Abstract
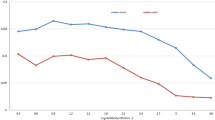
The present work was carried out to study the sero-prevalence of Haemonchus contortus infection in sheep by Indirect-Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay (Indirect-ELISA) using somatic antigen. Out of 100 abomasums screened, 57 found positive for H. contortus adult worms. A total of 250 serum samples which includes, 100 serum samples from local abattoir in and around shimoga region from the animals from which the abomasums were collected and 150 serum samples from migratory sheep were used to detect the circulating antibody against H. contortus by Indirect-ELISA using somatic antigen. Of the 57 sheep harboring adult worms in their abomasums, the serum samples showed positive reaction by Indirect-ELISA with somatic antigen. However, among 43 sheep which are not showing any adult worms of H. contortus in their abomasums, but their 21 serum samples showed positive reaction by Indirect-ELISA. The sensitivity and specificity of Indirect-ELISA was found to be 100 and 67.18 %, respectively. Also, the sero-prevalence of H. contortus infection was found to be 58.66 % out of 150 migratory sheep serum samples screened for detecting circulating antibodies of H. contortus by Indirect-ELISA using somatic antigen in and around shimoga region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attindehou S, Salifou S, Biaou CF, Gbati OB, Adamou-N’diaye M, Pangui LJ (2012) Epidemiology of haemonchosis in sheep and goats in Benin. J Parasitol Vector Biol 4(2):20–24
Bonfoh B, Zinsstag J, Ankers P, Pangui LJ, Pfister K (1995) Epidémiologie des nématodes gastro-intestinaux chez les petits ruminants dans la région des plateaux au Togo. Rev Elev Méd Vét Pays Trop 48(4):321–326
Bowmann DD (2009) Georgi’s Parasitology for Veterinarians, 9th edn. Saunders Elsevier, St. Louis
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principles of protein dye binding. Ann Biochem 72:248–252
Dagnachew S, Amamute A, Temesgen W (2011) Epidemiology of gastrointestinal helminthiasis of small ruminants in selected sites of North Gondar zone, Northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop Vet J 15(2):57–68
Lone BA, Chishti MZ, Ahmad F, Tak H, Hassan J (2012) Immunodiagnosis of Haemonchus contortus infection in sheep by indirect enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Iranian J Vet Res 13(1):49–53
McLaren M, Draper CC, Roberts JM (1979) Studies on the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay tests for Schistosoma mansoni infection. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 72:243–253
Mir RA, Chishti MZ, Zargar MA, Tak H, Ganie SA (2008) Excretory-Secretory antigens are better than crude antigens for serodiagnosis of Haemonchus contortus. Asian J Sci Res 1(2):171–175
Molina JM, Ruiz A, Rodriguez-Ponce E, Gutierrez AC, Gonzalez J, Hernandez S (1999) Cross-reactive antigens of Haemonchus contortus adult worms in Teladorsagia circumcincta infected goats. Vet Res 30:393–399
Prasad A, Nasir A, Singh N (2007) Dot-ELISA for the detection of preclinical Haemonchus contortus infections in sheep by using an adult somatic antigen and an immunoaffinity-purified fraction. J Parasit Dis 31:22–28
Qamar MF, Maqbool A, Khan MS, Ahmad N, Muneer MA (2011) Epidemiology of haemonchosis in sheep and goats under different managemental conditions. Vet World 2(11):413–417
Raza MA, Murtaza S, Bachaya HA, Dastager G, Hussain A (2009) Point prevalence of haemonchosis in sheep and goats slaughtered at Multan abattoir. J Anim Plant Sci 9(3):158–159
Schallig HD, Hornok JB, Cornelissen W (1995) Comparison of two enzyme immunoassays for the detection of Haemonchus contortus infections in sheep. Vet Parasitol 57(4):329–338
Sissay MM, Uggla A, Waller PJ (2007) Prevalence and seasonal incidence of nematode parasites and fluke infections of sheep and goats in Eastern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod 39(7):521–531
Soulsby EJL (1982) Helminths, arthropods and protozoa of domesticated animals, 7th edn. The English Language Book Society, Bailiere Tindall and Cassell Ltd, London, pp 763–773
Sultan K, Desouky AY, Elbahy NM, Elsiefy MA (2012) Evaluation of Indirect-ELISA in diagnosis of natural ovine cysticerciosis and haemonchosis. Online J Anim Feed Res 3:301–302
Tariq KA, Chishti MZ, Fayaz A, Shawl AS (2008) Epidemiology of gastrointestinal nematodes of sheep managed under traditional husbandry system in Kashmir valley. Vet Parasitol 158:138–143
Tariq KA, Chishti MZ, Ahmad F (2010) Gastro-intestinal nematode infections in goats relative to season, host sex and age from the Kashmir valley. Indian J Helminthol 84:93–97
Acknowledgment
The author is thankful to Dr. R.V. Prasad, Dean, Veterinary College, Shimoga for providing facility to carry out the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gowda, A.K.J. Sero-prevalence of Haemonchus contortus infection in sheep by Indirect-ELISA using somatic antigen. J Parasit Dis 40, 464–468 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-014-0527-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-014-0527-2