Abstract
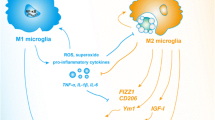
Microglia polarization to the classical M1 activation state is characterized by elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines; however, a full profile has not been generated in the early stages of a sterile inflammatory response recruiting only resident microglia. We characterized the initial M1 state in a hippocampal injury model dependent upon tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor signaling for dentate granule cell death. Twenty-one-day-old CD1 male mice were injected with trimethyltin (TMT 2.3 mg/kg, i.p.) and the hippocampus was examined at an early stage (24-h post-dosing) of neuronal death. Glia activation was assessed using a custom quantitative nuclease protection assay. We report elevated mRNA levels for glia response such as ionizing calcium-binding adapter molecule-1 and glial fibrillary acidic protein (Gfap); Fas, hypoxia inducible factor alpha, complement component 1qb, TNF-related genes (Tnf, Tnfaip3, Tnfrsfla); interleukin-1 alpha, Cd44, chemokine (C–C motif) ligand (Ccl)2, Cc14, integrin alpha M, lipocalin (Lcn2), and secreted phosphoprotein 1 (Spp1). These changes occurred in the absence of changes in matrix metalloproteinase 9 and 12, neural cell adhesion molecule, metabotropic glutamate receptor (Grm)3, and Ly6/neurotoxin 1 (Lynx1), as well as, a decrease in neurotrophin 3, glutamate receptor subunit epsilon (Grin)-2b, and neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor, type 3. The M2 anti-inflammatory marker, transforming growth factor beta-1 (Tgfb1) was elevated. mRNAs associated with early stage of injury-induced neurogenesis including fibroblast growth factor 21 and Mki67 were elevated. In the “non-injured” temporal cortex receiving projections from the hippocampus, Lynx1, Grm3, and Grin2b were decreased and Gfap increased. Formalin fixed-paraffin-embedded tissue did not generate a comparable profile.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andjus PR, Bataveljic D, Vanhoutte G, Mitrecic D, Pizzolante F, Djogo N, Nicaise C, Kengne FG, Gangitano C, Michetti F, van der Linden A, Pochet R, Bacic G (2009) In vivo morphological changes in animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Alzheimer’s-like disease: MRI approach. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 292:1882–1892
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B (Methodol) 57:289–300
Boche D, Perry VH, Nicoll JA (2013) Review: activation patterns of microglia and their identification in the human brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 39:3–18
Bruccoleri A, Harry GJ (2000) Chemical-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration and elevations in TNFalpha, TNFbeta, IL-1alpha, IP-10, and MCP-1 mRNA in osteopetrotic (op/op) mice. J Neurosci Res 62:146–155
Bruccoleri A, Brown H, Harry GJ (1998) Cellular localization and temporal elevation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 alpha, and transforming growth factor-beta 1 mRNA in hippocampal injury response induced by trimethyltin. J Neurochem 71:1577–1587
Carson MA, Thrash JC, Lo D (2004) Analysis of microglial gene expression: identifying targets for CNS neurodegenerative and autoimmune disease. Am J Pharmacogenomics 4:321–330
Chen GY, Nunez G (2010) Sterile inflammation: sensing and reacting to damage. Nat Rev Immunol 10:826–837
Chhor V, Le Charpentier T, Lebon S, Ore MV, Celador IL, Josserand J, Degos V, Jacotot E, Hagberg H, Savman K, Mallard C, Gressens P, Fleiss B (2013) Characterization of phenotype markers and neuronotoxic potential of polarised primary microglia in vitro. Brain Behav Immun 32:70–85
Chia WJ, Dawe GS, Ong WY (2011) Expression and localization of the iron-siderophore binding protein lipocalin 2 in the normal rat brain and after kainate-induced excitotoxicity. Neurochem Int 59:591–599
Choi JS, Kim HY, Cha JH, Choi JY, Lee MY (2007) Transient microglial and prolonged astroglial upregulation of osteopontin following transient forebrain ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1151:195–202
Colton CA (2009) Heterogeneity of microglial activation in the innate immune response in the brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 4:399–418
Colton CA, Wilcock DM (2010) Assessing activation states in microglia. CNS Neurol Disord 9:174–191
De Simone R, Vissicchio F, Mingarelli C, De Nuccio C, Visentin S, Ajmone-Cat MA, Minghetti L (2013) Branched-chain amino acids influence the immune properties of microglial cells and their responsiveness to pro-inflammatory signals. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:650–659
Durafourt BA, Moore CS, Zammit DA, Johnson TA, Zaguia F, Guiot MC, Bar-Or A, Antel JP (2012) Comparison of polarization properties of human adult microglia and blood-derived macrophages. Glia 60:717–727
Eng LF, Ghirnikar RS, Lee YL (2000) Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000). Neurochem Res 25:1439–1451
Figiel I, Dzwonek K (2007) TNFalpha and TNF receptor 1 expression in the mixed neuronal-glial cultures of hippocampal dentate gyrus exposed to glutamate or trimethyltin. Brain Res 1131:17–28
Funk JA, Gohlke J, Kraft AD, McPherson CA, Collins JB, Harry GJ (2011) Voluntary exercise protects hippocampal neurons from trimethyltin injury: possible role of interleukin-6 to modulate tumor necrosis factor receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Brain Behav Immun 6:1063–1077
Gasparova Z, Janega P, Stara V, Ujhazy E (2012) Early and late stage of neurodegeneration induced by trimethyltin in hippocampus and cortex of male Wistar rats. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 33:689–696
Geloso MC, Vercelli A, Corvino V, Repici M, Boca M, Haglid K, Zelano G, Michetti F (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 and caspase 3 expression in trimethyltin-induced apoptosis in the mouse hippocampus. Exp Neurol 175:152–160
Graeber MB (2010) Changing face of microglia. Science 330:783–788
Harry GJ, d’Hellencourt CL (2003) Dentate gyrus: alterations that occur with hippocampal injury. Neurotoxicology 24:343–356
Harry GJ, Tyler K, d’Hellencourt CL, Tilson HA, Maier WE (2002) Morphological alterations and elevations in tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1alpha, and IL-6 in mixed glia cultures following exposure to trimethyltin: modulation by proinflammatory cytokine recombinant proteins and neutralizing antibodies. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 180:205–218
Harry GJ, McPherson CA, Wine RN, Atkinson K, d’Hellencourt CL (2004) Trimethyltin-induced neurogenesis in the murine hippocampus. Neurotox Res 5:623–627
Harry GJ, d’Hellencourt CL, McPherson CA, Funk JA, Aoyama M, Wine RN (2008) Tumor necrosis factor p55 and p75 receptors are involved in chemical-induced apoptosis of dentate granule neurons. J Neurochem 106:281–298
Hoeffer CA, Klann E (2010) mTOR signaling: at the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci 33:67–75
Hu X, Li P, Guo Y, Wang H, Leak RK, Chen S, Gao Y, Chen J (2012) Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 43:3063–3070
Ibanez-Tallon I, Miwa JM, Wang HL, Adams NC, Crabtree GW, Sine SM, Heintz N (2002) Novel modulation of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by association with the endogenous prototoxin lynx1. Neuron 33:893–903
Jahnke GD, Brunssen S, Maier WE, Harry GJ (2001) Neurotoxicant-induced elevation of adrenomedullin expression in hippocampus and glia cultures. J Neurosci Res 66:464–474
Jang E, Lee S, Kim JH, Seo JW, Lee WH, Mori K, Nakao K, Suk K (2013) Secreted protein lipocalin-2 promotes microglial M1 polarization. FASEB J 27:1176–1190
Kettenmann H, Hanisch UK, Noda M, Verkhratsky A (2011) Physiology of microglia. Physiol Rev 91:461–553
Kigerl KA, Gensel JC, Ankeny DP, Alexander JK, Donnelly DJ, Popovich PG (2009) Identification of two distinct macrophage subsets with divergent effects causing either neurotoxicity or regeneration in the injured mouse spinal cord. J Neurosci 29:13435–13444
Kim SY, Choi YS, Choi JS, Cha JH, Kim ON, Lee SB, Chung JW, Chun MH, Lee MY (2002) Osteopontin in kainic acid-induced microglial reactions in the rat brain. Mol Cells 13:429–435
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Kumar A, Stoica BA, Sabirzhanov B, Burns MP, Faden AI, Loane DJ (2013) Traumatic brain injury in aged animals increases lesion size and chronically alters microglial/macrophage classical and alternative activation states. Neurobiol Aging 34:1397–1411
Lawson LJ, Perry VH, Dri P, Gordon S (1990) Heterogeneity in the distribution and morphology of microglia in the normal adult mouse brain. Neuroscience 39:151–170
Lee S, Park JY, Lee WH, Kim H, Park HC, Mori K, Suk K (2009) Lipocalin-2 is an autocrine mediator of reactive astrocytosis. J Neurosci 29:234–249
Lee DC, Ruiz CR, Lebson L, Selenica ML, Rizer J, Hunt JB Jr, Fojiani R, Reid P, Kammath S, Nash K, Dickey CA, Gordon M, Morgan D (2013) Aging enhances classical activation but mitigates alternative activation in the central nervous system. Neurobiol Aging 34:1610–1620
Little AR, Benkovic SA, Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP (2002) Chemically induced neuronal damage and gliosis: enhanced expression of the proinflammatory chemokine, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, without a corresponding increase in proinflammatory cytokines(1). Neuroscience 115:307–320
Little AR, Miller DB, Li S, Kashon ML, O’Callaghan JP (2012) Trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity: gene expression pathway analysis, q-RT-PCR and immunoblotting reveal early effects associated with hippocampal damage and gliosis. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34:72–82
Maier WE, Brown HW, Tilson HA, Luster MI, Harry GJ (1995) Trimethyltin increases interleukin (IL)-1 alpha, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA levels in rat hippocampus. J Neuroimmunol 59:65–75
McPherson CA, Aoyama M, Harry GJ (2011) Interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 regulation of neural progenitor cell proliferation with hippocampal injury: differential regulatory pathways in the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the adolescent and mature mouse brain. Brain Behav Immun 25:850–862
Michelucci A, Heurtaux T, Grandbarbe L, Morga E, Heuschling P (2009) Characterization of the microglial phenotype under specific pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory conditions: effects of oligomeric and fibrillar amyloid-β. J Neuroimmunol 210:3–12
Miron VE, Boyd A, Zhao JW, Yuen TJ, Ruckh JM, Shadrach JL, van Wijngaarden P, Wagers AJ, Williams A, Franklin RJ, Ffrench-Constant C (2013) Me microglia and macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination. Nature Neurosci. doi:10.1038/nn.3469
Miwa JM, Ibanez-Tallon I, Crabtree GW, Sanchez R, Sali A, Role LW, Heintz N (1999) Lynx1, an endogenous toxin-like modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the mammalian CNS. Neuron 23:105–114
Morita M, Imai H, Liu Y, Xu X, Sadamatsu M, Nakagami R, Shirakawa T, Nakano K, Kita Y, Yoshida K, Tsunashima K, Kato N (2008) FK506-protective effects against trimethyltin neurotoxicity in rats: hippocampal expression analyses reveal the involvement of periarterial osteopontin. Neuroscience 153:1135–1145
Mucha M, Skrzypiec AE, Schiavon E, Attwood BK, Kucerova E, Pawlak R (2011) Lipocalin-2 controls neuronal excitability and anxiety by regulating dendritic spine formation and maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:18436–18441
O’Callaghan JP, Sriram K (2005) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and related glial proteins as biomarkers of neurotoxicity. Expert Opin Drug Saf 4:433–442
Ogita K, Nishiyama N, Sugiyama C, Higuchi K, Yoneyama M, Yoneda Y (2005) Regeneration of granule neurons after lesioning of hippocampal dentate gyrus: evaluation using adult mice treated with trimethyltin chloride as a model. J Neurosci Res 82:609–621
Panickar KS, Norenberg MD (2005) Astrocytes in cerebral ischemic injury: morphological and general considerations. Glia 50:287–298
Patel AR, Ritzel R, McCullough LD, Liu F (2013) Microglia and ischemic stroke: a double-edged sword. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 5:73–90
Pathipati P, Muller S, Jiang X, Ferriero D (2013) Phenotype and secretory responses to oxidative stress in microglia. Dev Neurosci 35:241–245
Pechhold S, Stouffer M, Walker G, Martel R, Seligmann B, Hang Y, Stein R, Harlan DM, Pechhold K (2009) Transcriptional analysis of intracytoplasmically stained, FACS-purified cells by high-throughput, quantitative nuclease protection. Nat Biotechnol 27:1038–1042
Polman JA, Hunter RG, Speksnijder N, van den Oever JM, Korobko OB, McEwen BS, de Kloet ER, Datson NA (2012) Glucocorticoids modulate the mTOR pathway in the hippocampus: differential effects depending on stress history. Endocrinology 153:4317–4327
Reuhl KR, Cranmer JM (1984) Developmental neuropathology of organotin compounds. Neurotoxicology 5:187–204
Rimsza LM, Leblanc ML, Unger JM, Miller TP, Grogan TM, Persky DO, Martel RR, Sabalos CM, Seligmann B, Braziel RM, Campo E, Rosenwald A, Connors JM, Sehn LH, Johnson N, Gascoyne RD (2008) Gene expression predicts overall survival in paraffin-embedded tissues of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 112:3425–3433
Rimsza LM, Wright G, Schwartz M, Chan WC, Jaffe ES, Gascoyne RD, Campo E, Rosenwald A, Ott G, Cook JR, Tubbs RR, Braziel RM, Delabie J, Miller TP, Staudt LM (2011) Accurate classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma into germinal center and activated B-cell subtypes using a nuclease protection assay on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Clin Cancer Res 17:3727–3732
Roberts RA, Sabalos CM, LeBlanc ML, Martel RR, Frutiger YM, Unger JM, Botros IW, Rounseville MP, Seligmann BE, Miller TP, Grogan TM, Rimsza LM (2007) Quantitative nuclease protection assay in paraffin-embedded tissue replicates prognostic microarray gene expression in diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. Lab Invest 87:979–997
Santamaria MH, Corral RS (2013) Osteopontin-dependent regulation of Th1 and Th17 cytokine responses in Trypanosoma cruzi-infected C57BL/6 mice. Cytokine 61:491–498
Sierra A, Abiega O, Shahraz A, Neumann H (2013) Janus-faced microglia: beneficial and detrimental consequences of microglial phagocytosis. Front Cell Neurosci 7:6
Sofroniew MV (2005) Reactive astrocytes in neural repair and protection. Neuroscientist 11:400–407
Sofroniew MV (2009) Molecular dissection of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation. Trends Neurosci 32:638–647
Solovjov DA, Pluskota E, Plow EF (2005) Distinct roles for the alpha and beta subunits in the functions of integrin alphaMbeta2. J Biol Chem 280:1336–1345
Spradling KD, Lumley LA, Robison CL, Meyerhoff JL, Dillman JF (2011) Transcriptional responses of the nerve agent-sensitive brain regions amygdala, hippocampus, piriform cortex, septum, and thalamus following exposure to the organophosphonate anticholinesterase sarin. J Neuroinflammation 8:84
Stout RD, Jiang C, Matta B, Tietzel I, Watkins SK, Suttles J (2005) Macrophages sequentially change their functional phenotype in response to changes in microenvironmental influences. J Immunol 175:342–349
Streit WJ (1990) An improved staining method for rat microglial cells using the lectin from (GSA I-B4). J Histochem Cytochem 38:1683–1686
Streit WJ, Conde JR, Fendrick SE, Flanary BE, Mariani CL (2005) Role of microglia in the central nervous system’s immune response. Neurol Res 27:685–691
Viviani B, Corsini E, Pesenti M, Galli CL, Marinovich M (2001) Trimethyltin-activated cyclooxygenase stimulates tumor necrosis factor-alpha release from glial cells through reactive oxygen species. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 172:93–97
Wang H, Zhan Y, Xu L, Feuerstein GZ, Wang X (2001) Use of suppression subtractive hybridization for differential gene expression in stroke: discovery of CD44 gene expression and localization in permanent focal stroke in rats. Stroke 32:1020–1027
Woodcock T, Morganti-Kossmann MC (2013) The role of markers of inflammation in traumatic brain injury. Front Neurol 4:18
Yang J, Bielenberg DR, Rodig SJ, Doiron R, Clifton MC, Kung AL, Strong RK, Zurakowski D, Moses MA (2009) Lipocalin 2 promotes breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:3913–3918
Yin L, Lu L, Prasad K, Richfield EK, Unger EL, Xu J, Jones BC (2011) Genetic-based, differential susceptibility to paraquat neurotoxicity in mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:415–421
Yuzaki M (2010) Synapse formation and maintenance by C1q family proteins: a new class of secreted synapse organizers. Eur J Neurosci 32:191–197
Zhang D, Hu X, Qian L, O’Callaghan JP, Hong JS (2010) Astrogliosis in CNS pathologies: is there a role for microglia? Mol Neurobiol 41:232–241
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the NIEHS Microarray Core for their expert assistant with the initial microarray analysis used for selection of qNPA probes, Dr. Grace Kissling for statistical expertise, and Drs. Stephanie L. Smith-Roe and Chad Blystone of NIEHS for reviewing the final manuscript. This study was funded by the Division of Intramural Research and the Division National Toxicology Program, NIEHS/NIH (1Z01ES101623). The qNPA was conducted at HTG under an NTP contract with technical expertise from Dr John Luecke. The statements, opinions, or conclusions contained within this manuscript do not necessarily represent the statements, opinions, or conclusions of NIEHS, NIH, or the United States Government.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest associated with this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McPherson, C.A., Merrick, B.A. & Harry, G.J. In Vivo Molecular Markers for Pro-inflammatory Cytokine M1 Stage and Resident Microglia in Trimethyltin-Induced Hippocampal Injury. Neurotox Res 25, 45–56 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9422-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9422-3