Abstract
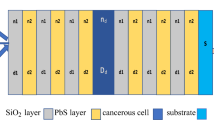
The identification and subsequent classification of different brain tissues is critical for detecting abnormalities during robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery that includes connection with the tissues. In this work, an optical sensor was designed to assess the refractive index (RI) of different brain tissues while the robotic surgery is performed. The proposed design is based on a two-dimensional photonic crystal biosensor powered by electromagnetic radiation. It operates within the wavelength range from 1648nm to 1794nm intended to effectively detect the changes in the RI of different tissues. Because the RI of abnormal tissues is significantly different from that of normal tissues, the sensor is capable of distinguishing tumors and cancer-infected brain tissues from normal brain tissues. The sensor exhibits different ranges of frequency, wavelength, and amplitude spectra, which respond to small changes that occur in the RI of the brain tissue. The simulation results showed that the photonic crystal biosensor has a high sensitivity of 4615.38nm/RIU, quality factor of 573, and detection limit of 0.0013 RIU.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Fulop J, Liu M, Blanda R, Kromer C, et al (2015) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2008-2012. Neuro Oncol17(Suppl 4):iv1-iv62. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not151
Udaka YT, Packer RJ (2018) Pediatric brain tumors. Neurol Clin 36:533–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03437-4
Lee DY, Kim J, Kim JS, Baek C, Noh G, Kim DN et al (2015) "Anisotropic patterning to reduce instability of concentric-tube robots" IEEE Trans Robot 31:1311–1323. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2015.2481283
Kim J, Choi W-Y, Kang S, Kim C, Cho K-J(2019) Continuously variable stiffness mechanism using non uniform patterns on coaxial tubes for continuum microsurgical robot. IEEE Trans Robot. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2019.2931480
Forbrigger C, Lim A, Onaizah O, Salmanipour S, Looi T, Drake J et al (2019) Cable-less, magnetically driven forceps for minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 4:1202–1207. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2019.2894504
Marcus HJ, Zareinia K, Gan LS, Yang FW, Lama S, Yang GZ et al (2014) Forces exerted during micro neurosurgery: a cadaver study. IntJ Med Robot 10:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.1568
Chortos A, Liu J, Bao ZA (2016) Pursuing prosthetic electronic skin. Nat Mater 15:937–950. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4671
Dai Y, Xue Y, Zhang JX (2016) Milling state identification based on vibration sense of a robotic surgical system. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63:6184–6193. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2016.2574981
Liang WY, Ma J, Tan KK (2018) Contact force control on soft membrane for an ear surgical device. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(12):9593–9603. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2018.2818647
Zhang T, Chen B, Zuo S (2021) A novel 3-DOF force sensing micro needle with integrated fiber bragg grating for microsurgery. IEEE Trans Ind Electron. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2021.3055173
Ferraro D et al (2021) Implantable Fiber Bragg Grating sensor for continuous heart activity monitoring: ex-vivo and in-vivo validation. IEEE Sensors J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3056530
Arabagi V, Felfoul O, Gosline AH, Wood RJ, Dupont PE (2016) Biocompatible pressure sensing skins for minimally invasive surgical instruments. IEEE Sensors J 16(1):1294–1303. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2015.2498481
Kim U, Lee DH, Yoon WJ, Hannaford B, Choi HR (2015) Force sensor integrated surgical forceps for minimally invasive robotic surgery. IEEE Trans Robot 31:1214–1224. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2015.2473515
Kim U, Kim YB, Seok DY, So J, Choi HR (2018) A surgical palpation probe with 6-axisforce/torque sensing capability for minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65:2755–2765. https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2017.2739681
Kim U, Kim YB, So J, Seok D, Choi HR (2018) Sensorized surgical forceps for robotic-assisted minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(12):9604-9613. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2018.2821626
Naidu AS, Patel RV, Naish MD (2017)Low-cost disposable tactile sensors for palpation in minimally invasive surgery. IEEE/ASMETrans Mechatron 22:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMECH.2016.2623743
Zhou D, Tadano K, Haraguchi (2020) Motion control and external force estimation of a pneumatically driven multi-DOF robotic forceps. Appl Sci 10:3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113679
Chi A, Sun XG, Xue N, Li T, Liu C (2018) Recent progress in Technologies for tactile sensors. Sensors 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18040948
Chen T et al (2020) Novel, flexible and ultra-thin pressure feedback sensor for miniaturized intra-ventricular neurosurgery robotic tools. IEEE Trans Ind Electron. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.2984427
Yablonovitch E (1987) Inhibited spontaneous emission in solid-state physics and electronics. Phys Rev Lett 58(23):2059–2062. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.58.2059
John S (1987) Strong localization of photons in certain disordered dielectric super lattices. Phys Rev Lett 58(20):2486–2489. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.58.2486
Lee C, Thillaigovindan J, Radhakrishnan R (2008) Design and modeling of nano mechanical sensors using silicon 2-D photonic crystals. J Light Wave Technol 26(7):839–846. https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2007.915273
Robinson S, Nakkeeran R (2013) Photonic crystal ring resonator-based add drop filters: a review. SPIE 52(6):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.OE.52.6.060901
Kuma VD (2003) Analysis and simulations of photonic crystal components for optical communication. Ph.D. dissertation, Helsinki University of Technology, Helsinki, Finland
Kang C, Phare C, Weiss SM (2010) Photonic crystal defects with increased surface area for improved refractive index sensing. In: Proceeding of Conference on Laser and Electro Optics and Quantum Electronics and laser Science, San Jose, California, United States, pp 1–2
Hsiao F, Lee C (2010) Computational study of photonic crystals nano-ring resonator for biochemical sensing. IEEE Sensors 10(7):1185–1191. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2010.2040172
Pal S, Guillermain E, Sriram R, Miller BL, Fauchet PM (2011) Silicon photonic crystal nano cavity coupled waveguides for error-corrected optical biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4024–4031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.03.024
Olyaee S, Najafgholinezhad S, Banaei HA (2013)Four-channel label-free photonic crystal biosensor using nano cavity resonators. Photonic Sens 3(3):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13320-013-0110-y
Dorfner D, Zabel T, Hurlimann T, Hauka N, Frandsen L, Rant U, Abstreiter G, Finley J (2009) Photonic crystal nanostructures for optical bio sensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 24(15):3688-3692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.05.014
Najafgholinezhad S, Olyaee S (2014) A photonic crystal biosensor with temperature dependency investigation of micro-cavity resonator. Optik-Int J Light Electron Optics 125:6562–6565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2014.08.043
Mohamed MS, Farahat M, Hameed O, Nihal FF, Areed MM, El-Okr, Obayya SSA (2016) Analysis of highly sensitive photonic crystal biosensor for glucose monitoring. ACES J 31(7):25–27
Mohammed NA, Hamed MM, Khalaf AAM, Alsayyari A, El-Rabaie S. High-sensitivity ultra-quality factor and remarkable compact blood components biomedical sensor based on nanocavity coupled photonic crystal. Result Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102478
Rakshit BiswasU (2020) Detection and analysis of hemoglobin concentration in blood with the help of photonic crystal based micro ring resonator structure. Opt Quant Electron 52:449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02566-4
Ajey SS, Bhanumathi HR, Srikanth PC et al (2020) Highly sensitive photonic crystal based biosensor for Bacillus cereus. Int j inf Tecnol 12:1393–1402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-020-00507-8
Robinson S, Nakkeeran R (2011) PCRR based bandpass filter for C and L+U bands of ITU T G.694.2 CWDM systems. Optics Photonics J 1(3):142–149. https://doi.org/10.4236/opj.2011.13024
Pelosi G, Coccioli R, Selleri S (1997) Quick finite elements for electromagnetic waves. Boston, London, England: Artech House 1–289. https://doi.org/10.1109/MEI.1999.793831
Hagness SC (2005) Computational electrodynamics: the finite-difference time-domain method. Artech House, Boston, pp 1–1038
Johnson SG, Joannopoulos JD (2000)Block-iterative frequency domain methods for Maxwell′s equation in a plane wave basis. Opt Express 11(3):173–190. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.8.000173
Guo S, Alloin S (2003) Simple plane wave implementation for photonic crystal calculation. Opt Express 11(2):167–175. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.11.000167
Scarmozzino R, Gopinath A, Pregla R, Helfert S (2000) Numerical techniques for modeling guided-wave photonic devices. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 6(1):150–162. https://doi.org/10.1109/2944.826883
Joannopoulos JD, Johnson SG, Winn JN, Meade RD (2008) Photonic crystals: molding the flow of light. Princeton University Press, Princeton
De Vos K, Bartolozzi I, Schacht E, Bienstman P, Baets R (2007)Silicon-on-insulator micro ring resonator for sensitive and label-free bio sensing. Opt Express 15(12):7610–7615. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.15.007610
Nouman WM, Abd El–Ghany SE-S, Sallam SM, Dawood A-FB, Aly AH (2020) Biophotonic sensor for rapid detection of brain lesions using1D photonic crystal. Opt Quant Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02409-2
Biwas TK, Gupta AK (2002) Retrieval of true color of the internal organ of CT images and attempt to tissue characterization by refractive index: initial experience. Indian J Radiol Imaging 12:169–178
Joonmi O, Eric TH, Danie P, Nelson SJ (2006) Measurement of in-vivo multi-component T2 relaxation times for brain tissue using multi-sliceT2 prep at 1.5 and 3T. JMRI 24:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2005.10.016
Graham SJ, Bronskill MJ (1996) MR measurement of relative water content and multi component T2 relaxation in human breast. Magn Reson Med 35:706–715. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.1910350512
Moffat B, Pope J (2002) The interpretation of multi-exponential water proton transverse relaxation in the human and porcine eye lens. Magn Reson Imaging 20:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0730-725X(02)00481-2
Grossman RI, Gomori JM, Ramer Kn, Lexa FJ, Schnall MD (1994) Magnetization transfer: theory and clinical application in neuro radiology. Radiographics 14:279–290. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.14.2.8190954
Papanikolaou N, Maniatis V, Pappas J, Roussakis A, Efthimiadou R, AndreouJ (2002) Biexponential T2 relaxation time analysis of the brain: correlation with magnetization transfer ratio. Invest Radiol 37:363–367. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004424-200207000-00001
Arunkumar R, Suaganya T, Robinson S (2019) Design and analysis of 2D photonic crystal based bio sensor to detect different blood components. Photonic Sens 9(1):69–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13320-018-0479-8
Olyaee S, Bahabady AM (2015) Designing a novel photonic crystal nano-ring resonator for biosensor application. Opt Quantum Electron 2015:1881–1888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-014-0053-6
Robinson S, Shanthi KV (2016) Analysis of protein concentration based on photonic crystal ring resonator. Int J Optics Photonics (IJOP) 10(2), Summer-Fall
Suganya T, Robinson S (2017) 2d photonic crystal based biosensor using rhombic ring resonator for glucose monitoring. ICTACT J Microelectron 03(01). https://doi.org/10.21917/ijme.2017.061
Shanthi KV, Robinson S (2014)Two-dimensional photonic crystal based sensor for pressure sensing. Photonic Sens 4(3):248–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13320-014-0198-8
Danaie M, Kiani B (2018) Design of a label-free photonic crystal refractive index sensor for biomedical applications. Photonics Nanostruct Fundam Appl 31:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.photonics.2018.06.004
Sharma S, Kumar A, Singh KhS, Tyagi HK (2021) 2D photonic crystal based biosensor for the detection of chikungunya virus. Optik 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166575
Chen Y, Yu F, Yang C, Song J, Tang L, Lin M, He J-J (2015) Label-free biosensing using cascaded double-microring resonators integrated with microfluidic channels. Optics Commun 344:129–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2015.01.028
Goyal AK, Pal S (2014) Design and simulation of high sensitive photonic crystal waveguide sensor. Optik - Int J Light Electron Opt. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2014.08.174
Omidniaee A, Karimi S, Farmani A (2021) Surface plasmon resonance-based SiO2 kretschmann configuration biosensor for the detection of blood glucose. Silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01081-9
Acknowledgements
The entire research work is carried out in University College of Engineering, Pattukkottai, which is one of the constituent college of Anna University, Chennai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.Asuvaran: Writing - original draft, Designing of sensor.
G.Elatharasan: Methodology, Investigation, Writing - review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
I give my consent for the publication of identifiable details, which can include images, graphs, simulation results within the text to be published in this journal and article. I have discussed this consent with my coauthor.
Conflict of Interest
Not applicable.
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
We declare all this manuscript is original, has not been published before and is not being considered for publication elsewhere. We know of no conflict of interest associated with this Publication, and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome. As a corresponding author, I confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved for the submission by all the co-authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asuvaran, A., Elatharasan, G. Design of Two-Dimensional Photonic Crystal-based Biosensor for Abnormal Tissue Analysis. Silicon 14, 7203–7210 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01442-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01442-4