Abstract
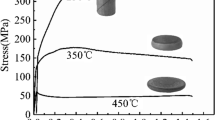
In this study, cyclic expansion extrusion (CEE), as a relatively new severe plastic deformation (SPD) process, is applied to a rare earth (RE) containing Mg alloy WE43. The effects of the processing temperature and the number of passes are also investigated. The results showed that dynamic recrystallization (DRX) occurred after CEE processing at 400°C, and a bimodal structure with ultrafine DRXed grains surrounded the unrecrystallized grains. However, the DRX at 330°C was retarded because of the existence of RE elements. The tensile tests showed that a simultaneous increase in the strength and the ductility of WE43 is obtained after CEE processing at 400°C via two passes. Furthermore, the highest ultimate tensile strength of 440 MPa was achieved after the second pass of CEE at 330°C, and the highest ductility of 21% was attained after the second pass of CEE at 400°C. The microhardness measurements showed that the hardness increased from HV 80 to HV 114 and HV 98 after two passes of CEE processing at 330 and 400°C, respectively. In conclusion, increasing the processing passes could increase the mechanical properties and the volume fraction of the recrystallized grains. Moreover, increasing the temperature reduced the strength and the microhardness even if the elongation increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ma, K. Zhang, X.G. Li, Y.J. Li, G.L. Shi, and J.W. Yuan, Influence of solution and aging on the microstructures and mechanical properties of complex deformed WE93 alloy, Mater. Des., 51(2013), p. 73.
W.Z. Chen, X. Wang, L.X. Hu, and E. Wang, Fabrication of ZK60 magnesium alloy thin sheets with improved ductility by cold rolling and annealing treatment, Mater. Des., 40(2012), p. 319.
M. Mabuchi, T. Asahina, H. Iwasaki, and K. Higashi, Experimental investigation of superplastic behaviour in magnesium alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol., 13(1997), No. 10, p. 825.
W. Püschl, Models for dislocation cross-slip in close-packed crystal structures: a critical review, Prog. Mater. Sci., 47(2002), No. 4, p. 415.
B. Smola, L. Joska, V. Březina, I. Stulíková, and F. Hnilica, Microstructure, corrosion resistance and cytocompatibility of Mg–5Y–4rare earth–0.5 Zr (WE54) alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 32(2012), No. 4, p. 659.
H. Windhagen, K. Radtke, A. Weizbauer, J. Diekmann, Y. Noll, U. Kreimeyer, R. Schavan, C. Stukenborg-Colsman, and H. WaizyEmail, Biodegradable magnesium-based screw clinically equivalent to titanium screw in hallux valgus surgery: short term results of the first prospective, randomized, controlled clinical pilot study, Biomed. Eng. Online, 12(2013), No. 1, p. 62.
B. O’Brien and W. Carroll, The evolution of cardiovascular stent materials and surfaces in response to clinical drivers: a review, Acta Biomater., 5(2009), No. 4, p. 945.
V. Neubert, I. Stulíková, B. Smola, B.L. Mordike, M. Vlach, A. Bakkar, and J. Pelcová, Thermal stability and corrosion behaviour of Mg–Y–Nd and Mg–Tb–Nd alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 462(2007), No. 1-2, p. 329.
C. Xu, K.N. Xia, and T.G. Langdon, Processing of a magnesium alloy by equal-channel angular pressing using a back-pressure, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2009), No. 1-2, p. 205.
A.P. Zhilyaev and T.G. Langdon, Using high-pressure torsion for metal processing: fundamentals and applications, Prog. Mater. Sci., 53(2008), No. 6, p. 893.
G. Faraji, M. Mashhadi, and H.S. Kim, Microstructure inhomogeneity in ultra-fine grained bulk AZ91 produced by accumulative back extrusion (ABE), Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528(2011), No. 13-14, p. 4312.
G. Faraji, M.M. Mashhadi, and H.S. Kim, Tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP) as a novel severe plastic deformation method for cylindrical tubes, Mater. Lett., 65(2011), No. 19-20, p. 3009.
J. Richert and M. Richert, A new method for unlimited deformation of metals and alloys, Aluminium, 62(1986), No. 8, p. 604.
N. Pardis, B. Talebanpour, R. Ebrahimi, and S. Zomorodian, Cyclic expansion-extrusion (CEE): a modified counterpart of cyclic extrusion-compression (CEC), Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528(2011), No. 25-26, p.7537.
M. Ensafi, G. Faraji, and H. Abdolvand, Cyclic extrusion compression angular pressing (CECAP) as a novel severe plastic deformation method for producing bulk ultrafine grained metals, Mater. Lett., 197(2017), p. 12.
G. Faraji, M.M. Mashhadi, K. Abrinia, and H.S. Kim, Deformation behavior in the tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP) as a noble SPD method for cylindrical tubes, Appl. Phys. A, 107(2012), No. 4, p. 819.
G. Faraji, P. Yavari, S. Aghdamifar, and M.M. Mashhadi, Mechanical and microstructural properties of ultra-fine grained AZ91 magnesium alloy tubes processed via multi pass tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP), J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 30(2014), No. 2, p. 134.
X. Zhang, G.Y. Yuan, and Z.Z. Wang, Mechanical properties and biocorrosion resistance of Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr alloy improved by cyclic extrusion and compression, Mater. Lett., 74(2012), p. 128.
N. Pardis, C. Chen, M. Shahbaz, R. Ebrahimi, and L.S. Toth, Development of new routes of severe plastic deformation through cyclic expansion-extrusion process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 613(2014), p. 357.
H. Sheikh and R. Ebrahimi, Investigation on texture evolution during cyclic expansion-extrusion (CEE) technique using crystal plasticity finite element modeling, J. Mater. Sci., 51(2016), No. 22, p. 10178.
N. Pardis, C. Chen, R. Ebrahimi, L.S. Toth, C.F. Gu, B. Beausir, and L. Kommel, Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of cyclic expansion-extrusion deformed pure copper, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 628(2015), p. 423.
S. Amani, G. Faraji, H.K. Mehrabadi, K. Abrinia, and H. Ghanbari, A combined method for producing high strength and ductility magnesium microtubes for biodegradable vascular stents application, J. Alloys Compd., 723(2017), p. 467.
Q.D. Wang, Y.J. Chen, M.P. Liu, J.B. Lin, and H.J. Roven, Microstructure evolution of AZ series magnesium alloys during cyclic extrusion compression, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), No. 9, p. 2265.
S.W. Xu, S. Kamado, N. Matsumoto, T. Honma, and Y. Kojima, Recrystallization mechanism of as-cast AZ91 magnesium alloy during hot compressive deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2009), No. 1-2, p. 52.
F.A. Slooff, J.S. Dzwonczyk, J. Zhou, J. Duszczyk, and L. Katgerman, Hot workability analysis of extruded AZ magnesium alloys with processing maps, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), No. 3, p. 735.
S.A. Farzadfar, É. Martin, M. Sanjari, E. Essadiqi, and S. Yue, Texture weakening and static recrystallization in rolled Mg–2.9 Y and Mg–2.9 Zn solid solution alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 47(2012), No. 14, p. 5488.
I.H. Jung, M. Sanjari, J. Kim, and S. Yue, Role of RE in the deformation and recrystallization of Mg alloy and a new alloy design concept for Mg–RE alloys, Scripta Mater., 102(2015), p. 1.
D. Griffiths, Explaining texture weakening and improved formability in magnesium rare earth alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol., 31(2015), No. 1, p. 10.
N. Stanford, The effect of rare earth elements on the behaviour of magnesium-based alloys: Part 2—recrystallisation and texture development, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 565(2013), p. 469.
W. Wlake, E. Hadasik, J. Przondziono, D. Kuc, I. Bednarczyk, and G. Niewiński, Plasticity and corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy WE43, Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng., 51(2011), No. 1, p. 16.
H. Beladi and M. Barnett, Influence of aging pre-treatment on the compressive deformation of WE54 alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 452-453(2007), p. 306.
S.A. Farzadfar, M. Sanjari, I.H. Jung, E. Essadiqi, and S. Yue, Role of yttrium in the microstructure and texture evolution of Mg, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528(2011), No. 22-23, p. 6742.
S.A. Farzadfar, É. Martin, M. Sanjari, E. Essadiqi, M.A. Wells, and S. Yue, On the deformation, recrystallization and texture of hot-rolled Mg–2.9Y and Mg–2.9Zn solid solution alloys-A comparative study, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 534(2012), Suppl. C, p. 209.
W. Guo, Q.D. Wang, B. Ye, M.P. Liu, T. Peng, X.T. Liu, and H. Zhou, Enhanced microstructure homogeneity and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy by repetitive upsetting, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 540(2012), p. 115.
S.K. Panigrahi, W. Yuan, R.S. Mishra, R. DeLorme, B. Davis, R.A. Howell, and K. Cho, A study on the combined effect of forging and aging in Mg–Y–RE alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 530(2011), p. 28.
J. She, F.S. Pan, W. Guo, A.T. Tang, Z.Y. Gao, S.Q. Luo, K. Song, Z.W. Yu, and M. Rashad, Effect of high Mn content on development of ultra-fine grain extruded magnesium alloy, Mater. Des., 90(2016), p. 7.
S. Amani, G. Faraji, and K. Abrinia, Microstructure and hardness inhomogeneity of fine-grained AM60 magnesium alloy subjected to cyclic expansion extrusion (CEE), J. Manuf. Processes, 28(2017), Part 1, p. 197.
F. Akbaripanah, F. Fereshteh-Saniee, R. Mahmudi, and H.K. Kim, Microstructural homogeneity, texture, tensile and shear behavior of AM60 magnesium alloy produced by extrusion and equal channel angular pressing, Mater. Des., 43(2013), p. 31.
Y. Estrin, L.S. Toth, A. Molinari, and Y. Bréchet, A dislocation-based model for all hardening stages in large strain deformation, Acta Mater., 46(1998), No. 15, p. 5509.
Q. Chen, D.Y. Shu, C.K. Hu, Z.D. Zhao, and B.G. Yuan, Grain refinement in an as-cast AZ61 magnesium alloy processed by multi-axial forging under the multitemperature processing procedure, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 541(2012), p. 98.
P. Minárik, R. Král, J. Čížek, and F. Chmelík, Effect of different c/a ratio on the microstructure and mechanical properties in magnesium alloys processed by ECAP, Acta Mater., 107(2016), p. 83.
H. Huang, Z.B. Tang, Y. Tian, G.Z. Jia, J.L. Niu, H. Zhang, J. Pei, and G.Y. Yuan, Effects of cyclic extrusion and compression parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–1.50 Zn–0.25 Gd alloy, Mater. Des., 86(2015), p. 788.
E. Orawan, The symposium on internal stresses in metals and alloys, Institute of Metals, London, 1948, p. 451.
M.F. Ashby, The theory of the critical shear stress and work hardening of dispersion-hardened crystals, Philos. Mag.: J. Theor. Exp. Appl. Phys., 14(1966), No. 132, p. 1157.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amani, S., Faraji, G. Recrystallization and mechanical properties of WE43 magnesium alloy processed via cyclic expansion extrusion. Int J Miner Metall Mater 25, 672–681 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-018-1614-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-018-1614-7