Abstract
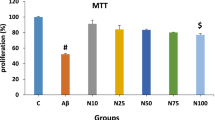
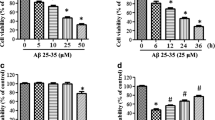
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive loss of cholinergic neurons. Amyloid beta is a misfolded protein that represents one of the key pathological hallmarks of AD. Numerous studies have shown that Aβ1–42 induces oxidative damage, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis, leading to cognitive decline in AD. Recently, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has been suggested to be a potential regulator of oxidative stress in mammalian cells. FGF21 has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce hyperglycemia, increase adipose tissue glucose uptake and lipolysis, and decrease body fat and weight loss by enhancing energy expenditure. In this study, we investigated the effect of FGF21 Aβ1–42 toxicity in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Our data shows that FGF21 significantly decreased Aβ1−42-induced toxic effects and repressed oxidative stress and apoptosis in cells exposed to Aβ1–42 peptide. Our investigation also confirmed that FGF21 pretreatment favorably affects HSP90/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Therefore, FGF21 represents a viable therapeutic strategy to abrogate Aβ1–42-induced cellular inflammation and apoptotic death in the SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambade A, Catalano D, Lim A, Mandrekar P (2012) Inhibition of heat shock protein (molecular weight 90 kDa) attenuates proinflammatory cytokines and prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in mice. Hepatology 55(5):1585–1595
Amin FU, Shah SA, Kim MO (2017) Vanillic acid attenuates Abeta1-42-induced oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in mice. Sci Rep 7:40753
Benilova I, Karran E, De Strooper B (2012) The toxic Abeta oligomer and Alzheimer’s disease: an emperor in need of clothes. Nat Neurosci 15(3):349–357
Benomar Y, Amine H, Crepin D, Al Rifai S, Riffault L, Gertler A, Taouis M (2016) Central resistin/TLR4 impairs adiponectin signaling, contributing to insulin and FGF21 resistance. Diabetes 65(4):913–926
Berglund ED, Li CY, Bina HA, Lynes SE, Michael MD, Shanafelt AB, Kharitonenkov A, Wasserman DH (2009) Fibroblast growth factor 21 controls glycemia via regulation of hepatic glucose flux and insulin sensitivity. Endocrinology 150(9):4084–4093
Blair LJ, Sabbagh JJ, Dickey CA (2014) Targeting Hsp90 and its co-chaperones to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 18(10):1219–1232
Bookout AL, de Groot MH, Owen BM, Lee S, Gautron L, Lawrence HL, Ding X, Elmquist JK, Takahashi JS, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2013) FGF21 regulates metabolism and circadian behavior by acting on the nervous system. Nat Med 19(9):1147–1152
Brahma MK, Adam RC, Pollak NM, Jaeger D, Zierler KA, Pocher N, Schreiber R, Romauch M, Moustafa T, Eder S, Ruelicke T, Preiss-Landl K, Lass A, Zechner R, Haemmerle G (2014) Fibroblast growth factor 21 is induced upon cardiac stress and alters cardiac lipid homeostasis. J Lipid Res 55(11):2229–2241
Butterfield DA (2002) Amyloid beta-peptide (1-42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: implications for neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease brain. A review. Free Radic Res 36(12):1307–1313
Butterfield DA, Castegna A, Lauderback CM, Drake J (2002) Evidence that amyloid beta-peptide-induced lipid peroxidation and its sequelae in Alzheimer’s disease brain contribute to neuronal death. Neurobiol Aging 23(5):655–664
Butterfield DA, Swomley AM, Sultana R (2013) Amyloid beta-peptide (1-42)-induced oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: importance in disease pathogenesis and progression. Antioxid Redox Signal 19(8):823–835
Cong WT, Ling J, Tian HS, Ling R, Wang Y, Huang BB, Zhao T, Duan YM, Jin LT, Li XK (2013) Proteomic study on the protective mechanism of fibroblast growth factor 21 to ischemia-reperfusion injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 91(11):973–984
De Sousa-Coelho AL, Relat J, Hondares E, Perez-Marti A, Ribas F, Villarroya F, Marrero PF, Haro D (2013) FGF21 mediates the lipid metabolism response to amino acid starvation. J Lipid Res 54(7):1786–1797
Dolezal V, Kasparova J (2003) Beta-amyloid and cholinergic neurons. Neurochem Res 28(3–4):499–506
Donnini S, Cantara S, Morbidelli L, Giachetti A, Ziche M (2006) FGF-2 overexpression opposes the beta amyloid toxic injuries to the vascular endothelium. Cell Death Differ 13(7):1088–1096
Douris N, Stevanovic DM, Fisher FM, Cisu TI, Chee MJ, Nguyen NL, Zarebidaki E, Adams AC, Kharitonenkov A, Flier JS, Bartness TJ, Maratos-Flier E (2015) Central fibroblast growth factor 21 browns white fat via sympathetic action in male mice. Endocrinology 156(7):2470–2481
Emanuelli B, Vienberg SG, Smyth G, Cheng C, Stanford KI, Arumugam M, Michael MD, Adams AC, Kharitonenkov A, Kahn CR (2014) Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism. J Clin Invest 124(2):515–527
Fon Tacer K, Bookout AL, Ding X, Kurosu H, John GB, Wang L, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Kuro-o M, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2010) Research resource: comprehensive expression atlas of the fibroblast growth factor system in adult mouse. Mol Endocrinol 24(10):2050–2064
Gilbert BJ (2013) The role of amyloid beta in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Pathol 66(5):362–366
Gómez-Sámano MÁ, Grajales-Gómez M, Zuarth-Vázquez JM, Navarro-Flores MF, Martínez-Saavedra M, Juárez-León ÓA, Morales-García MG, Enríquez-Estrada VM, Gómez-Pérez FJ, Cuevas-Ramos D (2017) Fibroblast growth factor 21 and its novel association with oxidative stress. Redox Biol 11(Supplement C):335–341
Heinitz K, Beck M, Schliebs R, Perez-Polo JR (2006) Toxicity mediated by soluble oligomers of beta-amyloid(1-42) on cholinergic SN56.B5.G4 cells. J Neurochem 98(6):1930–1945
Henderson B, Pockley AG (2010) Molecular chaperones and protein-folding catalysts as intercellular signaling regulators in immunity and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 88(3):445–462
Hochstrasser T, Hohsfield LA, Sperner-Unterweger B, Humpel C (2013) Beta-amyloid induced effects on cholinergic, serotonergic, and dopaminergic neurons is differentially counteracted by anti-inflammatory drugs. J Neurosci Res 91(1):83–94
Hua F, Ma J, Ha T, Xia Y, Kelley J, Williams DL, Kao RL, Browder IW, Schweitzer JB, Kalbfleisch JH, Li C (2007) Activation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling contributes to hippocampal neuronal death following global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. J Neuroimmunol 190(1–2):101–111
Huang N-Q, Jin H, Zhou S-y, Shi J-s, Jin F (2017) TLR4 is a link between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res 316(Supplement C):234–244
Inagaki T, Dutchak P, Zhao G, Ding X, Gautron L, Parameswara V, Li Y, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Esser V, Elmquist JK, Gerard RD, Burgess SC, Hammer RE, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2007) Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARalpha-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab 5(6):415–425
Kar S, Slowikowski SP, Westaway D, Mount HT (2004) Interactions between beta-amyloid and central cholinergic neurons: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Psychiatry Neurosci 29(6):427–441
Kim HW, Lee JE, Cha JJ, Hyun YY, Kim JE, Lee MH, Song HK, Nam DH, Han JY, Han SY, Han KH, Kang YS, Cha DR (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 21 improves insulin resistance and ameliorates renal injury in db/db mice. Endocrinology 154(9):3366–3376
Lehnardt S, Massillon L, Follett P, Jensen FE, Ratan R, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ, Vartanian T (2003) Activation of innate immunity in the CNS triggers neurodegeneration through a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(14):8514–8519
Leng Y, Wang Z, Tsai LK, Leeds P, Fessler EB, Wang J, Chuang DM (2015) FGF-21, a novel metabolic regulator, has a robust neuroprotective role and is markedly elevated in neurons by mood stabilizers. Mol Psychiatry 20(2):215–223
Liu Q, Li Y, Jiang W, Li Y, Zhou L, Song B, Liu X (2016) Inhibition of HSP90 promotes neural stem cell survival from oxidative stress through attenuating NF-kappaB/p65 activation. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:3507290
Makela J, Tselykh TV, Maiorana F, Eriksson O, Do HT, Mudo G, Korhonen LT, Belluardo N, Lindholm D (2014) Fibroblast growth factor-21 enhances mitochondrial functions and increases the activity of PGC-1alpha in human dopaminergic neurons via Sirtuin-1. Springerplus 3:2
Minoretti P, Gazzaruso C, Vito CD, Emanuele E, Bianchi M, Coen E, Reino M, Geroldi D (2006) Effect of the functional toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly polymorphism on susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 391(3):147–149
Mosconi L, Pupi A, De Leon MJ (2008) Brain glucose hypometabolism and oxidative stress in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1147:180–195
Movsesyan VA, Yakovlev AG, Dabaghyan EA, Stoica BA, Faden AI (2002) Ceramide induces neuronal apoptosis through the caspase-9/caspase-3 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299(2):201–207
Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N (2000) Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 1492(1):203–206
O'Neill LAJ, Golenbock D, Bowie AG (2013) The history of Toll-like receptors [mdash] redefining innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 13(6):453–460
O'Neill S, Humphries D, Tse G, Marson LP, Dhaliwal K, Hughes J, Ross JA, Wigmore SJ, Harrison EM (2015) Heat shock protein 90 inhibition abrogates TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB activity and reduces renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Sci Rep 5:12958
Ovsepian SV, Herms J (2013) Cholinergic neurons-keeping check on amyloid beta in the cerebral cortex. Front Cell Neurosci 7:252
Planavila A, Redondo I, Hondares E, Vinciguerra M, Munts C, Iglesias R, Gabrielli LA, Sitges M, Giralt M, van Bilsen M, Villarroya F (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against cardiac hypertrophy in mice. Nat Commun 4:2019
Rhein V, Baysang G, Rao S, Meier F, Bonert A, Muller-Spahn F, Eckert A (2009) Amyloid-beta leads to impaired cellular respiration, energy production and mitochondrial electron chain complex activities in human neuroblastoma cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29(6–7):1063–1071
Sa-Nguanmoo P, Tanajak P, Kerdphoo S, Satjaritanun P, Wang X, Liang G, Li X, Jiang C, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2016) FGF21 improves cognition by restored synaptic plasticity, dendritic spine density, brain mitochondrial function and cell apoptosis in obese-insulin resistant male rats. Horm Behav 85:86–95
Sarruf DA, Thaler JP, Morton GJ, German J, Fischer JD, Ogimoto K, Schwartz MW (2010) Fibroblast growth factor 21 action in the brain increases energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity in obese rats. Diabetes 59(7):1817–1824
Shi M, Liu C, Cook TJ, Bullock KM, Zhao Y, Ginghina C, Li Y, Aro P, Dator R, He C, Hipp MJ, Zabetian CP, Peskind ER, Hu SC, Quinn JF, Galasko DR, Banks WA, Zhang J (2014) Plasma exosomal alpha-synuclein is likely CNS-derived and increased in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 128(5):639–650
Singhal G, Fisher FM, Chee MJ, Tan TG, El Ouaamari A, Adams AC, Najarian R, Kulkarni RN, Benoist C, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E (2016) Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) protects against high fat diet induced inflammation and islet hyperplasia in pancreas. PLoS One 11(2):e0148252
Straub L, Wolfrum C (2015) FGF21, energy expenditure and weight loss—how much brown fat do you need? Mol Metab 4(9):605–609
Su JH, Zhao M, Anderson AJ, Srinivasan A, Cotman CW (2001) Activated caspase-3 expression in Alzheimer’s and aged control brain: correlation with Alzheimer pathology. Brain Res 898(2):350–357
Swomley AM, Forster S, Keeney JT, Triplett J, Zhang Z, Sultana R, Butterfield DA (2014) Abeta, oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: evidence based on proteomics studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(8):1248–1257
Takuma H, Tomiyama T, Kuida K, Mori H (2004) Amyloid beta peptide-induced cerebral neuronal loss is mediated by caspase-3 in vivo. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63(3):255–261
Tang SC, Arumugam TV, Xu X, Cheng A, Mughal MR, Jo DG, Lathia JD, Siler DA, Chigurupati S, Ouyang X, Magnus T, Camandola S, Mattson MP (2007) Pivotal role for neuronal Toll-like receptors in ischemic brain injury and functional deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(34):13798–13803
Toth, C. (2014) Chapter 32—diabetes and neurodegeneration in the brain. In: D. W. Zochodne and R. A. Malik (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 126. Elsevier, New York, p 489–511
Triantafilou M, Triantafilou K (2004) Heat-shock protein 70 and heat-shock protein 90 associate with Toll-like receptor 4 in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Biochem Soc Trans 32(Pt 4):636–639
Van Eldik LJ, Carrillo MC, Cole PE, Feuerbach D, Greenberg BD, Hendrix JA, Kennedy M, Kozauer N, Margolin RA, Molinuevo JL, Mueller R, Ransohoff RM, Wilcock DM, Bain L, Bales K (2016) The roles of inflammation and immune mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dementia 2(2):99–109
Wang H, Ma J, Tan Y, Wang Z, Sheng C, Chen S, Ding J (2010) Amyloid-beta1-42 induces reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagic cell death in U87 and SH-SY5Y cells. J Alzheimers Dis 21(2):597–610
Wolf BB, Schuler M, Echeverri F, Green DR (1999) Caspase-3 is the primary activator of apoptotic DNA fragmentation via DNA fragmentation factor-45/inhibitor of caspase-activated DNase inactivation. J Biol Chem 274(43):30651–30656
Wu D, Zhang X, Zhao M, Zhou AL (2015) The role of the TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in Abeta accumulation in primary hippocampal neurons. Sheng Li Xue Bao 67(3):319–328
Xu J, Stanislaus S, Chinookoswong N, Lau YY, Hager T, Patel J, Ge H, Weiszmann J, Lu SC, Graham M, Busby J, Hecht R, Li YS, Li Y, Lindberg R, Veniant MM (2009) Acute glucose-lowering and insulin-sensitizing action of FGF21 in insulin-resistant mouse models—association with liver and adipose tissue effects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297(5):E1105–E1114
Xu C, Liu J, Hsu LC, Luo Y, Xiang R, Chuang TH (2011) Functional interaction of heat shock protein 90 and Beclin 1 modulates Toll-like receptor-mediated autophagy. FASEB J 25(8):2700–2710
Yu Y, Bai F, Wang W, Liu Y, Yuan Q, Qu S, Zhang T, Tian G, Li S, Li D, Ren G (2015) Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects mouse brain against D-galactose induced aging via suppression of oxidative stress response and advanced glycation end products formation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 133(Supplement C):122–131
Zhang X, Yeung DCY, Karpisek M, Stejskal D, Zhou Z-G, Liu F, Wong RLC, Chow W-S, Tso AWK, Lam KSL, Xu A (2008) Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetes 57(5):1246–1253
Zhang X, Jiang W, Zhou AL, Zhao M, Jiang DR (2017) Inhibitory effect of oxymatrine on hepatocyte apoptosis via TLR4/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 23(21):3839–3849
Zilberter Y (2012) Understanding how the brain ensures its energy supply. Front Neuroenerg 4:9
Funding
This study was part of a M.Sc. thesis project that was approved and financially supported by Iran University of Medical Sciences in 2016 (grant#94-04-30- 26938).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amiri, M., Braidy, N. & Aminzadeh, M. Protective Effects of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Against Amyloid-Beta1–42-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells. Neurotox Res 34, 574–583 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9914-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9914-2