Abstract
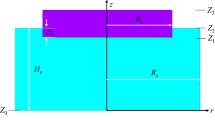
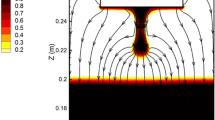
A mathematical model was developed to describe the interaction of multiple physical fields in a slag bath during electroslag remelting (ESR) process with a current-conductive mould. The distributions of current density, magnetic induction intensity, electromagnetic force, Joule heating, fluid flow and temperature were simulated. The model was verified by temperature measurements during remelting 12CrMoVG steel with a slag of 50wt%–70wt% CaF2, 20wt%-30wt% CaO, 10wt%–20wt% Al2O3, and ≤10wt% SiO2 in a 600 mm diameter current-conductive mould. There is a good agreement between the calculated temperature results and the measured data in the slag bath. The calculated results show that the maximum values of current density, electromagnetic force and Joule heating are in the region between the corner electrodes and the conductivity element. The characteristics of current density distribution, magnetic induction intensity, electromagnetic force, Joule heating, velocity patterns and temperature profiles in the slag bath during ESR process with current-conductive mould were analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- G :
-
Gravitational acceleration, m·s−2
- H :
-
Magnetic field intensity, A·m−1
- \(\hat H\) :
-
Complex amplitude of H
- \(\hat H_r\), \(\hat H_\theta\), \(\hat H_z\) :
-
Magnetic field intensities in r, θ and z directions, respectively
- \(\hat I\) :
-
Complex amplitude of the total current entering the slag bath
- \(\hat I_{Ingot}\) :
-
Complex amplitude of the total current entering the ingot
- \(\hat I_{CE}\) :
-
Complex amplitude of the total current entering the conductivity element
- J :
-
Current intensity, A·m−2
- \(\hat J\) :
-
Complex amplitude of J
- R m :
-
Inside radius of the mould, m
- R e :
-
Radius of the electrode, m
- R :
-
Radial coordinate, m
- Z :
-
Axial coordinate, m
- α :
-
Angle of cone on the electrode tip, (°)
- δ :
-
Electrical conductivity, Ω−1·m−1
- ω :
-
Angular frequency of current, rad·s−1
- μ :
-
Viscosity of slag, Pa·s−1
- μ 0 :
-
Magnetic permeability, H·m−1
- μ eff :
-
Effective viscosity, Pa·s−1
- μ t :
-
Turbulent viscosity, Pa·s−1
- ρ :
-
Density, kg·m−3
- β :
-
Thermal expansivity of slag, K−1
- S k :
-
Source item of kinetic energy of turbulence
- S ɛ :
-
Source item of dissipation rate of turbulence energy
- κ :
-
Kinetic energy of turbulence
- ɛ :
-
Dissipation rate of turbulence energy
- ξ :
-
Vorticity
- ψ :
-
Stream function
- t :
-
Time, s
- C p :
-
Specific heat of slag, J·kg−1·K−1
- ν :
-
Velocity, m/s
- T :
-
Temperature, K
- λ :
-
Thermal conductivity of slag bath, W·m−1·K−1
- λ t :
-
Turbulent thermal conductivity of slag bath, W·m−1·K−1
- Q Joule :
-
Joule heat generation, W·m−3
References
H. Holzgruber, W. Holzgruber, A. Scheriau, M. Knabl, M. Kubin, J. Korp, and R. Pierer, Investigation of the implications of the current conductive mold technology with respect to the internal and surface quality of ESR ingots, [in] Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Nancy, 2011, p.57.
D. Alghisi, M. Milano, and L. Pazienza, From ESR to continuous CC-ESRR process: development in remelting technology towards better products and productivity, Metall. Ital., 97(2005), p.21.
B.E. Paton and L.B. Medovar, Improving the electroslag remelting of steel and alloys, Steel Trans., 38(2008), p.1028.
X.M. Zang, Z.H. Jiang, and T.Y. Pan, Development and investigation of electroslag continuous casting, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 14(2007), p.302.
M. Choudhary and J. Szekely, Modelling of fluid flow and heat transfer in industrial-scale ESR system, Ironmaking Steelmaking, 5(1981), p. 225.
K.M. Kelkar, J. Mok, S.V. Patankar, and A. Mitchell, Computational modeling of electroslag remelting processes, J. Phys. IV, 120(2004), p.421.
K.M. Kelkar, S.V. Patankar, and A. Mitchell, Computational modeling of the electroslag remelting (ESR) process used for the production of ingots of high-performance alloys, [in] Proceedings of the 2005 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Materials Park, OH, 2005, p.137.
A.H. Dilawari and J. Szekely, Heat transfer and fluid flow phenomena in electroslag refining, Metall. Trans. B, 9(1978), p.77.
A.H. Dilawari and J. Szekely, A mathematical model of slag and metal flow in the ESR process, Metall. Trans. B, 8(1977), p.227.
J.H. Wei and Y.L. Ren, Mathematical simulation of magnetic field in ESR system, Acta Metall. Sin., 31(1995), p.51.
J.H. Wei and Y.L. Ren, Mathematical modeling of slag flow field in ESR system, Acta Metall. Sin., 30(1994), p.481.
A. Jardy, D. Ablitzer, and J.F. Wadier, Magnetohydrodynamic and thermal behavior of electroslag remelting slags, Metall. Trans. B, 22(1991), p.111.
M. Choudhary, J. Szekely, B. I. Medovar, and Y.G. Emelyanenko, The velocity field in the molten slag region of ESR systems: a comparison of measurements in a model system with theoretical predictions, Metall. Trans. B, 13(1982), p.35.
B.E. Launder and D.B. Spading, The numerical computation of turbulent flows, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 3(1974), p.269.
A. Kharicha, W. Schütenhöer, A. Ludwig, and R. Tanzer, Multiphase modelling of the slag region in ESR Process, [in] Proceedings of the 2007 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Nancy, 2007, p.107.
A. Kharicha, A. Mackenbrock, and A. Ludwig, Selected numerical investigations on ESR process, [in]_Proceedings of the 2007 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Nancy, 2007, p.113.
B.E. Paton, B.I. Medovar, M.G. Benz, R.H. Nafziger, and L.B. Medovar, ESR for titanium: yesterday, today, tomorrow, [in] Proceedings of the 9th World Conference on Titanium, St. Petersburg, 1999, p.1385.
A.D. Patel, An analysis of electromagnetic fields in ESR, [in] Proceedings of the 2005 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Materials Park, OH, 2005, p.173.
V. Weber, A. Jardy, B. Dussoubs, D. Ablitzer, S. Rybéron, V. Schmitt, S. Hans, and H. Poisson, A comprehensive model of the electroslag remelting process: description and validation, Metall. Trans. B, 40(2009), p.271.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was financially supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No.20100471452).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Fb., Zang, Xm., Jiang, Zh. et al. Comprehensive model for a slag bath in electroslag remelting process with a current-conductive mould. Int J Miner Metall Mater 19, 303–311 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-012-0555-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-012-0555-9