Abstract
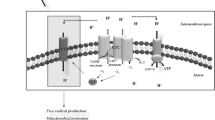
Increased bioenergetics demand can stimulate compensatory increases in glucose metabolism. We previously reported that neural cells expressing the brain uncoupling protein UCP4 exhibit enhanced dependency on glucose for support of cellular bioenergetics and survival. The switch from oxidative toward glycolytic metabolism reduces the production of toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increases cellular resistance to toxicity induced by 3-nitropropionic acid, a mitochondrial complex II inhibitor that compromises cellular bioenergetics. In this study we elucidate the underlying mechanism whereby expression of UCP4 promotes bioenergetics adaptation and cell survival. We found that activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) is necessary and sufficient for the increased dependency on glucose utilization. Pharmacological inhibition of ERKs not only abrogated bioenergetics adaptation but also reduced the activation of cAMP-responsive element-binding (CREB) protein suggesting that CREB protein signaling contributes in part to UCP4-dependent cell death rescue from 3-nitropropionic acid-induced toxicity. We also demonstrated that activation of ERKs by growth factors ameliorated the bioenergetics compromise and reduced cellular toxicity induced by 3-nitropropionic acid. Collectively, our results support the involvement of ERKs in UCP4 dependent bioenergetics adaptation and cell survival.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3-NP:
-
3-nitropropionic acid
- BAPTA-AM:
-
(5,5- dimethyl bis-(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic)-acetoxymethylester
- 6-NMDG:
-
6-(N-(7 nirobenz0-2-oxa-1-3-diazol-4-yl) amino-6-deoxy-glucose
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophin factor
- CREB:
-
cAMP-responsive element-binding
- DNP:
-
2,4-dinitrophenol
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- Glut1:
-
Glucose transporter 1
- Hif-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- SAPK/JNK:
-
Stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TrkA:
-
Tropomyosin-Related Kinase A
- UCP:
-
Uncoupling protein
References
Allsopp TE, Wyatt S, Paterson HF, Davies AM (1993) The proto-oncogene bcl-2 can selectively rescue neurotrophic factor-dependent neurons from apoptosis. Cell 73:295–307
Andrews ZB, Diano S, Horvath TL (2005a) Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins in the CNS: in support of function and survival. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:829–840
Andrews ZB, Horvath B, Barnstable CJ, Elsworth J, Yang L, Beal MF, Roth RH, Matthews RT, Horvath TL (2005b) Uncoupling protein-2 is critical for nigral dopamine cell survival in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 25:184–191
Arsenijevic D, Onuma H, Pecqueur C et al (2000) Disruption of the uncoupling protein-2 gene in mice reveals a role in immunity and reactive oxygen species production. Nat Genet 26:435–439
Bechmann I, Diano S, Warden CH, Bartfai T, Nitsch R, Horvath TL (2002) Brain mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2): a protective stress signal in neuronal injury. Biochem Pharmacol 64:363–367
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW et al (2001) SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13681–13686
Bergmann A, Agapite J, McCall K, Steller H (1998) The Drosophila gene hid is a direct molecular target of Ras-dependent survival signaling. Cell 95:331–341
Brouillet E, Jacquard C, Bizat N, Blum D (2005) 3-Nitropropionic acid: a mitochondrial toxin to uncover physiopathological mechanisms underlying striatal degeneration in Huntington’s disease. J Neurochem 95:1521–1540
Browne SE, Beal MF (2004) The energetics of Huntington’s disease. Neurochem Res 29:531–546
Burkhalter J, Fiumelli H, Allaman I, Chatton JY, Martin JL (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulates energy metabolism in developing cortical neurons. J Neurosci 23:8212–8220
Cavanaugh JE, Ham J, Hetman M, Poser S, Yan C, Xia Z (2001) Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and ERK5 by neurotrophins, neuronal activity, and cAMP in neurons. J Neurosci 21:434–443
Chan SL, Fu W, Zhang P, Cheng A, Lee J, Kokame K, Mattson MP (2004) Herp stabilizes neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis and mitochondrial function during endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 279:28733–28743
Chan SL, Liu D, Kyriazis GA, Bagsiyao P, Ouyang X, Mattson MP (2006) Mitochondrial uncoupling protein-4 regulates calcium homeostasis and sensitivity to store depletion-induced apoptosis in neural cells. J Biol Chem 281:37391–37403
Chen C, Pore N, Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F, Maity A (2001) Regulation of glut1 mRNA by hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Interaction between H-ras and hypoxia. J Biol Chem 276:9519–9525
Cheng B, Goodman Y, Begley JG, Mattson MP (1994) Neurotrophin-4/5 protects hippocampal and cortical neurons against energy deprivation- and excitatory amino acid-induced injury. Brain Res 650:331–335
Chu AC, Ho PW, Kwok KH, Ho JW, Chan KH, Liu HF, Kung MH, Ramsden DB, Ho SL (2008) Mitochondrial UCP4 attenuates MPP(+)- and dopamine-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial depolarization, and ATP deficiency in neurons and is interlinked with UCP2 expression. Free Radic Biol Med 46:810–820
Costes S, Broca C, Bertrand G, Lajoix AD, Bataille D, Bockaert J, Dalle S (2006) ERK1/2 control phosphorylation and protein level of cAMP-responsive element-binding protein: a key role in glucose-mediated pancreatic beta-cell survival. Diabetes 55:2220–2230
Crews CM, Alessandrini A, Erikson RL (1992) The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science 258:478–480
De la Monte SM, Wands JR (2006) Molecular indices of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction occur early and often progress with severity of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 9:167–181
Deierborg Olsson T, Wieloch T, Diano S, Warden CH, Horvath TL, Mattiasson G (2008) Overexpression of UCP2 protects thalamic neurons following global ischemia in the mouse. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1186–1195
Derdak Z, Mark NM, Beldi G, Robson SC, Wands JR, Baffy G (2008) The mitochondrial uncoupling protein-2 promotes chemoresistance in cancer cells. Cancer Res 68:2813–2819
Diano S, Matthews RT, Patrylo P, Yang L, Beal MF, Barnstable CJ, Horvath TL (2003) Uncoupling protein 2 prevents neuronal death including that occurring during seizures: a mechanism for preconditioning. Endocrinology 144:5014–5021
Echtay KS (2007) Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins—what is their physiological role? Free Radic Biol Med 43:1351–1371
Echtay KS, Roussel D, St-Pierre J et al (2002) Superoxide activates mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Nature 425:96–99
Franceschini D, Giusti P, Skaper SD (2006) MEK inhibition exacerbates ischemic calcium imbalance and neuronal cell death in rat cortical cultures. Eur J Pharmacol 553:18–27
Fridell YW, Sánchez-Blanco A, Silvia BA, Helfand SL (2005) Targeted expression of the human uncoupling protein 2 (hUCP2) to adult neurons extends life span in the fly. Cell Metab 1:145–152
Gjedde A, Marret S (2001) Glycolysis in neurons, not astrocytes, delays oxidative metabolism of human visual cortex during sustained checker-board stimulation in vivo. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:1384–1392
Guo ZH, Mattson MP (2000) Neurotrophic factors protect cortical synaptic terminals against amyloid and oxidative stress-induced impairment of glucose transport, glutamate transport and mitochondrial function. Cereb Cortex 10:50–57
Hara T, Hamada J, Yano S, Morioka M, Kai Y, Ushio Y (2003) CREB is required for acquisition of ischemic tolerance in gerbil hippocampal CA1 region. J Neurochem 86:805–814
Jover-Mengual T, Zukin RS, Etgen AM (2007) MAPK signaling is critical to estradiol protection of CA1 neurons in global ischemia. Endocrinology 148:1131–1143
Kirschner PB, Jenkins BG, Schulz JB, Finkelstein SP, Matthews RT, Rosen BR, Beal MF (1996) NGF, BDNF and NT-5, but not NT-3 protect against MPP+ toxicity and oxidative stress in neonatal animals. Brain Res 713:178–185
Korde AS, Pettigrew LC, Craddock SD, Maragos WF (2005) The mitochondrial uncoupler 2, 4-dinitrophenol attenuates tissue damage and improves mitochondrial homeostasis following transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 94:1676–1684
Krauss S, Zhang C-Y, Lowell BB (2005) The mitochondrial uncoupling-protein homologues. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:248–256
Landis GN, Tower J (2005) Superoxide dismutase evolution and life span regulation. Mech Ageing Dev 126:365–379
Ley R, Balmanno K, Hadfield K, Weston C, Cook SJ (2003) Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway promotes phosphorylation and proteasome-dependent degradation of the BH3-only protein Bim. J Biol Chem 278:18811–18816
Liévens JC, Rival T, Iché M, Chneiweiss H, Birman S (2005) Expanded polyglutamine peptides disrupt EGF receptor signaling and glutamate transporter expression in Drosophila. Hum Mol Genet 14:713–724
Lim JH, Lee ES, You HJ, Lee JW, Park JW, Chun YS (2004) Ras-dependent induction of HIF-1alpha785 via the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway: a novel mechanism of Ras-mediated tumor promotion. Oncogene 23:9427–9431
Liu D, Chan SL, de Souza-Pinto NC, Slevin JR, Wersto RP, Zhan M, Mustafa K, de Cabo R, Mattson MP (2006) Mitochondrial UCP4 mediates an adaptive shift in energy metabolism and increases the resistance of neurons to metabolic and oxidative stress. Neuromolecular Med 8:389–414
Loomis WF, Lipmann F (1948) Reversible inhibition of the coupling between phosphorylation and oxidation. J Biol Chem 173:807–808
Lum JJ, Bui T, Gruber M, Gordan JD, DeBerardinis RJ, Covello KL, Simon MC, Thompson CB (2007) The transcription factor HIF-1alpha plays a critical role in the growth factor-dependent regulation of both aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis. Genes Dev 21:1037–1049
Mandavilli BS, Boldogh I, Van Houten B (2005) 3-nitropropionic acid-induced hydrogen peroxide, mitochondrial DNA damage, and cell death are attenuated by Bcl-2 overexpression in PC12 cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 133:215–223
Mao W, Yu XX, Zhong A, Li W, Brush J, Sherwood SW, Adams SH, Pan G (1999) UCP4, a novel brain-specific mitochondrial protein that reduces membrane potential in mammalian cells. FEBS Lett 443:326–330
Martin JL, Avkiran M, Quinlan RA, Cohen P, Marber MS (2001) Antiischemic effects of SB203580 are mediated through the inhibition of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase: evidence from ectopic expression of an inhibition-resistant kinase. Circ Res 89:750–752
Mattiasson G, Shamloo M, Gido G, Mathi K, Tomasevic G, Yi S, Warden CH, Castilho RF, Melcher T, Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Nikolich K, Wieloch T (2003) Uncoupling protein-2 prevents neuronal death and diminishes brain dysfunction after stroke and brain trauma. Nat Med 9:1062–1067
Mattson MP, Liu D (2002) Energetics and oxidative stress in synaptic plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Neuromolecular Med 2:215–231
Mazzio E, Soliman KF (2003) D-(+)-glucose rescue against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium toxicity through anaerobic glycolysis in neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res 962:48–60
Mills EM, Xu D, Fergusson MM, Combs CA, Xu Y, Finkel T (2002) Regulation of cellular oncosis by uncoupling protein 2. J Biol Chem 277:27385–27392
Miwa S, Brand MD (2003) Mitochondrial matrix reactive oxygen species production is very sensitive to mild uncoupling. Biochem Soc Trans 31:1300–1301
Morelli A, Grasso M, Calissano P (1986) Effect of nerve growth factor on glucose utilization and nucleotide content of pheochromocytoma cells (clone PC12). J Neurochem 47:375–381
Oliveira JM, Chen S, Almeida S, Riley R, Gonçalves J, Oliveira CR, Hayden MR, Nicholls DG, Ellerby LM, Rego AC (2006) Mitochondrial-dependent Ca2+ handling in Huntington’s disease striatal cells: effect of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Neurosci 26:11174–11186
Orrenius S, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondrial oxidative stress: implications for cell death. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:143–183
Powers WJ, Videen TO, Markham J, McGee-Minnich L, Antenor-Dorsey JV, Hershey T, Perlmutter JS (2007) Selective defect of in vivo glycolysis in early Huntington’s disease striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2945–2949
Ravikumar B, Stewart A, Kita H, Kato K, Duden R, Rubinsztein DC (2003) Raised intracellular glucose concentrations reduce aggregation and cell death caused by mutant huntingtin exon 1 by decreasing mTOR phosphorylation and inducing autophagy. Hum Mol Genet 12:985–994
Richard DE, Berra E, Gothié E, Roux D, Pouysségur J (1999) p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1. J Biol Chem 274:32631–32637
Richard D, Clavel S, Huang Q, Sanchis D, Ricquier D (2001) Uncoupling protein 2 in the brain: distribution and function. Biochem Soc Trans 29:812–817
Rosen LB, Ginty DD, Weber MJ, Greenberg ME (1994) Membrane depolarization and calcium influx stimulate MEK and MAP kinase via activation of Ras. Neuron 12:1207–1221
Salehi A, Delcroix JD, Mobley WC (2003) Traffic at the intersection of neurotrophic factor signaling and neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci 26:73–80
Sanchis D, Fleury C, Chomiki N, Goubern M, Huang Q, Neverova M, Grégoire F, Easlick J, Raimbault S, Lévi-Meyrueis C, Miroux B, Collins S, Seldin M, Richard D, Warden C, Bouillaud F, Ricquier D (1998) BMCP1, a novel mitochondrial carrier with high expression in the central nervous system of humans and rodents, and respiration uncoupling activity in recombinant yeast. J Biol Chem 273:34611–34615
Semenza GL, Jiang BH, Leung SW, Passantino R, Concordet JP, Maire P, Giallongo A (1996) Hypoxia response elements in the aldolase A, enolase 1, and lactate dehydrogenase A gene promoters contain essential binding sites for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 271:32529–32537
Shaywitz AJ, Greenberg ME (1999) CREB: a stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu Rev Biochem 68:821–861
Shimazaki K, Ishida A, Kawai N (1994) Increase in bcl-2 oncoprotein and the tolerance to ischemia-induced neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus. Neurosci Res 20:95–99
Song C, Perides G, Liu YF (2002) Expression of full-length polyglutamine-expanded Huntingtin disrupts growth factor receptor signaling in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Biol Chem 277:6703–6707
Speakman JR, Talbot DA, Selman C, Snart S, McLaren JS, Redman P et al (2004) Uncoupled and surviving: individual mice with high metabolism have greater mitochondrial uncoupling and live longer. Aging Cell 3:87–95
Starkov AA (1997) Mild uncoupling of mitochondria. Biosci Rep 17:273–279
Strand AD, Baquet ZC, Aragaki AK, Holmans P, Yang L, Cleren C, Beal MF, Jones L, Kooperberg C, Olson JM, Jones KR (2007) Expression profiling of Huntington’s disease models suggests that brain-derived neurotrophic factor depletion plays a major role in striatal degeneration. J Neurosci 27:11758–11768
Stuart JA, Cadenas S, Jekabsons MB, Roussel D, Brand MD (2001) Mitochondrial proton leak and the uncoupling protein 1 homologues. Biochim Biophys Acta 1504:144–158
Sugino T, Nozaki K, Takagi Y, Hattori I, Hashimoto N, Moriguchi T, Nishida E (2000) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases after transient forebrain ischemia in gerbil hippocampus. J Neurosci 20:4506–4514
Tsakiridis T, McDowell HE, Walker T, Downes CP, Hundal HS, Vranic M, Klip A (1995) Multiple roles of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in regulation of glucose transport, amino acid transport, and glucose transporters in L6 skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology 136:4315–4322
Vidal-Puig AJ, Grujic D, Zhang CY, Hagen T, Boss O, Ido Y, Szczepanik A, Wade J, Mootha V, Cortright R, Muoio DM, Lowell BB (2000) Energy metabolism in uncoupling protein 3 gene knockout mice. J Biol Chem 275:16258–16266
Williams ZR, Goodman CB, Soliman KF (2007) Anaerobic glycolysis protection against 1-methy-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) toxicity in C6 glioma cells. Neurochem Res 32:1071–1080
Xing J, Kornhauser JM, Xia Z, Thiele EA, Greenberg ME (1998) Nerve growth factor activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways to stimulate CREB serine 133 phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 18:1946–1955
Yung HW, Wyttenbach A, Tolkovsky AM (2004) Aggravation of necrotic death of glucose-deprived cells by the MEK1 inhibitors U0126 and PD184161 through depletion of ATP. Biochem Pharmacol 68:351–360
Zuccato C, Cattaneo E (2007) Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Huntington’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 81:294–330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Z., Chigurupati, S., Bagsiyao, P. et al. The Brain Uncoupling Protein UCP4 Attenuates Mitochondrial Toxin-Induced Cell Death: Role of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases in Bioenergetics Adaptation and Cell Survival. Neurotox Res 16, 14–29 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9039-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9039-8