2016) Recent global trends in the prevalence and incidence of dementia, and survival with dementia. Alzheimers Res Ther 8:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-016-0188-8
Probert L (2015) TNF and its receptors in the CNS: the essential, the desirable and the deleterious effects. Neuroscience 302:2–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.06.038
Ramesh G, MacLean AG, Philipp MT (2013) Cytokines and chemokines at the crossroads of neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, and neuropathic pain. Mediat Inflamm 2013:480739. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/480739
Razmara A, Duckles SP, Krause DN, Procaccio V (2007) Estrogen suppresses brain mitochondrial oxidative stress in female and male rats. Brain Res 1176:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2007.08.036
Rivera CM, Grossardt BR, Rhodes DJ, Rocca WA (2009) Increased mortality for neurological and mental diseases following early bilateral oophorectomy. Neuroepidemiology 33:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1159/000211951
Rocca WA, Grossardt BR, Shuster LT (2010) Oophorectomy, menopause, estrogen, and cognitive aging: the timing hypothesis. NDD 7:163–166. https://doi.org/10.1159/000289229
Rocca WA, Grossardt BR, Miller VM et al (2012) Premature menopause or early menopause and risk of ischemic stroke. Menopause 19:272–277. https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0b013e31822a9937
Salminen A, Huuskonen J, Ojala J, Kauppinen A, Kaarniranta K, Suuronen T (2008) Activation of innate immunity system during aging: NF-kB signaling is the molecular culprit of inflamm-aging. Ageing Res Rev 7:83–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2007.09.002
Scheyer O, Rahman A, Hristov H et al (2018) Female sex and Alzheimer’s risk: the menopause connection. https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2018.34
Scott EL, Zhang Q, Vadlamudi RK, Brann DW (2014) Premature menopause and risk of neurological disease: Basic mechanisms and clinical implications. Mol Cell Endocrinol 389:2–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2014.01.013
Sherwin BB (1996) Hormones, mood, and cognitive functioning in postmenopausal women. Obstet Gynecol 87:20S–26S. https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(95)00431-9
Shih R-H, Wang C-Y, Yang C-M (2015) NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: a mini review. Front Mol Neurosci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00077
Shivarama Shetty M, Sajikumar S (2017) ‘Tagging’ along memories in aging: synaptic tagging and capture mechanisms in the aged hippocampus. Ageing Res Rev 35:22–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.12.008
Siebert C, Kolling J, Scherer EBS, Schmitz F, da Cunha MJ, Mackedanz V, de Andrade RB, Wannmacher CM, Wyse AT (2014) Effect of physical exercise on changes in activities of creatine kinase, cytochrome c oxidase and ATP levels caused by ovariectomy. Metab Brain Dis 29:825–835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9564-x
Siebert C, Pierozan P, Kolling J, Dos Santos TM, Sebotaio MC, Marques EP, Biasibetti H, Longoni A, Ferreira F, Pessoa-Pureur R, Netto CA, Wyse ATS (2017) Vitamin D3 reverses the hippocampal cytoskeleton imbalance but not memory deficits caused by ovariectomy in adult Wistar rats. NeuroMolecular Med 19:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-017-8449-7
Siebert C, Bertó CG, Ferreira FS, Moreira DS, Dos Santos TM, Wyse ATS (2018a) Vitamin D partially reverses the increase in p-NF-κB/p65 immunocontent and interleukin-6 levels, but not in acetylcholinesterase activity in hippocampus of adult female ovariectomized rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 71:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2018.08.008
Siebert C, dos Santos TM, Bertó CG et al (2018b) Vitamin D Supplementation Reverses DNA damage and telomeres shortening caused by ovariectomy in hippocampus of Wistar rats. Neurotox Res 34:538–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9909-z
Silva-Palacios A, Ostolga-Chavarría M, Zazueta C, Königsberg M (2018) Nrf2: Molecular and epigenetic regulation during aging. Ageing Res Rev 47:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2018.06.003
Sohrabji F, Okoreeh A, Panta A (2019) Sex hormones and stroke: beyond estrogens. Horm Behav 111:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2018.10.010
Souza DG, Bellaver B, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A (2013) Characterization of adult rat astrocyte cultures. PLoS ONE 8:e60282. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060282
Spooren A, Kolmus K, Laureys G et al (2011) Interleukin-6, a mental cytokine. Brain Res Rev 67:157–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2011.01.002
Steardo L, Bronzuoli MR, Iacomino A et al (2015) Does neuroinflammation turn on the flame in Alzheimer’s disease? Focus on astrocytes. Front Neurosci 9:259. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00259
Strle K, Zhou JH, Shen WH, Broussard SR, Johnson RW, Freund GG, Dantzer R, Kelley KW (2001) Interleukin-10 in the brain. Crit Rev Immunol 21:427–449
Takahashi TA, Johnson KM (2015) Menopause. Med Clin North Am 99:521–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2015.01.006
Tovar-y-Romo LB, Penagos-Puig A, Ramírez-Jarquín JO (2016) Endogenous recovery after brain damage: molecular mechanisms that balance neuronal life/death fate. J Neurochem 136:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13362
Tsakiris S, Deliconstantinos G (1984) Influence of phosphatidylserine on (Na+ + K+)-stimulated ATPase and acetylcholinesterase activities of dog brain synaptosomal plasma membranes. Biochem J 220:301–307
Verkhratsky A, Parpura V (2016) Astrogliopathology in neurological, neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders. Neurobiol Dis 85:254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.03.025
Viña J, Lloret A (2010) Why women have more Alzheimer’s disease than men: gender and mitochondrial toxicity of amyloid-beta peptide. J Alzheimers Dis 20(Suppl 2):S527–S533. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2010-100501
Waynforth HB, Flecknell PA (2004) Experimental and surgical technique in the rat, 2nd edn. repr. Elsevier, Acad. Press, Amsterdam
Wise PM, Dubal DB, Wilson ME, Rau SW, Böttner M (2001) Minireview: neuroprotective effects of estrogen-new insights into mechanisms of action. Endocrinology 142:969–973. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.142.3.8033
Wyse ATS, Netto CA (2015) Menopause and mitochondrial dysfunction: the value of coenzyme Q10. In: Hargreaves IP, Hargreaves AK (eds) Coenzyme Q: From Fact to Fiction. Nova Biomedical, New York, pp 171–183
Yaffe K, Sawaya G, Lieberburg I, Grady D (1998) Estrogen therapy in postmenopausal women: effects on cognitive function and dementia. JAMA 279:688–695. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.279.9.688
Zádori D, Veres G, Szalárdy L, Klivényi P, Vécsei L (2018) Alzheimer’s disease: recent concepts on the relation of mitochondrial disturbances, excitotoxicity, neuroinflammation, and kynurenines. J Alzheimers Dis 62:523–547. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-170929
Zanatta Â, Cecatto C, Ribeiro RT, Amaral AU, Wyse AT, Leipnitz G, Wajner M (2018) S-adenosylmethionine promotes oxidative stress and decreases Na+, K+-ATPase activity in cerebral cortex supernatants of adolescent rats: implications for the pathogenesis of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase deficiency. Mol Neurobiol 55:5868–5878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0804-z
Zhang L-N, Sun Y-J, Wang L-X, Gao Z-B (2016) Glutamate Transporters/Na+, K+-ATPase involving in the neuroprotective effect as a potential regulatory target of glutamate uptake. Mol Neurobiol 53:1124–1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9071-4
Funding
This work was supported by Edital Universal of Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq-Brazil) and INCT (EN 465671/2014-4)/CNPq-Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The ethical standards followed the official governmental guidelines issued by the Brazilian Federation of Societies for Experimental Biology, following the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and Arouca Law (Law no. 11.794/2008).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wyse, A.T., Siebert, C., Bobermin, L.D. et al. Changes in Inflammatory Response, Redox Status and Na+, K+-ATPase Activity in Primary Astrocyte Cultures from Female Wistar Rats Subject to Ovariectomy. Neurotox Res 37, 445–454 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00128-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00128-5