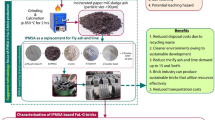
Abstract
Red mud is a type of highly alkaline waste residue produced in the process of alumina smelting by the Bayer process. Based on the idea of medium calcium content, solid wastes such as red mud and fly ash were used to prepare non-burnt bricks; and the mass ratio of CaO/SiO2 was selected in the range of 0.88–1.42. Mechanical properties and durability were investigated with a compressive strength test. X-ray diffractometry (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) techniques were used to characterize the hydration characteristic. The environmental performance was analyzed by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP). The results indicated that the mechanical properties and the durability were optimal when the mass ratio of CaO/SiO2 was 1.23. The hydration products were mostly C-S-H gel, ettringite, Na4Ca(Si10Al16)O32·12H2O and Ca3Al2(SiO4)(OH)8. They were responsible for the strength development, and the CaO/SiO2 mass ratio of 1.23 had the best polymerized structure. The results of an environmental performance test showed that the heavy metals in the raw materials were well-solidified in the brick. Therefore, this paper provides an effective solution for use of solid wastes in building material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.P. Wang, T.C. Sun, J. Kou, Z.C. Li, and Y. Tian, Feasibility of co-reduction roasting of a saprolitic laterite ore and waste red mud, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 25(2018), No. 6, p. 591.
X.L. Nan, T.A. Zhang, Y. Liu, and Z.H. Dou, Analysis of comprehensive utilization of red mud in China, Chin. J. Process Eng., 10(2010), No. 1, p. 264.
X.B. Zhu, W. Li, and X.M. Guan, Research status of comprehensive utilization of red mud, Multipurpose Util. Miner. Resour., 1(2016), p. 7.
S.H. Liu, X.M. Guan, C.H. Feng, and M. Qiu, Progress on red mud stockpiling and utilization, Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc., 34(2015), No. 8, p. 2194.
N. Zhang, H.X. Li, and X.M. Liu, Hydration kinetics of cementitious materials composed of red mud and coal gangue, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 23(2016), No. 10, p. 1215.
J.K. Yang, J. Hou, B. Qi, W. Liu, H.S. Guo, and B. Xiao, Pilot-scale production and industrialization of the no-fired bricks from red mud in aluminium industry, Environ. Eng., 24(2006), No. 4, p. 52.
F. Yang, T. Han, X.Z. Jin, H.Q. Wang, and X.T. Yang, Formula of baking-free bricks made of red mud and fly ash, Res. Appl. Build. Mater., 2(2015), No. 1, p. 1.
A.K. Mandal, H.R. Verma, and O.P. Sinha, Utilization of aluminum plant’s waste for production of insulation bricks, J. Cleaner Prod., 162(2017), p. 949.
S.W. Zhang, C.J. Liu, Z.K. Luan, X.J. Peng, and Y.Q. Wang, Preparation of Fe modified red mud and its adsorption characteristics of arsenate, Acta Scientiate Circumstantiae, 27(2007), No. 12, p. 1972.
W.X. Hu, T.G. Zhang, and X.Z. Zhang, Study on the mixing ratio and mechanical properties of carbide fly ash new environment-friendly unfired brick, New Chem. Mater., 39(2011), No. 8, p. 84.
P. Chindaprasirt, C. Jaturapitakkulb, and T. Sinsiric, Effect of fly ash fineness on microstructure of blended cement paste, Constr. Build. Mater., 21(2007), No. 7, p. 1534.
Z. Wang, Q.C. Guo, X.H. Jiang, P.K. Hou, and J.S. Qian, Sulphate activating of electrolytic manganese residue to fly ash, Non-Met. Mines, 34(2011), No. 4, p. 5.
Z.Y. Xu, X. Wang, B. Jin, and L.S. Yang, Study on mechanical properties of desulphurized gypsum-fly ash brick, Non-Met. Mines, 41(2018), No. 6, p. 89.
S.J. Gao, W. Ni, L.P. Zhu, Z.J. Wang, and J.J. Wang, Effect of gypsum on strength performance of cemented backfilling materials of red mud-slag system, J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.), 44(2013), No. 6, p. 2259.
N. Zhang, X.M. Liu, and H.H. Sun, Hydration characteristics of intermediate-calcium based cementitious materials from red mud and coal gangue, Chin. J. Mater. Res., 28(2014), No. 5, p. 325.
P. Zhang, W.S. Zhang, J.X. Wei, J.Y. Ye, W. Zhu, and C. Lei, Influence of curing conditions on the strength, hydration properties of geopolymer synthesized from red mud and slag, New Build. Mater., 40(2017), No. 10, p. 1.
X.M. Liu, X.B. Zhao, H.F. Yin, J.L. Chen, and N. Zhang, Intermediate-calcium based cementitious materials prepared by MSWI fly ash and other solid wastes: hydration characteristics and heavy metals solidification behavior, J. Hazard. Mater., 349(2018), p. 262.
T.C. Ling, K.H. Mo, L. Qu, J.J. Yang, and L. Guo, Mechanical strength and durability performance of autoclaved lime-saline soil brick, Constr. Build. Mater., 146(2017), p. 403.
N. Zhang, H.H. Sun, X.M. Liu, and J.X. Zhang, Early-age characteristics of red mud-coal gangue cementitious material, J. Hazard. Mater., 167(2009), p. 927.
I.G. Lodeiro, D.E. Macphee, A. Palomo, and A. Fernández-Jiménez, Effect of alkalis on fresh C-S-H gels. FTIR analysis, Cem. Concr. Res., 39(2009), No. 3, p. 147.
I. Garcia-Lodeiro, A. Palomo, A. Fernández-Jiménez, and D.E. Macphee, Compatibility studies between N-A-S-H and C-A-S-H gels. Study in the ternary diagram Na2O-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O, Cem. Concr. Res., 41(2011), No. 9, p. 923.
Z.H. Pan, L. Cheng, Y.N. Lu, and N.L. Yang, Hydration products of alkali-activated slag-red mud cementitious material, Cem. Concr. Res., 32(2002), No. 3, p. 357.
Y.L. Zhang, X.M. Liu, Y.T. Xu, B.W. Tang, Y.G. Wang and E. Mukiza, Preparation and characterization of cement treated road base material utilizing electrolytic manganese residue, J. Cleaner Prod., 232(2019), p. 980.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51574024), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-TP-18-005B1), and Technological Research and Development Programs of China Railways Corporation (No. 2017G006-J).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Yt., Yang, B., Liu, Xm. et al. Investigation of the medium calcium based non-burnt brick made by red mud and fly ash: durability and hydration characteristics. Int J Miner Metall Mater 26, 983–991 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1814-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1814-9