Abstract
Purpose
Although silicon is not an essential element in sensu stricto for plant growth, it affects plant stress resistance and may affect the composition of cell wall compounds, especially of grasses. Where silicon availability alters the stoichiometry of macro nutrients in grasses, data on the interaction with calcium and micro nutrients are rare and hence are focussed on in this study.
Methods
The effect of silicon availability on calcium and micro nutrient content of the leaf blades of common reed, Phragmites australis, were assessed in a pot experiment with three levels of silicon supply.
Results
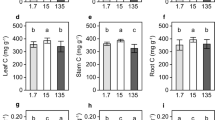
Calcium and micro nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry in leaf blades is altered by changing silicon availability during plant growth. In addition, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) reveals that elevated silicon supply promotes silica deposition and changes the element content of micro and macro nutrients in the near epidermis tissue of P. australis leaves.
Conclusion
Silicon availability has a major impact on calcium and micro nutrient content and stoichiometry in grasses. This in turn may considerably affect the nutrient cycling in grass dominated ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schaller J, Brackhage C, Gessner MO, Bäuker E, Dudel EG (2012) Plant Biol 14:392–396
Schoelynck J, Bal K, Backx H, Okruszko T, Meire P, Struyf E (2010) New Phytol 186(2):385–391
Struyf E, Van Damme S, Gribsholt B, Bal K, Beauchard O, Middelburg JJ, Meire P (2007) Aquat Bot 87(2):134–140
Schaller J, Brackhage C, Paasch S, Brunner E, Bäucker E, Dudel EG (2013) Sci Total Environ 442:6–9
Cornelis JT, Delvaux B, Cardinal D, Andre L, Ranger J, Opfergelt S (2010) Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74(14):3913–3924
Melzer SE, Knapp AK, Kirkman KP, Smith MD, Blair JM, Kelly EF (2010) Biogeochemistry 97(2–3):263–278
Eneji AE, Inanaga S, Muranaka S, Li J, Hattori T, An P, Tsuji W (2008) J Plant Nutr 31(2):355–365
Fawe A, Abou-Zaid M, Menzies JG, Belanger RR (1998) Phytopathology 88(5):396–401
Ma JF (2004) Soil Sci Plant Nutr 50(1):11–18
Sangster AG (1970) Ann Bot 34(1):245–257
Epstein E (1999) Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Molec Biol 50:641–664
Borrelli N, Fernández HM, Altamirano SM, Osterrieth M (2011) Aquat Bot 94(1):29–36
White PJ (2001) J Exp Bot 52(358):891–899
Bush DS (1995) Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Molec Biol 46:95–122
Ma JF, Takahashi E (1993) Plant Soil 148(1):107–113
Ma JF, Takahashi E (1990) Plant Soil 126(1):115–119
Horiguchi T, Morita S (1987) J Plant Nutr 10(17):2299–2310
Horiguchi T (1988) Soil Sci Plant Nutr 34(1):65–73
Iwasaki K, Maier P, Fecht M, Horst WJ (2002) Plant Soil 238(2):281–288
Iwasaki K, Maier P, Fecht M, Horst WJ (2002) J Plant Physiol 159(2):167–173
Williams DE, Vlamis J (1957) Plant Physiol 32(5):404–409
Shi QH, Bao ZY, Zhu ZJ, He Y, Qian QQ, Yu JQ (2005) Phytochemistry 66(13):1551–1559
Kamenidou S, Cavins TJ, Marek S (2010) Sci Hortic 123(3):390–394
Li J, Leisner SM, Frantz J (2008) J Am Soc Hortic Sci 133(5):670–677
Kaya C, Tuna AL, Sonmez O, Ince F, Higgs D (2009) J Plant Nutr 32(10):1788–1798
Struyf E, Kotowski W, Jacobs S, Van Damme S, Bal K, Opdekamp W, Backx H, Van Pelt D, Meire P (2011) Hydrobiologia 674(1):41–50
Struyf E, Smis A, Van Damme S, Garnier J, Govers G , Van Wesemael B, Conley DJ, Batelaan O, Frot E, Clymans W, Vandevenne F, Lancelot C, Goos P, Meire P (2010) Nat Commun1
Güsewell S, Freeman C (2005) Funct Ecol 19(4):582–593
(2002) DIN-EN-13805 Deutsches Institut für Normung. Berlin, pp 11
(2004) DIN-EN-ISO-17294-2 Deutsches Institut für Normung: Berlin, pp 24
Zimmermann F, Opfermann M, Bäucker E, Fiebig J, Nebe W (2000) Forstwiss Cent bl 119(4):193–207
Loneraga J, Snowball K (1969) Aust J Agric Res 20(3):465–472
Loneraga J, Snowball K, Simmons WJ (1968) Aust J Agric Res 19(6):845–852
Bussler W (1963) Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernährung, Düngung Bodenkunde 100(1):53–58
Marschner H (2003) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London
Willats WGT, McCartney L, Mackie W, Knox JP (2001) Plant Mol Biol 47(1–2):9–27
Webb MA (1999) Plant Cell 11(4):751–761
Wissemeier AH, Horst WJ (1992) Plant Soil 143(2):299–309
Pittman JK (2005) New Phytol 167(3):733–742
Okuda A, Takahashi E (1962) Japan J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 33:1–8
Horst WJ, Fecht M, Naumann A, Wissemeier AH, Maier P (1999) J Plant Nutr Soil Sci Z Pflanzenernahr Bodenkd 162(3):263–274
Li P, Song AL, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Liang YC (2012) Plant Soil 354(1–2):407–419
Führs H, Gotze S, Specht A, Erban A, Gallien S, Heintz D, Van Dorsselaer A, Kopka J, Braun HP, Horst WJ (2009) J Exp Bot 60(6):1663–1678
Fox TC, Guerinot ML (1998) Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Molec Biol 49:669–696
Palmer CM, Guerinot ML (2009) Nat Chem Biol 5(5):333–340
Salt DE, Baxter I, Lahner B (2008) Ionomics and the study of the plant ionome. In: Annual review of plant biology vol. 59. Annual Reviews, Palo Alto, pp 709–733.
Schaller J, Brackhage C, Dudel E (2012) Environ Exp Bot 77(3):283–287
Torre M, Rodriguez AR, Sauracalixto F (1992) J Agric Food Chem 40(10):1762–1766
Liang YC, Sun WC, Zhu YG, Christie P (2007) Environ Pollut 147(2):422–428
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brackhage, C., Schaller, J., Bäucker, E. et al. Silicon Availability Affects the Stoichiometry and Content of Calcium and Micro Nutrients in the Leaves of Common Reed. Silicon 5, 199–204 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-013-9145-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-013-9145-3