Abstract
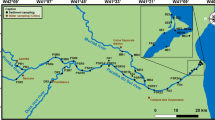
In order to understand the importance of amorphous silica (ASi) in transport of bio-reactive Si from catchment areas to the seas in northern anthropogenically influenced catchments, we investigated the seasonal evolution of ASi concentrations and load patterns together with environmental variables along the Vantaa River estuary in southern Finland during one year. A clear seasonal variation was observed in the ASi dynamics of the river with highest loads during spring, when 79% of the yearly ASi load was discharged. The main reason for this appeared to be the high discharge of the river and concomitant high load of ASi. About 38% of the annual bio-reactive Si load of the river consisted of ASi. The ASi concentration in the river varied from 11 to 192 \(\upmu \)mol L. About 3% of the ASi load accumulated in the sediments of the estuary. The role of ASi in the riverine transport of bio-reactive can be very important in northern agricultural catchments and phytoliths probably play a significant role in the transport of ASi from catchment areas to the sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reynolds C (1980) The ecology of freshwater phytoplankton. Cambridge U. Press, Cambridge
Conley DJ, Malone TC (1992) Annual cycle of dissolved silicate in Chesapeake Bay implications for the production and fate of phytoplankton biomass. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 81:121–128
Brzezinski MA, Villareal TA, Lipschultz F (1998) Silica production and the contribution of diatoms to new and primary production in the central North Pacific. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 167:89–104
Leynaert A, Tréguer P, Lancelot C (2001) Silicic acid limitation of Equatorial Pacific diatom populations: evidence from 32Si kinetic experiments. Deep-Sea Res 48:639–660
Smayda T (1990) Novel and nuisance phytoplankton blooms in the sea: evidence for a global epidemic. In: Granéli E, Sundström B, Edler L, Anderson DM (eds) Toxic Marine Phytoplankton
Humborg C, Conley D, Rahm L, Wulff F, Cociasu A, Ittekkot V (2000) Silicon retention in river basins: far-reaching effects on biogeochemistry and aquatic food webs in coastal marine environments. Ambio 29:45–50
Smetacek V (1980) The supply of food to the benthos. In: Farsham M (ed) Flows of energy and material in marine ecosystems. Theory and practice. NATO conference series IV, Marine Sciences. Plenum Press, N.Y., London
Sommer U, Gliwicz ZM, Lampert W, Duncan, A, (1986) The PEG-model of seasonal succession of planktonic events in fresh waters. Arch Hydrobiol 106:433–471
Passow U, Alldredge AL, Logan BE (1994) The role of particulate carbohydrate exudates in the flocculation of diatom blooms. Deep-Sea Res 41:335–357
Tréguer P, Pondaven P (2000). Global change. Silica control of carbon dioxide. Nature 406:358–359
Tréguer P, Nelson DM, Van Bennekom AJ, DeMaster DJ, Leynaert A, Quéguiner B (1995) The silica balance in the world ocean – a reestimate. Science 268:375–379
Rabosky DL, Sorhannus U (2009) Diversity dynamics of marine planktonic diatoms across the Cenozoic. Nature 457:183–186
Smis A, Van Damme S, Struyf E, Clymans W, Van Wesemael B, Frot E, Vandevenne F, Van Hoestenberghe T, Govers G, Meire P (2011) A trade-off between dissolved and amorphous silica transport during peak flow events (Scheldt river basin, Belgium): impacts of precipitation intensity on terrestrial Si dynamics in strongly cultivated catchments. Biogeochem 106:475–487
Bluth GJS, Kump LR (1994) Lithologic and climatologic controls of river chemistry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:2341–2359
Conley DJ, Schelske C, Stoermer E (1993) Modification of the biogeochemical cycle of silica with eutrophication. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 101:179–192
Rahm L, Conley D, Sandén P, Wulff F, Stålnacke, P (1996) Time series analysis of nutrient inputs to the Baltic Sea and changing DSi:DIN ratios. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 130:221–228
Conley DJ, Stålnacke P, Pitkänen H, Wilander A (2000) The transport and retention of dissolved silicate in rivers from Sweden and Finland. Limnol Oceanogr 45:1850–1853
Garnier, J, Leporcq B, Sanchez N, Philippon X (1999) Biogeochemical mass-balances (C, N, P, Si) in three large reservoirs of the Seine Basin (France). Biogeochem 47:119–146
Humborg C, Blomqvist S, Avsan E, Bergensund Y, Smedberg E, Brink J, Morth CM (2002) Hydrological alterations with river damming in northern Sweden: implications for weathering and river biogeochemistry. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 16:1039
Papush L, Danielsson A (2006) Silicon in the marine environment: dissolved silica trends in the Baltic Sea. Est Coast Sci 67:53–66
Danielsson A (2008) Alterations in nutrient limitations – scenarios of a changing Baltic Sea. J Mar Syst 73:263–283
Spilling K, Tamminen T, Andersen T, Kremp A (2010) Nutrient kinetics modeled from time series of substrate depletion and growth: dissolved silicate uptake of Baltic Sea spring diatoms. Mar Biol 157:427–436
Tyrrell T, Schneider B, Charalampopoulou A, Riebesell U (2008) Coccolithophores and calcite saturation state in the Baltic and Black Seas. Biogeosci Disc 5:485–494
Conley DJ, Humborg C, Smedberg E, Rahm L, Papush L, Danielsson A, Clarke A, Pastuszak M, Aigars J, Ciuffa D, Morth C (2008) Past, present and future state of the biogeochemical Si cycle in the Baltic Sea. J Mar Syst 73:338–346
Conley DJ, Likens GE, Buso D, Saccone L, Bailey SW, Johnson C (2008) Deforestation causes increased dissolved silicate losses in the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest. Glob Chang Biol 14:2548–2554
Humborg C, Pastuszak M, Aigars J, Siegmund H, Morth CM, Ittekkot V (2006) Decreased silica land-sea fluxes through damming in the Baltic Sea catchment: significance of particle trapping and hydrological alterations. Biogeochem 77:265–281
Humborg C, Smedberg E, Blomqvist S, Mörth K-M, Brink J, Rahm L, Danielsson Å, Sahlberg J (2004) Nutrient variations in boreal and subarctic Swedish rivers: landscape control of land-sea fluxes. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1871–1883
Conley DJ (1997) Riverine contribution of biogenic silica to the oceanic silica budget. Limnol Oceanogr 42:774–777
Alexandre A, Meunier J-D, Colin F, Koud J-M (1997) Plant impact on the biogeochemical cycle of silicon and related weathering processes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:677–682
Hurd DC (1983) Physical and chemical properties of siliceous skeletons. In: Aston SR (ed) Silicon geochemistry and biogeochemistry
Struyf E, Smis A, Van Damme S, Meire P, Conley DJ (2009) The global biogeochemical silica cycle. Silicon 1:207–213
Saccone L, Conley DJ, Koning E, Sauer D, Sommer M, Kaczorek D, Blecker SW, Kelly EF (2007) Assessing the extraction and quantification of amorphous silica in soils of forest and grassland ecosystems. Eur J Soil Sci 58:1446–1446
Sauer D (2006) Review of methodologies for extracting plant-available and amorphous Si from soils and aquatic sediments. Biogeochem 80:89–108
Piperno D (2006) Phytoliths: a comprehensive guide for archaeologists and paleoecologists. AltaMira Press, Lanham MD
Smithson F (1956) Plant opal in soil. Nature 178:107–107
Clarke J (2003) The occurrence and significance of biogenic opal in the regolith. Earth Sci Rev 60:175–194
Cary L, Alexandre A, Meunier J, Boeglin J, Braun J (2005) Contribution of phytoliths to the suspended load of biogenic silica in the Nyong basin rivers (Cameroon). Biogeochem 74:101–114
Fabres J, Tesi T, Velez J, Batista F, Lee C, Calafat A, Heussner S, Palanques A, Miserocchi S (2008) Seasonal and event-controlled export of organic matter from the shelf towards the Gulf of Lions continental slope. Cont Shelf Res 28:1971–1983
Gouze E, Raimbault P, Garcia N, Bernard G, Picon P (2008) Nutrient and suspended matter discharge by tributaries into the Berre Lagoon (France): the contribution of flood events to the matter budget. Compt Rend Geosci 340:233–244
Woodward J, Foster IDL (1997) Erosion and suspended sediment transfer in river catchments: environment controls, processes and problems. Geography 357:353–376
Walling DE (1999) Linking land use, erosion and sediment yields in river basins. Hydrobiol 410:223–240
Struyf E, Smis A, Van Damme S, Garnier J, Govers G, Van Wesemael B, Conley D J, Batelaan O, Frot E, Clymans W, Vandevenne F, Lancelot C, Goos P, Meire P (2010) Historical land use change has lowered terrestrial silica mobilization. Nat Commun 1:129
Soininen J, Könönen K (2004) Comparative study of monitoring South-Finnish rivers and streams using macroinvertebrate and benthic diatom community structure. Aquat Ecol 38:63–75
Werner D (1977) The biology of diatoms. In: Burnett JH, Baker HG, Beevers H, Whatley FR (eds) Botanical monographs, vol 13
Morisawa M (1968) Streams: their dynamics and morphology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Soininen J (2004) Assessing the current related heterogeneity and diversity patterns of benthic diatom communities in a turbid and a clear water river. Aquat Ecol 38:495–501
Grady AE, Scanlon TM, Galloway, JN (2007) Declines in dissolved silica concentrations in western Virginia streams (1988–2003): Gypsy moth defoliation stimulates diatoms? J Geophys Res 112:G01009
Pastuszak M, Conley DJ, Humborg C, Witek Z, Sitek S (2008) Silicon dynamics in the Oder estuary, Baltic Sea. J Marine Syst 2008:250–262
Conley DJ, Johnstone RW (1995) Biogeochemistry of N, P and Si in Baltic Sea sediments: response to a simulated deposition of a spring diatom bloom. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 122:265–276
Nelson DM, Dortch Q (1996) Silicic acid depletion and silicon limitation in the plume of the Mississippi River: evidence from kinetic studies in spring and summer. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 122136:163–178
DeMaster DJ, Smith Jr WO, Nelson DM, Aller JY (1996) Biogeochemical processes in Amazon shelf waters: chemical distributions and uptake rates of silicon, carbon and nitrogen. Cont Shelf Res 16:617–643
Ragueneau O, Lancelot C, Egorov V, Vervlimmeren J, Cociasu A, Deliat G, Krastev A, Daoud N, Rousseau V, Popovitchev V, Brion N, Popa L, Cauwet G (2002) Biogeochemical transformations of inorganic nutrients in the mixing zone between the Danube River and the north-western Black Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54:321–336
Chou L, Wollast R (2006) Estuarine silicon dynamics. In: Ittekkot V, Unger D, Humborg C, An TC (ed) The silicon cycle, human perturbations and impacts on aquatic systems
Anderson GF (1986) Silica, diatoms and a freshwater productivity maximum in Atlantic Coastal Plain estuaries, Chesapeake Bay. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 22:183–197
Michalopoulos P, Aller RC (2004) Early diagenesis of biogenic silica in the Amazon delta: alteration, authigenic clay formation and storage. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:1061–1085
Michalopoulos P, Aller RC, Reeded RJ (2000) Conversion of diatoms to clays during early diagenesis in tropical, continental shelf muds. Geology 28:1095
Michalopoulos P, RC Aller (1995) Rapid clay mineral formation in Amazon delta sediments: reverse weathering and oceanic elemental cycles. Science 270:614–617
CLC (2000) Corine Land Cover 2000 seamless vector database, European Union. http://www.eea.europa.eu/dataand-maps/data/ds_resolveuid/89364B1A-548D-4CE1-84A4-D6C5AD4712C0. Accessed 7 Oct 2011
Tikkanen M (1989) Geomorphology of the Vantaanjoki drainage basin, southern Finland. Fennia 167:19–72
Ragueneau O, Savoye N, Del Amo Y, Cotton J, Tardiveau B, Leynaert A (2005) A new method for the measurement of biogenic silica in suspended matter of coastal waters: using Si:Al ratios to correct for the mineral interference. Cont Shelf Res 25:697–710
DeMaster D (1981) The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine environment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:1715–1732
Hughes HJ Sondag F, Cocquyt C, Laraque A, Pandi A, André L, Cardinal D (2011) Effect of seasonal biogenic silica variations on dissolved silicon fluxes and isotopic signatures in the Congo River. Limnol Oceanogr 56:551–561
Carbonnel V, Lionard M, Muylaert K, Chou L (2009) Dynamics of dissolved and biogenic silica in the freshwater reaches of a macrotidal estuary (The Scheldt, Belgium). Biogeochem 96: 49–72
Mullin J, Riley J (1955) The colometric determination of silicate with special reference to sea and natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 12:162–176
Verta M, Mattila T, Mehtonen J, Silvo K, Mannio J, Londesborough S, Väisänen S, Lahti K (2009) SOCOPSE, source control of priority substances in Europe. Report on Vantaa River case study, pp 1–43
Schwertmann U (1964) Differenzierung der Eisenoxide des Bodens durch Extraktion mit Ammoniumoxalat-Lösung, Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernährung, Düngung. Bodenkunde 105:194–202
Jackson ML, Lim HC, Zelazny LW (1986) Oxides, hydroxides, and aluminosilicates. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 1, 2nd ed
Cornelis J Titeux H, Ranger J, Delvaux B (2011) Identification and distribution of the readily soluble silicon pool in a temperate forest soil below three distinct tree species. Plant Soil 342:36–369
Utermöhl H (1958) Zur Vervollkomnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton-Metodik. Mitt in Ver Limnol 9:1–38
Tikkanen T, Willen T (1992) Växtplanktonflora. Naturvårdsverket, Solna
Lentfer CJ, Boyd WE (1999) An assessment of techniques for the deflocculation and removal of clays from sediments used in phytolith analysis. J Archaeol Sci 26:31–44
Korhonen J (2007) Suomen vesistöjen virtaaman ja vedenkorkeuden vaihtelut (Discharge and water level variations in lakes and rivers in Finland: in Finnish with English abstract). Finnish Environ 45:1–120
Smayda TJ (1980) Phytoplankton species succession. In: Morris I (ed) The physiological ecology of phytoplankton. Studies in ecology, vol 7. Blackwell, Oxford
Gasiūnaitė ZR, Cardoso AC, Heiskanen A-S, Henriksen P, Kauppila P, Olenina I, Pilkaitytė R, Purina I, Razinkovas A, Sagert S, Schubert H, Wasmund N (2005) Seasonality of coastal phytoplankton in the Baltic Sea: influence of salinity and eutrophication. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 65:239–252
Spilling K (2007) On the ecology of cold-water phytoplankton in the Baltic Sea. W & A de Nottbeck Foundation Sci Rep 31:1–59
Edwards AMC, Liss PS (1973) Evidence for buffering of dissolved silicon in fresh waters. Nature 243:341–342
Sigleo AC, Frick WE (2007) Seasonal variations in river discharge and nutrient export to a Northeastern Pacific estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 73:368–378
Schemel LE (1986) Chemical variability in the Sacramento River and in Northern San Francisco Bay. Estuaries 9:270–283
Loucaides S, Cahoon LB, Henry EJ (2007) Effect of watershed impervious cover on dissolved silica loading in storm flow. J Am Water Resour Assoc 43:841–849
Heiskanen AS (1996) Distribution and sinking rates of phytoplankton, detritus, and particulate biogenic silica in the Laptev Sea and Lena River (Arctic Siberia). Mar Chem 53:229–245
Alajärvi E, Horppila J, Keskitalo J, Lehtovaara A, Malinen T, Olin M, Pekkarinen M, Rask M, Ruuhijärvi J, Sammalkorpi I, Savola P, Tallberg P, Taponen T, Villa L (2002) Rehevöityneiden järvien hoitokalastuksen vaikutukset. In: Olin M, Ruuhijärvi J (eds) Kala- ja Riistaraportteja nro 262 (Finnish Game and Fisheries Research Institute reports 262)
Claquin P, Leynaert A, Sferratore A, Garnier J, Ragueneau O (2006) Physiological ecology of diatoms along the river-sea continuum. In: Ittekkot V, Unger D, Humborg C, Tac An N (eds) The silicon cycle: human perturbations and impacts on aquatic systems
Stanley KG, Robertson EC, d’Entremont R, Hubbard T, Kujath M (2011) Phytolith assaying using a micron-scale electrokinetic sorting ring. Archaeol Anthropol Sci 3:309–323
Watteau F, Villemin G (2001) Ultrastructural study of the biogeochemical cycle of silicon in the soil and litter of a temperate forest. Eur J Soil Sci 52:385–396
Sommer M, Kaczorek D, Kuzyakov Y, Breuer J (2006) Silicon pools and fluxes in soils and landscapes—a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 169:310–329
Siipola V, Mäntyniemi S, Lehtimäki M, Tallberg P (2012) Separating biogenic and adsorbed pools of silicon in sediments using Bayesian inference. Silicon. doi:10.1007/s12633-012-9120-4
White RE (2006) Principles and practice of soil science: the soil as a natural resource, 4th ed. Wiley-Blackwell, New York
Blanco-Canqui H, Lal R (2008) Principles of soil conservation and management. Springer, Berlin
Blecker SW, McCulley RL, Chadwick OA, Kelly EF (2006) Biologic cycling of silica across a grassland bioclimosequence. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 20:GB3023
Puustinen M (1999) Viljelymenetelmien vaikutus pintaeroosion ja ravinteiden huuhtoutumiseen (Effect of soil tillage on surface erosion and nutrient transport: in Finnish with English abstract). Suomen ympäristö 285, Suomen ympäristökeskus (The Finnish Environment 285, Finnish Environment Institute), Helsinki
Puustinen M, Tattari S, Koskiaho J, Linjama J (2007) Influence of seasonal and annual hydrological variations on erosion and phosphorus transport from arable areas in Finland. Soil Till Res 93:44–55
Conley DJ (2002) Terrestrial ecosystems and the global biogeochemical silica cycle. Global Biogeochem Cycles 16:1121
Farmer VC, Delbos E, Miller JD (2005) The role of phytolith formation and dissolution in controlling concentrations of silica in soil solutions and streams. Geoderma 127:71–79
Ahtiainen M (1992) The effects of forest clear-cutting and scarification on the water quality of small brooks. Hydro Biol 243–244:465–473
Vuorenmaa J, Rekolainen S, Lepistö L, Kenttämies K, Kauppila P (2002) Losses of nitrogen and phosphorus from agricultural and forest areas in Finland during the 1980s and 1990s. Environ Monit Assess 76:213–248
Arthur MA, Coltharp GB, Brown DL (1998) Effects of best management practices on forest streamwater quality in Eastern Kentucky. J Am Water Resour Assoc 34:481–495
Kubin E, Ylitolonen A, Välitalo J, Eskelinen J (2000) Prevention of nutrient leaching from a forest regeneration area using overland flow fields. In: Haigh M, Krecek J (eds) Environmental reconstruction in headwater areas
Lacey ST (2000) Runoff and sediment attenuation by undisturbed and lightly disturbed forest buffers. Water Air Soil Pollut 122:121–138
Syversen N, Borch H (2005) Retention of soil particle fractions and phosphorus in cold climate buffer zones. Ecol Eng 25:382–394
Uusi-Kämppä, J (2005) Phosphorus purification in buffer zones in cold climates. Ecol Eng 24:491–502
Pellikka K, Räsänen M, Viljamaa H (2007) Kasviplanktonin suhde ympäristömuuttujiin Helsingin ja Espoon merialueella vuosina 1969–2003 (The relationship between phytoplankton and environmental variables in the sea area outside Helsinki and Espoo in 1969–2003: in Finnish with English abstract). Helsingin kaupungin ympäristökeskuksen julkaisuja 5/2007 (Publications by City of Helsinki Environment Centre 5/2007)
Loucaides S, Van Cappellen P, Behrends T (2008) Dissolution of biogenic silica from land to ocean: role of salinity and pH. Limnol Oceanogr 53:1614–1621
Hamm CE (2002) Interactive aggregation and sedimentation of diatoms and clay-sized lithogenic material. Limnol Oceanogr 47:1790–1795
Tallberg P, Räike A, Lukkari K, Leivuori M, Lehtoranta J, Pitkänen H (2011) Horizontal and vertical distribution of biogenic silica in coastal and profundal sediments from the North-eastern Baltic Sea (Gulf of Finland). Boreal Environ Res 17 (in press)
Lewin J (1961) The dissolution of silica from diatom walls. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 21:182–198
Rippey B (1983) A laboratory study of the silicon release process from a lake sediment (Lough Neagh, Northern Ireland). Arch Hydrobiol 96:417–433
Fraysse F, Pokrovsky O, Schott J, Meunier J (2009) Surface chemistry and reactivity of plant phytoliths in aqueous solutions. Chem Geol 258:197–206
Barker P, Fontes J-C, Gasse F, Druart J-C (1994) Experimental dissolution of diatom silica in concentrated salt solutions and implications for paleoenvironmental reconstruction. Limnol Oceanogr 39:99–110
Bidle K, Azam F (1999) Accelerated dissolution of diatom silica by marine bacterial assemblages. Nature 397:508–512
Conley DJ, Schelske CL (1993) Potential role of sponge spicules in influencing the silicon biogeochemistry of Florida Lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:296–302
Hallmark C, Wilding L, Smeck N (1982) Silicon. Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties. Agron Monogr 9:263–273
Aston S (1983) Natural water and atmospheric chemistry of silicon. In: Aston S (ed) Silicon geochemistry and biogeochemistry. Academic Press, Inc, London
Brinkman A (1993) A double-layer model for ion adsorption onto metal oxides, applied to experimental data and to natural sediments of Lake Veluwe, The Netherlands. Hydrobiol 253:31–45
Aston S (1980) Nutrients, dissolved gases and general biogeochemistry in estuaries. In: Olausson ECI (ed) Chemistry and biogeochemistry of estuaries
Shen Z, Zhou S, Pei S (2008) Transfer and transport of phosphorus and silica in the turbidity maximum zone of the Changjiang estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 78:481–492
Gehlen M (2002) The role of adsorption-desorption surface reactions in controlling interstitial Si(OH)4 concentrations and enhancing Si(OH)4 turn-over in shallow shelf seas. Cont Shelf Res 22:1529–1529
Loucaides S, Michalopoulos P, Presti M, Koning E, Behrends T, Van Cappellen P (2010) Seawater-mediated interactions between diatomaceous silica and terrigenous sediments: results from long-term incubation experiments. Chem Geol 270:68–79
Presti M, Michalopoulos P (2008) Estimating the contribution of the authigenic mineral component to the long-term reactive silica accumulation on the western shelf of the Mississippi River Delta. Cont Shelf Res 28:823–838
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehtimäki, M., Tallberg, P. & Siipola, V. Seasonal Dynamics of Amorphous Silica in Vantaa River Estuary. Silicon 5, 35–51 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-012-9126-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-012-9126-y