Abstract
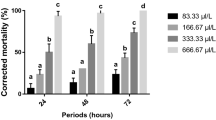
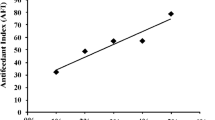
Zeugodacus cucurbitae is a major pest of cucurbit plants which in India itself is responsible for causing considerable damage to vegetables. In the present study, the effect of the secondary plant metabolite chrysin was investigated on the growth, development and oviposition behaviour of melon fruit fly. Chrysin effect on Z. cucurbitae larvae was studied by incorporating it in artificial diet at 5, 25, 125, 625 and 3125 ppm concentrations with water as a control. The larval and total developmental periods were prolonged, while percentage pupation and adult emergence of first, second and third instar larvae were inhibited with chrysin treatment. The adverse effect of chrysin was considerably greater on first instar larvae where no adults emerged at the highest concentration of 3125 ppm. The larval weight, mean relative growth rate and food assimilated also declined significantly with treatment. Also, evaluation of chrysin for oviposition deterrent activity revealed reduced oviposition by females under choice as well as no-choice conditions. The findings indicated potential use of chrysin in pest management studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All authors declare that they have no objection to the availability of data and materials.
References
Abou-Zaid, M. M., Beninger, C. W., Arnason, J. T., & Nozzolillo, C. (1993). The effect of one flavone, two catechins and four flavonols on mortality and growth of the European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis Hubner). Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 21, 415–420.
Atteyat, M., Abu-Romann, S., Abu-Darwish, M., & Ghabeish, I. (2012). Impact of flavonoids against woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausmann) and its sole parasitoid, Aphelinus mali (Hald.). Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 4, 227–236.
Beninger, C. W., & Abou-Zaid, M. M. (1997). Flavonol glycosides from four pine species that inhibit early instar gypsy moth (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) development. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 25(6), 505–512.
Boué, S. M., & Raina, A. K. (2003). Effects of plant flavonoids on fecundity, survival, and feeding of the Formosan subterranean termite. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 29(11), 2575–2584.
Dhillon, M. K., Singh, R., Naresh, J. S., & Sharma, H. C. (2005). The melon fruit fly, Bactrocera cucurbitae: A review of its biology and management. Journal of Insect Science, 5, 1–16.
Diaz Napal, G. N., Defagó, M. T., Valladares, G. R., & Palacios, S. M. (2010). Response of Epilachna paenulatato to two flavonoids, pinocembrin and quercetin, in a comparative study. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 36, 898–904.
Dixit, G., Praveen, A., Tripathi, T., Yadav, V. K., & Verma, P. C. (2017). Herbivore-responsive cotton phenolics and their impact on insect performance and biochemistry. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 20, 341–351.
Erb, M., & Kliebenstein, D. J. (2020). Plant secondary metabolites as defenses, regulators, and primary metabolites: The blurred functional trichotomy. Plant Physiology, 184(1), 39–52.
Feeny, P. P. (1968). Effect of oak leaf tannins on larval growth of the winter moth Operophtera brumata. Journal of Insect Physiology, 14, 805–817.
Gokhale, M., Gautam, D., & Khanna, A. (2017). A Comparative GC-MS Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in the Different Fractions of Root Extract of Oroxylum indicum (L.) Vent. Analytical Chemistry Letters, 7(3), 410–420.
Goławska, S., & Łukasik, I. (2012). Antifeedant activity of luteolin and genistein against the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Journal of Pest Science, 85, 443–450.
Goławska, S., Sprawka, I., Łukasik, I., & Goławski, A. (2014). Are naringenin and quercetin useful chemicals in pest-management strategies? Journal of Pest Science, 87, 173–180.
Gupta, J. N., Verma, A. N., & Kashyap, R. K. (1978). An improved method for mass rearing for melon fruit fly Dacus cucurbitae Coquillett. Indian Journal of Entomology, 40, 470–471.
Isman, M. B., & Duffey, S. S. (1982). Toxicity of tomato phenolic compounds to the fruitworm, Heliothis zea. Entomologia Experimentalis Et Applicata, 31, 370–376.
Jakhar, S., Kumar, V., Choudhary, P. K., & Lal, B. (2020). Estimation losses due to fruit fly, Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) on long melon in semi-arid region of Rajasthan. Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies, 8(6), 632–635.
Kapoor, V. C. (1993). Economic fruit flies. In V. C. Kapoor (Ed.), Indian fruit flies (Insecta: Diptera: Tephritidae) (pp. 130–131). Oxford and DBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd.
Khan, H. A. A. (2019). Characterization of permethrin resistance in a Musca domestica strain: Resistance development, cross-resistance potential and realized heritability. Pest Management Science, 75(11), 2969–2974.
Khan, Z. R., & Saxena, R. C. (1985). Behavioural and physiological responses of Sogatella furcifera (Homoptera: Delphacidae) to selected resistant and susceptible rice cultivars. Journal of Economic Entomology, 78, 1280–1286.
Khare, S., Singh, N. B., Singh, A., Hussain, I., Niharika, K., Yadav, V., Bano, C., Yadav, R. K., & Amist, N. (2020). Plant secondary metabolites synthesis and their regulations under biotic and abiotic constraints. Journal of Plant Biology, 63(3), 203–216.
Lattanzio, V., Lattanzio, V. M. T., & Cardinali, A. (2006). Role of phenolics in the resistance mechanisms of plants against fungal pathogens and insects. In F. Imperato (Ed.), Phytochemistry: Advances in Research (pp. 23–67). Research Signpost.
Liu, D., Yuan, Y., Li, M., & Qiu, X. (2015). Effects of dietary quercetin on performance and cytochrome P450 expression of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 105, 771–777.
Lopez, N., Guevara, P., Perez-Amador, M. C., Villaruel, J. L., & Herrera, J. (2005). Flavones in leaves of two maize lines. Phyton-Revista Internacional de Botanica Experimental, 54, 187–190.
Mani, R., & Natesan, V. (2018). Chrysin: Sources, beneficial pharmacological activities, and molecular mechanism of action. Phytochemistry, 145, 187–196.
Mansour, M. H. (1981). Efficiency of two allelochemicals on the conversion of ingested and digested food into the body tissues of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.)(Lepid., Noctuidae). Journal of Applied Entomology, 92, 493–499.
Martinez, S. S., & Emden, H. F. V. (2001). Growth disruption, abnormalities and mortality of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisduval)(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) caused by azadirachtin. Neotropical Entomology, 30, 113–125.
Mierziak, J., Kostyn, K., & Kulma, A. (2014). Flavonoids as important molecules of plant interactions with the environment. Molecules, 19(10), 16240–16265.
Mitchell, M. J., Keogh, D. P., Crooks, J. R., & Smith, S. L. (1993). Effects of plants flavonoids and other allelochemicals on insect cytochrome P-450 dependent steroid hydroxylase activity. Insect Biochemistry Molecular Biology, 23, 65–71.
Movva, V., & Pathipati, U. R. (2017). Feeding-induced phenol production in Capsicum annuum L. influences Spodoptera litura F. larval growth and physiology. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 95(1), 21387.
Nenaah, G. E. (2013). Potential of using flavonoids, latex and extracts from Calotropis procera(Ait.) as grain protectants against two coleopteran pests of stored rice. Industrial Crops and Products, 45, 327–334.
Nomura, M., & Itioka, T. (2002). Effects of synthesized tannin on the growth and survival of a generalist herbivorous insect, the common cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Applied Entomology and Zoology, 37, 285–289.
Oberdörster, E., Clay, M. A., & Cottam, D. M. (2001). Common phytochemicals are ecdysteroid agonists and antagonists: A possible evolutionary link between vertebrate and invertebrate steroid hormones. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 77, 229–238.
Onyilagha, J. C., Lazorko, J., Gruber, M. Y., Soroka, J. J., & Erlandson, M. A. (2004). Effect of flavonoids on feeding preference and development of the crucifer pest Mamestra configurata Walker. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 30, 109–124.
Pavela, R., & Herda, G. (2007). Repellent effects of pongam oil on settlement and oviposition of the common greenhouse whitefly Trialeurodes vaporariorum on chrysanthemum. Insect Science, 14(3), 219–224.
Puri, S., Singh, S., & Sohal, S. K. (2020). Growth retarding effect of curcumin on Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) larvae. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/03235408.2020.1857134.
Rajkumar, S., & Jebanesan, A. (2009). Larvicidal and oviposition activity of Cassia obtusifolia Linn (Family: Leguminosae) leaf extract against malarial vector, Anopheles stephensi Liston (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitology Research, 104, 337–340.
Rao, K. V., Chattopadhyay, S. K., & Reddy, G. C. (1990). Flavonoids with mosquito larval toxicity. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 38, 1427–1430.
Righi-Assia, A. F., Khelil, M. A., Medjdoub-Bensaad, F., & Righi, K. (2010). Efficacy of oils and powders of some medicinal plants in biological control of the pea weevil (Callosobruchus chinensis L.). African Journal of Agricultural Research, 5(12), 1474–1481.
Salazar, J. R., Torres, P., Serrato, B., Dominguez, M., Alarcon, J., & Cespedes, C. L. (2015). Insect growth regulator (IGR) effects of Eucalyptus citriodora Hook (Myrtaceae). Boletín Latinoamericano y Del Caribe De Plantas Medicinales y Aromáticas, 14, 403–422.
Salunke, B. K., Kotkar, H. M., Mendki, P. S., Upasani, S. M., & Maheshwari, V. L. (2005). Efficacy of flavonoids in controlling Callosobruchus chinensis (L.)(Coleoptera: Bruchidae), a post-harvest pest of grain legumes. Crop Protection, 24(10), 888–893.
Sharma, R., & Sohal, S. K. (2013). Bioefficacy of quercetin against melon fruit fly. Bulletin of Insectology, 66, 79–83.
Sharma, R., & Sohal, S. K. (2016). Oviposition response of melon fruit fly, Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) to different phenolic compounds. Journal of Biopesticides, 9(1), 46.
Shaver, T. N., & Lukefar, M. J. (1969). Effect of flavonoid pigments and gossypol on growth and development of the bollworm, tobacco budworm and pink bollworm. Journal of Economic Entomology, 63, 643–646.
Simmonds, M. S. (2003). Flavonoid–insect interactions: Recent advances in our knowledge. Phytochemistry, 64(1), 21–30.
Simmonds, M. S. J. (2001). Importance of flavonoids in insect-plant interactions: Feeding and oviposition. Phytochemistry, 56, 245–252.
Singh, S., & Singh, R. P. (1998). Neem (Azadirachtin indica) seed kernel extracts and Azadirachtin as oviposition deterrent against melon fly (Bactrocera cucurbitae) and oriental fruit fly (Bactrocera dorsalis). Phytoparasitica, 26, 191–197.
Srivastava, B. G. (1975). A chemically defined diet for Dacus cucurbitae(Coq.) larvae under aseptic conditions. Entomology News Letter, 5, 24.
Todd, G. W., Getahun, A., & Cress, D. C. (1971). Resistance in barley to the greenbug, Schizaphis graminum.1. Toxicity of phenolic and flavonoid compounds and related substances. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 64, 718–721.
Upasani, S. M., Kotkar, H. M., Mendki, P. S., & Maheshwari, V. L. (2003). Partial characterization and insecticidal properties of Ricinus communis L foliage flavonoids. Pest Management Science: Formerly Pesticide Science, 59(12), 1349–1354.
Virgilio, M., Jordaens, K., Verwimp, C., White, I. M., & De Meyer, M. (2015). Higher phylogeny of frugivorous flies (Diptera, Tephritidae, Dacini): Localised partition conflicts and a novel generic classification. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 85, 171–179.
Waiss, A. C., Chan, B. G., Elliger, C. A., Wiseman, B. R., McMillian, W. W., Widstrom, N. W., Zuber, M. S., & Keaster, A. J. (1979). Maysin, a flavone glycoside from corn silks with antibiotic activity toward corn earworm. Journal of Economic Entomology, 72, 256–258.
War, A. R., Buhroo, A. A., Hussain, B., Ahmad, T., Nair, R. M., & Sharma, H. C. (2020). Plant Defense and Insect Adaptation with Reference to Secondary Metabolites. In J. M. Mérillon & K. Ramawat (Eds.), Co-Evolution of Secondary Metabolites. Reference Series in Phytochemistry (pp. 795–822). Springer.
War, A. R., Paulraj, M. G., Hussain, B., Buhroo, A. A., Ignacimuthu, S., & Sharma, H. C. (2013). Effect of plant secondary metabolites on legume pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera. Journal of Pest Science, 86, 399–408.
White, I. M., & Elson-Harris, M. (1992). Fruit Flies of Economic Significance: Their Identification and Bionomics. CAB International.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge University Grants Commission (UGC)-BSR, UGC-SAP (NO.F.4-4/2016/DRS-I (SAP-II)) and Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for providing financial aid to carry out the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SP carried out the bioassays and biochemical studies. SP and SS analyzed the data. SKS contributed in the experimental design. All authors contributed in writing the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puri, S., Singh, S. & Sohal, S.K. Inhibitory effect of chrysin on growth, development and oviposition behaviour of melon fruit fly, Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Phytoparasitica 50, 151–162 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-021-00940-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-021-00940-w