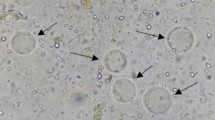
Abstract
Metronidazole is the most-used pharmaceutical for the treatment of infection by Blastocystis. However, studies have reported resistance of the microorganism towards this pharmaceutical. In Mexico, studies concerning the prevalence of this parasite and its relationship to Irritable Bowel Syndrome have been carried out. To evaluate the in vitro effect of metronidazole and the compound 1,3-bis-(4-phenyl-[1,2,3] triazole-1-il)2-propanol over Blastocystis, as well as the prevalence of Blastocystis in patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. A prospective, transversal design study (April 2016–April 2017) of 51 samples of patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome, obtained from the ISSEMyM Medical Center in Toluca, Mexico. For the identification of Blastocystis was done in three serial stool samples through direct microscopic examination and the Ritchie technique. The in vitro susceptibility test towards metronidazole and the triazolic compound was done through a microculture in concentrations of 1 to 1000 µg/mL, each one in triplicate. A 31.3% prevalence of Blastocystis was observed in the population, with greater prevalence in women (30.2%) than in men (25%). In the susceptibility test, a CL50 of 64 µg/mL was obtained for metronidazole, in comparison to the CL50 of 250 µg/mL for 1,3-bis-(4-phenyl-[1,2,3] triazole-1-il)2-propanol. This molecule in development has an effect for the treatment of infection by Blastocystis in vitro in patients with IBS and therefore, more studies should be performed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar C, Lucia J (2009) An overview of Blastocystis hominis infection and published experience in hemophilic population. J Coag Disorders 1(1):1–4
Alarcón RSR, Amato Neto V, Gakiya E, Bezerra RC (2007) Observações sobre Blastocystis hominis e Cyclospora cayetanensis em exames parasitológicos efetuados rotineiramente. Rev Soc Med Trop 40:253–255
Barassa B, Bueno VS (2000) Estudo comparativo entre os métodos de centrífugo-flutuação e de centrífugo-sedimentação no diagnóstico coproparasitológico. Lecta-USF 18:65–73
Batista L, Pérez J, Rosinach M, Gonzalo E, Sainz E, Loras C, Forné M, Esteve M, Fernández F (2017) Low efficacy of metronidazole in the eradication of Blastocystis hominis in symtomatic patients: case series and systmatic literatura reviw. Gatroenterol Hepatol 40(6):381–387
Beyham Y, Yilmaz H, Cengiz Z, Ekici A (2015) Clinical significance and prevalence of Blastocystis hominis in Van, Turkey. Saudi Med J. 9(36):1118–1121
Das R, Khalil S, Mirdha B, Makharia G, Dattagupta S, Chaudhry R (2016) Molecular characterization and subtyping of Blastocystis species in irritable bowel syndrome patients from North India. PLoS ONE 11(1):e0147055
Dogruman A, Simsek Z, Boorom K, Ekici E, Tuncer C, Kustimur (2010) Comparison of methods for detection of Blastocytsis infection in routinely submitted stool samples, and also in IBS/IBD Patients in Ankira, Turkey. PLoS One 5(11):e15484. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015484v
Duda A, Kosick D, Lanocha N, Kolodziejczyk L, Lanocha A (2015) The prevalence of Blastocystis hominis and other protozoan parasites in soldiers returning from peacekeeping missions. Am J Trop Med Hyg 92(4):805–806
González J, Pérez VM, Jiménez DO, Lopez-Valdez G, Corona D, Cuevas-Yañez E (2011) Effect of temperature on triazole and bistriazole formation through copper-catalyzed alkyne–azide cycloaddition. Tetrahedron Lett 52:3514
Jiménez G, Martínez F, Reyes G, Ramírez M, Arroyo E, Romero V, Stark D, Souza S, Martínez H, Elisser A, Olivo A, Maravilla P (2012) Blastocystis infection is associated with irritable bowel syndrome in a Mexican patient population population. Parasitol Res 110(3):1269–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2626-7
Keri R, Patil S, Budagumpi S, Nagaraja B (2015) Triazole: a promisisng agent. Chem Biol Drug Des 86(4):410–423
Khoshnood S, Rafiei A, Saki J, Alizadeh K (2015) Prevalence and genotype characterization of Blastocystis hominis among the Baghmalek people in Southwestern Iran in 2013–2014. Microbiol. 8(10):e23930
Kurt Ö, Al FD, Tanyüksel M (2016) Eradication of Blastocystis in humans: Really necessary for all. Parasitol Int 65(6):797–801
Longstreth G, Thompson W, Chey W, Hougton L, Mearin E, Spiller R (2006) Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 130(5):1480–1491. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.061
Mearin F, Ciriza C, Mínguez M, Rey E, Mascort J, Peña E, Cañones P, Júdez J (2016) Guía de Práctica Clínica: síndrome del intestino irritable con estreñimiento y estreñimiento funcional en adultos. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 6(108):332–363
Miceli M, Kauffman C (2015) Isavuconazole: a new broad-spectrum triazole antifungal agent. Clin Infect Dis 61(10):1558–1565
Mirza H, Tan K (2014) Intra-subtype variation in enteroadhesion accounts for differences in epithelial barrier disruption and is associated with metronidazole resistance in Blastocystis subtype-7. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8(5):e2885. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002885
Mirza H, Upcroft DJ, Tan K (2011) A rapid, high-throughput viability assay for Blastocystis spp reveals metronidazole resistances and extensive subtipe-dependent variations in drug susceptibilities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2(5):637–648
Mostafa S, Abd K, Salah Z, Mostafa S (2015) Prevalence and diagnostic approach for a nebleted protozoo Blastocystis hominis. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 5(1):51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2222-1808(14)60626-5
Occhipinti K, Smith J (2012) Irritable bowel syndrome: a review and update. Clin Colon Rectal 25:46–52
Phillips BP, Zierdt CH (1976) Blastocystis hominis: pathogenic potential in human patients and in gnotobiotes. Exp Parasitol 39(3):358–364
Quinlivan J, Wu Jy, Upmacis R (2015) Crystal structure of metronidazolium tetrachloridoaurate. Acta Cryst 71:810–812
Rajic B, Arapovic J, Raguz K, Boskovic M, Babic S, Maslac S (2015) Eradication of Blastocystis hominis prevents the development of simtomatic Hashimoto’s thyroiditid: a case report. J Infect Dev Ctries 9(7):788–791
Ramirez M, Hernandez R, Lopez E, Moncada D, Rodriguez A, Pagaza C, Gonzales A, Flisser A, Kawa A, Maravilla P (2010) Parasites in Mexican patients with irritable bowel síndrome: a case-control study. Parasit Vectors 96(3):1–3
Roberts T, Stark D, Harkness Jy, Ellis J (2014) Update on the pathogenic potencial and treatment options for Blastocystis sp. Gut Pathogens 6:17
Roberts T, Bush S, Ellis J, Harkness J, Stark D (2015) In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Blastocystis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59(8):4417–4423. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.04832-14 Epub 2015 May 18
Schmulson and Drossman (2017) What is new in Rome IV. J Neorogastroenterol Motility 33(2):2093–2887
Sekar U, Shanthi M (2013) Blastocystis: consensus of treatment and controversies. Trop Parasitol 3(1):35–39
Shawky A, Maha M, Reham A, Mohamed H (2011) The pathogenic role of different Blastocystis hominis genotypes isolated from patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Arab J Gastroenterol 12:194–200
Sinagra E, Pompei G, Tomasello G, Cappello F, Morreale G, Amvrosiadis G, Rossi F, Lo monte A, Rizzo A, Raimondo D (2016) Inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome: Myth or new treatment target? World J Gastroenterol 7:2242–2255
Stark D, Van Hal S, Marriott D, Ellis J, Harkness J (2007) Irritable bowel syndrome: a review on the role of intestinal protozoa and the importance of their detection and diagnosis. Int J Parasitol 37:11–20
Stensvold R, Brillowska D, Nielsen H, Arendrup M (2006) Detection of Blastocystis hominis in unpreserved stool specimens by using polymerase chain reaction. J Parasitol 92(5):1081–1087. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-840R.1
Strober W (2001) Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Curr Prot Immunol 21(3B):A.3B.1–A.3B.2
Tamalee R, Ellis J, Harkness J, Marriott D, Stark D (2014) Treat failure in patients with chronic Blastocystis infection. J Med Microbiol 63:252–257. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.065508-0
Tamalee R, Stephen B, Ellis J, Harkness J, Stark D (2015) In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Blastocystis. Anitimicrob Agents Chemother 59(8):4417–4423. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.04832-14
Tan KS (2008) New insights on classification, identification, and clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp. Clin Microbiol Rev 21(4):639–665
Tungtrongchitr A, Manatsathi S, Kositchaiwat C, Ongrotchanakun J, Munkong N, Chinabutr P, Leelakusolvong E, Chaicumpa W (2004) Blastocystis hominis infection in irritable bowel síndrome patients. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 35(3):705–710
Ustün Sy, Turgay N (2006) Blastocystis hominis and bowel diseases. Turkiye Parasitol Derg 30(1):72–76
Wu Z, Mirza H, Tan K (2014) Intra-Subtype variation in enteroadhesion accounts for differences in epitelial barrier disruption and is associated with metronidazole resistance in Blastocystis subtype-7. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8(5):e2885. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002885
Yakoob J, Jafri W, Jafri N, Khan R, Islam M, Beg M, Zaman V (2004) Irritable bowel síndrome: in search of an etiology: role of Blastocystis hominis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 70(40):383–385
Yakoob J, Abbas Z, Asim M, Naz S, Awan S, Hamid S, Jafri W (2011) In vitro sensitive of Blastocystis hominis to garlic, ginger, White cumin, and black pepper used in diet. Parasitol Res 109:379–385
Ye W, Yao Q, Yu S, Gong P, Qin M (2017) Synthesis and antitumor activity of triazole—containing srafennib analogs. Molecules 22(10):E1759
Acknowledgements
To CONACyT, chemist Zamudio-Chávez of HGI Valentín Gómez Farías, to the Zamser Clinical Analysis Laboratory of Ixtlahuaca and to Caballero-Vásquez, P.MD, of the ISSEMyM Medical Center of Toluca, Mexico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GF-L, ZC-S and SB-JG collected the samples and performed the coprological assays. GF-L, performed inoculation parasites, viability of the cells and determination of MIC, CV-P performed the Rome IV criteria used for the diagnosis of IBS. CY-E performed the Synthesis of the molecule. SB-JG and MA-E formulated the idea and MA-E, contributed with critical comments. GF-L and SB-JG obtained the authorizations. All authors participated during the discussion and writing of the manuscript and approved its final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The Ethics and Research Committee of the Medical Center ISSEMyM approved the study Reference Number 015/16.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Flores, L., Santillán-Benítez, J., Cuevas-Yáñez, E. et al. Evaluation of the effect of 1,3-bis-(4-phenyl-[1,2,3] triazole-1-il)2-propanol in comparison with metronidazole in an in vitro culture of Blastocystis in samples of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Parasit Dis 43, 506–512 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-019-01118-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-019-01118-2