Abstract
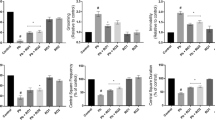
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) exposure produces profound damage to the developing as well as adult central nervous system. Locomotor activities which are closely linked to dopaminergic neurotransmission are often impaired in PCBs toxicity. Targeting PCBs-induced oxidative stress using natural antioxidants is an attractive approach. Quercetin, a flavonoid is a safe and potent neuroprotective antioxidant. In this study, we sought to examine the protective role of quercetin against PCBs-induced neurodegeneration and dysfunction of dopaminergic receptors in the cerebellar region of adult male rats. They were divided into four groups. Group I received only vehicle (corn oil) intraperitoneally (i.p); Group II received Aroclor 1254 at a dose of 2 mg/kg bwt/day (i.p); Group III received Aroclor 1254 (i.p) and simultaneously quercetin (50 mg/kg bwt/day) through gavage; Group IV received quercetin alone (gavage). After 30 days treatment, rats were euthanized. The cerebellum was dissected from each rat brain, the levels of hydrogen peroxide, lipid peroxidation, protein carbonyl content, and activities of creatine kinase, acetylcholine esterase, membrane-bound ATPases were evaluated. Expressions of dopaminergic receptors and tyrosine hydroxylase in cerebellum were studied by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and western blot analysis, respectively. The PCBs-induced neurodegeneration was assessed by histological studies. Results proclaim that PCBs disturb dopaminergic receptors and also causes neurodegeneration in cerebellum via production of ROS. Simultaneous quercetin treatment had scavenged the free radicals induced by PCBs and protected dopaminergic receptors dysfunction in rat cerebellum.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accili D, Fishburn CS, Drago J, Steiner H, Lachowicz JE, Park BH, Gauda EB, Lee EJ, Cool MH, Sibley DR, Gerfen CR, Westphal H, Fuchs S (1996) A targeted mutation of the D3 dopamine receptor gene is associated with hyperactivity in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:1945–1949
Aksenova MV, Aksenov MY, Markesbery WR, Butterfield DA (1999) Aging in a dish: age-dependent changes of neuronal survival, protein oxidation, and creatine kinase BB expression in long-term hippocampal cell culture. J Neurosci Res 58:308–317
Allen RG, Tresini M (2000) Oxidative stress and gene regulation. Free Radic Biol Med 28:463–499 Review
Alsharif NZ, Lawson T, Stohs SJ (1994) Oxidative stress induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachloro dibenzo-p-dioxin is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor complex. Toxicology 92:39–51
Anane R, Creppy EE (2001) Lipid peroxidation as pathway of aluminium cytotoxicity in human skin fibroblast cultures: prevention by superoxide dismutase + catalase and vitamins E and C. Hum Exp Toxicol 20:477–481
Andres RH, Ducray AD, Schlattner U, Wallimann T, Widmer HR (2008) Functions and effects of creatine in the central nervous system. Brain Res Bull 76:329–343
Baik JH, Picetti R, Saiardi A, Thiriet G, Dierich A, Depaulis A, Le Meur M, Borrelli E (1995) Parkinsonian-like locomotor impairment in mice lacking dopamine D2 receptors. Nature 377:424–428
Brouwer A, Morse DC, Lans MC, Schuur AG, Murk AJ, Klasson-Wehler E, Bergman A, Visser TJ (1998) Interactions of persistent environmental organohalogens with the thyroid hormone system: mechanisms and possible consequences for animal and human health. Toxicol Ind Health 14:59–84
Caudle WM, Richardson JR, Delea KC, Guillot TS, Wang M, Pennell KD (2006) Polychlorinated biphenyl-induced reduction of dopamine transporter expression as a precursor to Parkinson´s disease-associated dopamine toxicity. Toxicol Sci 92:490–499
Cho JY, Kim IS, Jang YH, Kim AR, Lee SR (2006) Protective effect of quercetin, a natural flavonoid against neuronal damage after transient global cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett 404:330–335
Choksi NY, Kodavanti PRS, Tilson HA, Booth RG (1997) Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) on brain dopamine tyrosine hydroxylase activity and dopamine synthesis in rats. Fundam AppI Toxicol 39:76–80
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Daemen FJ, de Pont JJ, Lion F, Bonting SL (1970) Na+ K+ activated adenosine triphosphatase in retinae of rats with and without inherited retinal dystrophy. Vision Res 5:435–438
Devasagayam TP, Tarachand U (1987) Decreased lipid peroxidation in the rat kidney during gestation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 145:134–138
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new raid colorimetric determination of AchE activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Floyd RA (1999) Antioxidants, oxidative stress, and degenerative neurological disorders. Exp Biol Med 222:236–245
Heo HJ, Lee CY (2004) Protective effects of quercetin and vitamin C against oxidative stress-induced neurodegeneration. J Agric Food Chem 52:7514–7517
Hjerten S, Pan H (1983) Purification and characterization of two forms of low affinity calcium ion ATPase from erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Acta 755:457–466
Kodavanti PRS, Tilson HA (2000) Neurochemical effects of environmental toxicants: in vitro and in vivo correlations on second messenger pathways. Ann NY Acad Sci 919:97–105
Koufen P, Stark G (2000) Free radical induced inactivation of creatine kinase: sites of interaction, protection, and recovery. Biochim Biophys Acta 1501:44–50
Levine RL, Williams JA, Stadtman ER, Shater E (1994) Carbonyl, assays for determination of oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 233:346–357
Mervis RF, Bachstetter AD, Harry GJ, Tilson HA, Kodavanti PS (2002) Longlasting neurostructural consequences in the rat hippocampus by developmental exposure to a mixture of polychlorinated biphenyls. The Toxicologist, p 133 (abstract 647)
Mishra OP, Delivoria Papadopoulos M, Canillane G, Wagerle LC (1989) Active sites of Na+/K+ ATPase. Neurochem Res 14:845–851
Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG (1998) Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 78:189–225
Murugesan P, Kanagaraj P, Yuvaraj S, Balasubramanian K, Aruldhas MM, Arunakaran J (2005a) The inhibitory effects of polychlorinated biphenyl Aroclor 1254 on Leydig cell LH receptors, steroidogenic enzymes and antioxidant enzymes in adult rats. Reprod Toxicol 20:117–126
Murugesan P, Senthilkumar J, Balasubramanian K, Aruldhas MM, Arunakaran J (2005b) Impact of polychlorinated biphenyl Aroclor 1254 on testicular antioxidant system in adult rats. Human Exp Toxicol 24:61–66
Naidu PS, Kulkarni SK (2004) Quercetin, a bioflavonoid, reverses haloperidol induced catalepsy. Methods find Exp Clin Pharmacol 26:323–326
Nguon K, Baxter MG, Sajdel-Sulkowska EM (2005) Perinatal exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls differentially affects cerebellar development and motor functions in male and female rat neonates. Cerebellum 4:112–122
Norstrom K, Czub G, McLachlan MS, Hu D, Thorne PS, Hornbuckle KC (2010) External exposure and bioaccumulation of PCBs in humans living in a contaminated urban environment. Environ Int 36:855–861
Ohinishi T, Suzuki T, Suzuki Y, Ozawa K (1982) A comparative study of plasma membrane magnesium ion ATPase activities in normal, regenerating and malignant cells. Biochem Biophys Acta 684:67–74
Okinaka S, Sugita H, Momoi H, Toyokura Y, Watanbe T, Ebashi F, Ebashi S (1964) Cysteine stimulated serum creatinine kinase in health & disease. J Lab Clin Med 64:299–305
Pick E, Keisari Y (1980) A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J Immunol Methods 38:161–170
Pratheepa kumari R, Selvakumar K, Bavithra S, Zumaana R, Krishnamoorthy G, Arunakaran J (2011) Role of quercetin on PCBs (Aroclor-1254) induced impairment of dopaminergic receptor mRNA expression in cerebral cortex of adult male rats. Neurochem Res. doi:10.1007/s11064-011-0449-7
Pu F, Mishima K, Irie K, Motohashi K, Tanaka Y, Orito K, Egawa T, Kitamura Y, Egashira N, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M (2007) Neuroprotective effects of quercetin and rutin on spatial memory impairment in an 8-arm radial maze task and neuronal death induced by repeated cerebral ischemia in rats. J Pharmacol Sci 104:329–334
Roegge CS, Schantz SL (2006) Motor function following developmental exposure to PCBS and/or MEHG. Neurotoxicol Teratol 28:260–277
Schantz SL (1996) Developmental neurotoxicity of PCBs in humans: what do we know and where do we go from her? Neurotoxicol Teratol 18:217–227
Schneider AR, Porter ET, Baker JE (2007) Polychlorinated biphenyl release from resuspended Hudson River sediment. Environ Sci Technol 4:1097–1103
Seegal RF, Bush B, Brosch KO (1991) Subchronic exposure of the adult rat to Aroclor 1254 yields regionally-specific changes in central dopaminergic function. Neurotoxicology 12:55–66
Seegal RF, Okoniewski RJ, Brosch KO, Bemis JC (2002) Polychlorinated biphenyls alter extraneuronal but not tissue dopamine concentrations in adult rat striatum: an in vivo microdialysis study. Environ Health Perpsect 110:1113–1117
Selvakumar K, Sheerin Banu L, Krishnamoorthy G, Venkataraman P, Elumalai P, Arunakaran J (2011) Differential expression of androgen and estrgen receptors in PCB (Aroclor 1254) exposed rats: protective role of alpha-tocopherol. Exp Toxicol pathol 63:105–112
Sridevi N, Venkataraman P, Senthilkumar K, Krishnamoorthy G, Arunakaran J (2007) Oxidative stress modulates membrane bound ATPases in brain regions of PCB(Aroclor 1254) exosed rats: protective role of alpha-tocopherol. Biomed pharmaco therap 61:435–440
Sridhar M, Venkataraman P, Dhanammal S, Arunkumar A, Aruldhas MM, Srinivasan N, Arunakaran J (2004) Impact of polychlorinated biphenyl (Aroclor 1254) and vitamin C on antioxidant system of rat ventral prostate. Asian J Androl 6:19–22
Sun Su Wen, Yu Hu Qing, Zhang Hong, Zheng Yuan Lin, Wang Jian Jun, Luo Lan (2007a) Quercetin attenuates spontaneous behavior and spatial memory impairment in d-galactose-treated mice by increasing brain antioxidant capacity. Nutrition Res 27:169–175
Sun SW, Yu HQ, Zhang H, Zheng YL, Wang JJ, Luo L (2007b) Quercetin attenuates spontaneous behavior and special memory impairment in d-galactose treated mice by increasing brain antioxidant capacity. Nutrition Research 27:169–175
Tsakiris S, Angelogianni P, Schulpis KH, Stavridis JC (2000) Protective effect of l-phenylalanine on rat brain acetylcholinesterase inhibition induced by free radicals. Clin Biochem 33:103–106
Vallone D, Picetti R, Borrelli E (2000) Structure and function of dopamine receptors. Neurol Biobehav Rev 24:125–132
Venkataraman P, Muthuvel R, Krishnamoorthy G, Arunkumar A, Sridhar M, Srinivasan N, Balasubramanian K, Aruldhas MM, Arunakaran J (2007) PCB (Aroclor1254) enhance oxidative damage in rat brain regions: protective role of ascorbic acid. Neurotoxicology 28:490–498
Venkataraman P, Krishnmoorthy G, Vengatesh G, Srinivasan N, Aruldhas MM, Arunakaran J (2008) Protective role of melatonin on PCB(Aroclor 1254) induced oxidative stress and changes in membrane bound ATPases and acetylcholine esterase in cerebellum, cerebral cortex and hippocampus of adult rat brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 26:585–591
Venkataraman P, Selvakumar K, Krishnamoorthy G, Muthusami S, Rameshkumar R, Prakash S, Arunakaran J (2010) Effect of melatonin on PCB (Aroclor 1254) induced neuronal damage and changes in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase-4 mRNA expression in cerebral cortex, cerebellum and hippocampus of adult rats. Neuro Res 66:189–197
Wyse ATS, Streck PL, Worm P, Wanjer A, Ritter F, Netto CA (2000) Preconditioning prevents the inhibition of Na+/K+ ATPases activity after brain ischemia. Neurochem Res 25:969–973
Acknowledgment
The support for this study from UGC RFSMS and DST PURSE, New Delhi is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bavithra, S., Selvakumar, K., Pratheepa Kumari, R. et al. Polychlorinated Biphenyl (PCBs)-Induced Oxidative Stress Plays a Critical Role on Cerebellar Dopaminergic Receptor Expression: Ameliorative Role of Quercetin. Neurotox Res 21, 149–159 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-011-9253-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-011-9253-z