Abstract
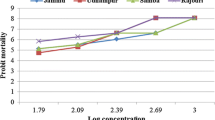
The resistance status of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from Noorpur Bet village of Ludhiana district, Punjab was evaluated against malathion by Adult Immersion Test. The adult female ticks showed an upward trend in the mortality percentage with increase in drug concentration. The regression graph of probit mortality of ticks plotted against log values of progressively increasing concentrations of malathion was utilized for the determination of slope of mortality (95 % confidence intervals) which was 2.469 ± 0.5744 (0.6413–4.297) whereas, the value of goodness of fit (R2) was 0.8603. The LC50 (95 % CI) and LC95 (95 % CI) were recorded as 1875.05 (1725.14–2,038) and 8,654 (7296.8–10263.8) ppm, respectively and the resistance factor was 3.46 (Level I). The slope of egg mass (95 % CI) was −0.1500 ± 0.04071 (−0.2795 to −0.02045) and was negative because with the increasing concentrations of acaricide the ticks died. The reproductive index when plotted against increasing log concentrations of malathion revealed a slope value of −0.414 ± 0.055. Further, a significant variation (p = 0.0049) was recorded in the inhibition of oviposition among the various groups treated with increasing concentrations of malathion.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baffi MA, de Souza GRL, de Souza CS, Ceron CR, Bonetti AM (2008) Esterase enzymes involved in pyrethroid and organophosphate resistance in a Brazilian population of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari, Ixodidae). Mol Biochem Parasitol 160:70–73
Basu A, Haldar DP (1997) A note on the effect of continuous use of Sevin 50 WP on some cattle ticks. J Vet Parasitol 11:183–184
Baxter GD, Barker SC (1998) Acetylcholinesterase cDNA of the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus: characterization and role in organophosphate resistance. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 28:581–589
Benavides OE, Romero NA, Rodriguez JL, Silva ZJ (1999) Evidencia preliminar de la aparicion de resistenciaa lactonas macrociclicas en cepas de garrapata Boophilus microplus en Colombia. In: Memorias IV Seminarios Internacional de Parasitologia, Puerto Vallarta, Jalisco, Mexico, pp 264–266
Castro-Janer E, Rifran L, Piaggio J, Gil A, Miller RJ, Schumaker TTS (2009) In vitro tests to establish LC50 and discriminating concentrations for fipronil against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) and their characterization. Vet Parasitol 162:120–128
Chaudhary RP, Naithani RC (1964) Resistance to BHC in the cattle tick Boophilus microplus in India. Bull Ent Res 55:405–410
FAO (2004) Resistance management and integrated parasite control in ruminants guidelines. Animal Production and Health Division, FAO, Rome, pp 25–77
Finney DJ (1962) Probit analysis−a statistical treatment of the response curve. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1–318
Haque M, Jyoti, Singh NK, Rath SS, Ghosh S (2011) Epidemiology and seasonal dynamics of ixodid ticks of dairy animals of Punjab state, India. Indian J Anim Sci 81:661–664
Jongejan F, Uilenberg G (1994) Ticks and control methods. Rev Sci Tech Off Int Epiz 13:1201–1226
Jonsson NN, Miller RJ, Robertson JL (2007) Critical evaluation of the modified-adult immersion test with discriminating dose bioassay for Boophilus microplus using American and Australian isolates. Vet Parasitol 146:307–315
Khan MH, Srivastava SC (1977) In vitro tests with some ixodicides against cattle tick B. microplus. Indian J Anim Health 16:137–140
Kumar S (1999) Studies on acaricides resistance in common ixodid ticks of Punjab. M.V.Sc thesis, PAU, Ludhiana
Kumar S, Paul S, Sharma AK, Kumar R, Tewari SS, Chaudhuri P, Ray DD, Rawat AKS, Ghosh S (2011) Diazinon resistant status in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from different agroclimatic zones of India. Vet Parasitol 181:274–281
Li AY, Davey RB, Miller RJ, George JE (2003) Resistance to coumaphos and diazinon in Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) and evidence for the involvement of an oxidative detoxification mechanism. J Med Entomol 40:482–490
Li AY, Davey RB, Miller RJ, George JE (2004) Detection and characterization of amitraz resistance in the southern cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol 41:193–200
Mendes MC, Pereira JR, Prado AP (2007) Sensitivity of Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) to pyrethroids and organophosphate in farms in the vale do paraiba region, Sao Paulo, Brazil. Arq Inst Biol 74:81–85
Miller RJ, Davey RB, George JE (2005) First report of organophosphate-resistant Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) within the United States. J Med Entomol 42:912–917
Minjauw B, McLeod A (2003) Tick-borne diseases and poverty. The impact of ticks and tick borne diseases on the livelihood of small scale and marginal livestock owners in India and eastern and southern Africa. Research report, DFID Animal Health Programme, Centre for Tropical Veterinary Medicine, University of Edinburgh, U K, pp 59–60
Rath SS, Kumar S, Joia BS (2006) Resistance to diazinon and malathion in Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) populations from Punjab, India. J Insect Sci 19:74–81
Sangwan AK, Chhabra MB, Singh S (1993) Acaricide resistance status of common livestock ticks in Haryana. Indian Vet J 70:20–24
Sharma AK, Kumar R, Kumar S, Nagar G, Singh NK, Rawat SS, Dhakad ML, Rawat AKS, Ray DD, Ghosh S (2012) Deltamethrin and cypermethrin resistance status of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from six agro-climatic regions of India. Vet Parasitol 188:337–345
Shaw RD (1966) Culture of an organophosphorus resistant strain of Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) and assessment of its resistance spectrum. Bull Entomol Res 56:398–405
Singh NK, Jyoti Haque M, Rath SS (2010) Studies on acaricide resistance in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus against synthetic pyrethroids by adult immersion test with a discriminating dose. J Vet Parasitol 24:207–208
Singh NK, Jyoti, Haque M, Singh H, Rath SS (2012a) Prevalence of ixodid ticks in dairy animals of different farm types in Punjab. In: Sandhu, SK et al (eds) Proc. International Conference on Sustainable Agriculture for Food and Livelihood Security, Crop Improvement, Ludhiana, pp 1491–1492
Singh NK, Haque M, Rath SS, Jyoti (2012b) Deltamethrin resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus in Ludhiana. Indian Vet J 89:23–25
Singh NK, Gelot IS, Singh V, Jyoti, Rath SS (2013) Detection of amitraz resistance in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus from North Gujarat, India. J Parasites Dis. doi:10.1007/s12639-013-0280-y
Vatsya S, Yadav CL (2011) Evaluation of acaricide resistance mechanisms in field populations of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from India. Int J Acarol 37:405–410
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi for funding through Women Scientist Scheme (WOS-A) Project no. SR/WOS-A/LS-493/2011 to senior author. Sincere thanks are also due to the Director of Research, GADVASU, Ludhiana for providing facilities to carry out the research study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jyoti, Singh, N.K., Singh, H. et al. Malathion resistance in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus from Ludhiana district, Punjab. J Parasit Dis 38, 343–346 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-013-0322-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-013-0322-5