Abstract
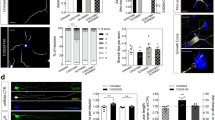
We have previously reported evidence of BDNF upregulation and increased neurogenesis in rat organotypic hippocampal slice cultures (OHSC) after a transient excitotoxic injury to the hippocampal CA1 area induced by low concentrations of the AMPA/kainate receptor agonist domoic acid (DOM). The changes observed in OHSC were consistent with observations in vivo, where low concentrations of DOM administered to rats during perinatal development caused increased BDNF and TrkB expression in the resulting adult animals. The in vivo low dose-DOM treatment also results in permanent alterations in hippocampal structure and function, including abnormal formation of dentate granule cell axons projecting to area CA3 (mossy fiber sprouting). Our objective in the current study is to determine if low concentrations of DOM induce mossy fiber sprouting and/or synaptogenesis in OHSC in order to facilitate future studies on the mechanisms of structural hippocampal plasticity induced by DOM. We report herein that application of a low concentration of DOM (2 μM) for 24 h followed by recovery induced a significant increase in the expression of the mossy fiber marker ZnT3 that progressed over time in culture. The DOM insult (2 μM, 24 h) also resulted in a significant upregulation of both the presynaptic marker synaptophysin and the postsynaptic marker PSD-95. All of the observed effects were fully antagonized by co-administration of the AMPA/kainate antagonists CNQX or NBQX but only partly by the NMDA antagonist CPP and not by the calcium channel blocker nifedipine. We conclude that exposure of OHSC to concentrations of DOM below those required to induce permanent neurotoxicity can induce a progressive change in hippocampal structure that can effectively model DOM effects in vivo.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams B, Sazgar M, Osehobo P, Van der Zee CE, Diamond J, Fahnestock M, Racine RJ (1997) Nerve growth factor accelerates seizure development, enhances mossy fiber sprouting, and attenuates seizure-induced decreases in neuronal density in the kindling model of epilepsy. J Neurosci 17:5288–5296
Barde YA (1989) Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron 2:1525–1534
Bausch SB (2006) Potential roles for hyaluronan and CD44 in kainic acid-induced mossy fiber sprouting in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Neuroscience 143:339–350
Ben-Ari Y, Represa A (1990) Brief seizure episodes induce long-term potentiation and mossy fibre sprouting in the hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 13:312–318
Bengzon J, Kokaia Z, Ernfors P, Kokaia M, Leanza G, Nilsson OG, Persson H, Lindvall O (1993) Regulation of neurotrophin and trkA, trkB and trkC tyrosine kinase receptor messenger RNA expression in kindling. Neuroscience 53:433–446
Berman FW, Murray TF (1997) Domoic acid neurotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule neurons is mediated predominantly by NMDA receptors that are activated as a consequence of excitatory amino acid release. J Neurochem 69:693–703
Bernard PB, MacDonald DS, Gill DA, Ryan CL, Tasker RA (2007) Hippocampal mossy fiber sprouting and elevated trkB receptor expression following systemic administration of low dose domoic acid during neonatal development. Hippocampus 17:1121–1133
Binder DK, Routbort MJ, McNamara JO (1999) Immunohistochemical evidence of seizure-induced activation of trk receptors in the mossy fiber pathway of adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 19:4616–4626
Butler TR, Smith KJ, Berry JN, Sharrett-Field LJ, Pendergast MA (2009) Sex differences in caffeine neurotoxicity following chronic ethanol exposure and withdrawal. Alcohol Alcohol 44:567–574
Chavis P, Westbrook G (2001) Integrins mediate functional pre- and postsynaptic maturation at a hippocampal synapse. Nature 411:317–321
Chi ZH, Wang X, Cai JQ, Stoltenberg M, Danscher G, Wang ZY (2008) Zinc transporter 3 immunohistochemical tracing of sprouting mossy fibres. Neurochem Int 52:1305–1309
De Simoni A, Griesinger CB, Edwards FA (2003) Development of rat CA1 neurones in acute versus organotypic slices: role of experience in synaptic morphology and activity. J Physiol 550:135–147
Doucette TA, Bernard PB, Husum H, Perry MA, Ryan CL, Tasker RA (2004) Low doses of domoic acid during postnatal development produce permanent changes in rat behaviour and hippocampal morphology. Neurotox Res 6:555–563
Ernfors P, Bengzon J, Kokaia Z, Persson H, Lindvall O (1991) Increased levels of messenger RNAs for neurotrophic factors in the brain during kindling epileptogenesis. Neuron 7:165–176
Fernandez-Sanchez MT, Novelli A (1996) Characterization of neurotoxicity by the amnesic shellfish toxin domoate in cultured neurons. Neurologia 11:29–39
Frederickson CJ, Suh SW, Silva D, Frederickson CJ, Thompson RB (2000) Importance of zinc in the central nervous system: the zinc-containing neuron. J Nutr 130:1471S–1483S
Gall CM, Isackson PJ (1989) Limbic seizures increase neuronal production of messenger RNA for nerve growth factor. Science 245:758–761
Gill DA, Ramsay SL, Tasker RA (2010) Selective reductions in subpopulations of GABAergic neurons in a developmental rat model of epilepsy. Brain Res 1331:114–123
Hampson DR, Huang XP, Wells JW, Walter JA, Wright JL (1992) Interaction of domoic acid and several derivatives with kainic acid and AMPA binding sites in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 218:1–8
Holmes GL, Gairsa JL, Chevassus-Au-Louis N, Ben-Ari Y (1998) Consequences of neonatal seizures in the rat: morphological and behavioral effects. Ann Neurol 44:845–857
Holmes GL, Khazipov R, Ben-Ari Y (2002) Seizure-induced damage in the developing human: relevance of experimental models. Prog Brain Res 135:321–334
Inada C, Le Thi X, Tsuneyama K, Fujiwara H, Miyata T, Matsumoto K (2013) Endogenous acetylcholine rescues NMDA-induced long-lasting hippocampal cell damage via stimulation of muscarinic M(1) receptors: elucidation using organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Eur J Pharmacol 699:150–159
Isackson PJ, Huntsman MM, Murray KD, Gall CM (1991) BDNF mRNA expression is increased in adult rat forebrain after limbic seizures: temporal patterns of induction distinct from NGF. Neuron 6:937–948
Jakobsen B, Tasker A, Zimmer J (2002) Domoic acid neurotoxicity in hippocampal slice cultures. Amino Acids 23:37–44
Jane DE, Lodge D, Collingridge GL (2009) Kainate receptors: pharmacology, function and therapeutic potential. Neuropharmacology 56:90–113
Jo SM, Won MH, Cole TB, Jensen MS, Palmiter RD, Danscher G (2000) Zinc-enriched (ZEN) terminals in mouse olfactory bulb. Brain Res 865:227–236
Jung NY, Lee KG, Won R, Lee BH (2013) Neuroprotective effects of α-tocotrienol of kainic acid-induced neurotoxicity in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Int J Mol Sci 14:18256–18268
Kelly BL, Vassar R, Ferreira A (2005) Beta-amyloid-induced dynamin 1 depletion in hippocampal neurons. A potential mechanism for early cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 280:31746–31753
Lahteinen S, Pitkanen A, Saarelainen T, Nissinen J, Koponen E, Castren E (2002) Decreased BDNF signalling in transgenic mice reduces epileptogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 15:721–734
Lu B, Figurov A (1997) Role of neurotrophins in synapse development and plasticity. Rev Neurosci 8:1–12
Maru E, Kanda M, Ashida H (2002) Functional and morphological changes in the hippocampal neuronal circuits associated with epileptic seizures. Epilepsia 43(Suppl 9):44–49
Mathern GW, Babb TL, Leite JP, Pretorius K, Yeoman KM, Kuhlman PA (1996) The pathogenic and progressive features of chronic human hippocampal epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 26:151–161
Mattson MP (2003) Excitotoxic and excitoprotective mechanisms: abundant targets for the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Neuromolecular Med 3:65–94
McGonigal R, Tabatadze N, Routtenberg A (2012) Selective presynaptic terminal remodeling induced by spatial, but not cued, learning: a quantitative confocal study. Hippocampus 22:1242–1255
Mitsuya K, Nitta N, Suzuki F (2009) Persistent zinc depletion in the mossy fiber terminals in the intrahippocampal kainate mouse model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 50:1979–1990
Mizuhashi S, Nishiyama N, Matsuki N, Ikegaya Y (2001) Cyclic nucleotide-mediated regulation of hippocampal mossy fiber development: a target-specific guidance. J Neurosci 21:6181–6194
Mulholland PJ, Self RL, Harris BR, Littleton JM, Prendergast MA (2004) (-)-nicotine ameliorates corticosterone’s potentiation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated cornu ammonis 1 toxicity. Neuroscience 125:671–682
Nakajima K, Honda S, Tohyama Y, Imai Y, Kohsaka S, Kurihara T (2001) Neurotrophin secretion from cultured microglia. J Neurosci Res 65:322–331
Nakajima K, Tohyama Y, Kohsaka S, Kurihara T (2002) Ceramide activates microglia to enhance the production/secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) without induction of deleterious factors in vitro. J Neurochem 80:697–705
Noraberg J, Kristensen BW, Zimmer J (1999) Markers for neuronal degeneration in organotypic slice cultures. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 3:278–290
Novelli A, Kispert J, Fernandez-Sanchez MT, Torreblanca A, Zitko V (1992) Domoic acid-containing toxic mussels produce neurotoxicity in neuronal cultures through a synergism between excitatory amino acids. Brain Res 577:41–48
Palmiter RD, Cole TB, Quaife CJ, Findley SD (1996) ZnT-3, a putative transporter of zinc into synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14934–14939
Perez-Gomez A, Tasker RA (2012) Enhanced neurogenesis in organotypic cultures of rat hippocampus after transient subfield-selective excitotoxic insult induced by domoic acid. Neuroscience 208:97–108
Perez-Gomez A, Tasker RA (2013) Transient domoic acid excitotoxicity increases BDNF expression and activates both MEK- and PKA-dependent neurogenesis in organotypic hippocampal slices. BMC Neurosci 14:72
Perez-Gomez A, Novelli A, Fernandez-Sanchez MT (2010) Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitor palytoxin enhances vulnerability of cultured cerebellar neurons to domoic acid via sodium-dependent mechanisms. J Neurochem 114:28–38
Perl TM, Bedard L, Kosatsky T, Hockin JC, Todd EC, Remis RS (1990) An outbreak of toxic encephalopathy caused by eating mussels contaminated with domoic acid. N Engl J Med 322:1775–1780
Pozzo-Miller LD, Gottschalk W, Zhang L, McDermott K, Du J, Gopalakrishnan R, Oho C, Sheng ZH, Lu B (1999) Impairments in high-frequency transmission, synaptic vesicle docking, and synaptic protein distribution in the hippocampus of BDNF knockout mice. J Neurosci 19:4972–4983
Pringle AK, Schmidt W, Deans JK, Wulfert E, Reymann KG, Sundstrom LE (2003) 7-Hydroxylated epiandrosterone (7-OH-EPIA) reduces ischaemia-induced neuronal damage both in vivo and in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 18:117–124
Qin L, Marrs GS, McKim R, Dailey ME (2001) Hippocampal mossy fibers induce assembly and clustering of PSD95-containing postsynaptic densities independent of glutamate receptor activation. J Comp Neurol 440:284–298
Qiu S, Curras-Collazo MC (2006) Histopathological and molecular changes produced by hippocampal microinjection of domoic acid. Neurotoxicol Teratol 28:354–362
Qiu S, Pak CW, Curras-Collazo MC (2006) Sequential involvement of distinct glutamate receptors in domoic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rat mixed cortical cultures: effect of multiple dose/duration paradigms, chronological age, and repeated exposure. Toxicol Sci 89:243–256
Reibel S, Larmet Y, Carnahan J, Marescaux C, Depaulis A (2000) Endogenous control of hippocampal epileptogenesis: a molecular cascade involving brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuropeptide Y. Epilepsia 41(Suppl 6):S127–S133
Rekart JL, Routtenberg A (2010) Overexpression of GAP-43 reveals unexpected properties of hippocampal mossy fibers. Hippocampus 20(46–57):8
Renard A, Crepel F, Audinat E (1995) Evidence for two types of non-NMDA receptors in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells maintained in slice cultures. Neuropharmacology 34:335–346
Robert F, Bert L, Stoppini L (2002) Blockade of NMDA-receptors or calcium-channels attenuates the ischaemia-evoked efflux of glutamate and phosphoethanolamine and depression of neuronal activity in rat organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. C R Biol 325:495–504
Routbort MJ, Bausch SB, McNamara JO (1999) Seizures, cell death, and mossy fiber sprouting in kainic acid-treated organotypic hippocampal cultures. Neuroscience 94:755–765
Sabbagh MN, Corey-Bloom J, Tiraboschi P, Thomas R, Masliah E, Thal LJ (1999) Neurochemical markers do not correlate with cognitive decline in the Lewy body variant of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 56:1458–1461
Sari P, Kerr DS (2001) Domoic acid-induced hippocampal CA1 hyperexcitability independent of region CA3 activity. Epilepsy Res 47:65–76
Stoppini L, Buchs PA, Muller D (1991) A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods 37:173–182
Strain SM, Tasker RA (1991) Hippocampal damage produced by systemic injections of domoic acid in mice. Neuroscience 44:343–352
Tartaglia N, Du J, Tyler WJ, Neale E, Pozzo-Miller L, Lu B (2001) Protein synthesis-dependent and -independent regulation of hippocampal synapses by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Biol Chem 276:37585–37593
Tasker RA, Strain SM (1998) Synergism between NMDA and domoic acid in a murine model of behavioural neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 19:593–597
Tasker RA, Connell BJ, Strain SM (1991) Pharmacology of systemically administered domoic acid in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 69:378–382
Teitelbaum JS, Zatorre RJ, Carpenter S, Gendron D, Evans AC, Gjedde A, Cashman NR (1990) Neurologic sequelae of domoic acid intoxication due to the ingestion of contaminated mussels. N Engl J Med 322:1781–1787
Tiraboschi P, Hansen LA, Alford M, Masliah E, Thal LJ, Corey-Bloom J (2000) The decline in synapses and cholinergic activity is asynchronous in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 55:1278–1283
Tryphonas L, Truelove J, Iverson F (1990a) Acute parenteral neurotoxicity of domoic acid in cynomolgus monkeys (M. fascicularis). Toxicol Pathol 18:297–303
Tryphonas L, Truelove J, Nera E, Iverson F (1990b) Acute neurotoxicity of domoic acid in the rat. Toxicol Pathol 18:1–9
Tyler WJ, Pozzo-Miller LD (2001) BDNF enhances quantal neurotransmitter release and increases the number of docked vesicles at the active zones of hippocampal excitatory synapses. J Neurosci 21:4249–4258
Van der Zee CE, Rashid K, Le K, Moore KA, Stanisz J, Diamond J, Racine RJ, Fahnestock M (1995) Intraventricular administration of antibodies to nerve growth factor retards kindling and blocks mossy fiber sprouting in adult rats. J Neurosci 15:5316–5323
Vanderklish PW, Bahr BA (2000) The pathogenic activation of calpain: a marker and mediator of cellular toxicity and disease states. Int J Exp Pathol 81:323–339
Vincent P, Mulle C (2009) Kainate receptors in epilepsy and excitotoxicity. Neuroscience 158:309–323
Walls SA, Rosenwasser AM, Devaud LL (2013) Sex and regional differences in effects of chronic intermittent ethanol exposure on subsequent excitotoxic challenges in hippocampal slice cultures. Neurosci Lett 29:550–556
Wang Z, Danscher G, Kim YK, Dahlstrom A, Mook Jo S (2002) Inhibitory zinc-enriched terminals in the mouse cerebellum: double-immunohistochemistry for zinc transporter 3 and glutamate decarboxylase. Neurosci Lett 321:37–40
Wenzel HJ, Cole TB, Born DE, Schwartzkroin PA, Palmiter RD (1997) Ultrastructural localization of zinc transporter-3 (ZnT-3) to synaptic vesicle membranes within mossy fiber boutons in the hippocampus of mouse and monkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12676–12681
Xu GP, Dave KR, Vivero R, Schmidt-Kastner R, Sick TJ, Perez-Pinzon MA (2002) Improvement in neuronal survival after ischemic preconditioning in hippocampal slice cultures. Brain Res 952:153–158
Xu B, Michalski B, Racine RJ, Fahnestock M (2004) The effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) administration on kindling induction, Trk expression and seizure-related morphological changes. Neuroscience 126:521–531
Zafra F, Lindholm D, Castren E, Hartikka J, Thoenen H (1992) Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor mRNA in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci 12:4793–4799
Zhao C, Teng EM, Summers RG Jr, Ming GL, Gage FH (2006) Distinct morphological stages of dentate granule neuron maturation in the adult mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci 26:3–11
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms. Emily McGuire for expert technical assistance. This work was funded by Atlantic Innovation Fund Grant 193639. The facilities of the Atlantic Center for Comparative Biomedical Research were made available at no cost to the investigators.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Gómez, A., Tasker, R.A. Enhanced Mossy Fiber Sprouting and Synapse Formation in Organotypic Hippocampal Cultures Following Transient Domoic Acid Excitotoxicity. Neurotox Res 25, 402–410 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9450-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9450-z