Abstract
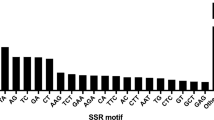
Expressed sequence tags (ESTs) are the source of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) that can be used to develop molecular markers for the study of polymorphism and genetic diversity. In the present investigation, 30 EST simple sequence repeats (SSR) primer sets derived from three formae speciales of Fusarium oxysporum: melonis (Fom), cucumerium (Foc), and lycopersici (Fol) – were tested for transferability to Fusarium udum. The majority of SSR loci contain trinucleotide (63.70%) while fewer contain di- (27.41%), tetra- (5.64%) and penta-nucleotide (3.22%) repeats. The number of alleles at these SSR loci ranged from one to three, with an average of 1.4 alleles per locus. CAG (24.19%) and AC (16.93%) were the most abundant motifs identified. Three markers (FomSSR-8, FolSSR-2 and FolSSR-4) were found highly informative for genetic characterization of F. udum and very useful in distinguishing the polymorphism rate of the markers at specific locus; however, polymorphic information content (PIC) was maximum (0.597) in FocSSR-7. In terms of cross species transferability, 70% of the primer sets of Fom-SSR and Fol-SSR and 30% of the Foc-SSR produced an amplicon in F. udum isolates. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first set of EST SSR markers developed and assessed for the variability, genetic analysis and evolutionary relationships of the F. udum population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baird, R. E., Wadl, P. A., Allen, T., McNeill, D., Wang, X., Moulton, J. K., et al. (2010). Variability of United States isolates of Macrophomina phaseolina based on simple sequence repeats and cross genus transferability to related genera within botryosphaeriaceae. Mycopathologia, 170, 169–180.
Barbará, T., Martinelli, G., Fay, M. F., Mayo, S. J., & Lexer, C. (2007). Population differentiation and species cohesion in two closely related plants adapted to neotropical high-altitude ‘inselbergs’, Alcantarea imperialis and A. geniculata. Molecular Ecology, 16, 1981–1992.
Bogale, M., Wingfield, B. D., Wingfield, M. J., & Steenkamp, E. T. (2005). Simple sequence repeat markers for species in the Fusarium oxysporum complex. Molecular Ecology Notes, 5, 622–624.
Bogale, M., Wingfield, B. D., Wingfield, M. J., & Steenkamp, E. T. (2006). Characterization of Fusarium oxysporum isolates from Ethiopia using AFLP, SSR and DNA sequence analyses. Fungal Diversity, 23, 51–66.
Botstein, D., White, K. L., Skolnick, M., & Davis, R. W. (1980). Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. American Journal of Human Genetics, 32, 314–33l.
Cristancho, M., & Escobar, C. (2008). Transferability of SSR markers from related Uredinales species to the coffee rust Hemileia vastatrix. Genetics and Molecular Research, 7, 1186–1192.
Dracatos, P. M., Dumsday, J. L., Olle, R. S., Cogan, N. O. I., Dobrowolski, M. P., Fugimori, M., et al. (2006). Additions and corrections: Development and characterization of EST-SSR markers from the crown rust pathogen of ryegrass (Puccinia coronata Corda f. sp. lolii). Genome, 49, 1341.
Dutech, C., Enjalbert, J., Fournier, E., Delmotte, F., Barrès, B., Carlier, J., et al. (2007). Challenges of microsatellite isolation in fungi. Fungal Genetics Biology, 44, 933–949.
Garnica, D. P., Pinzón, A. M., Quesada-Ocampo, L. M., Bernal, A. J., Barreto, E., Grünwald, N. J., et al. (2006). Survey and analysis of microsatellites from transcript sequences in Phytophthora species: frequency, distribution, and potential as markers for the genus. BMC Genomics, 7, 245.
Gauthier, N., Clouet, C. D., Fargues, J., & Bon, M. C. (2007). Microsatellite variability in the entomopathogenic fungus Paecilomyces fumosoroseus: genetic diversity and population structure. Mycologia, 99, 693–704.
Goodwin, S. B. (2007). Back to basics and beyond: increasing the level of resistance to Septoria tritici blotch in wheat. Australian Plant Pathology, 36, 532–538.
Haware, M. P., & Nene, Y. L. (1982). Races of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. ciceri. Plant Disease, 66, 809–810.
Jaccard, P. (1908). Nouvelle recherches sur la distribution florale. Bulletin de la Société Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles, 44, 223–270.
Kannaiyan, J., Nene, Y. L., Reddy, M. V., Ryan, J. G., & Raju, T. N. (1984). Prevalence of pigeonpea diseases and associated crop losses in Asia, Africa and the Americas. Tropical Pest Management, 30, 62–71.
Kim, T. S., Booth, J. G., Gauch, H. G., Jr., Sun, Q., Park, J., Lee, Y. H., et al. (2008). Simple sequence repeats in Neurospora crassa: distribution, polymorphism and evolutionary inference. BMC Genomics, 9, 31.
Kiprop, E. K., Mwang’ombe, A. W., Baudoin, J.-P., Kimani, P. M., & Mergeai, G. (2005). Genetic variability among Fusarium udum isolates from pigeonpea. African Crop Science Journal, 13, 163–172.
Kumar, S., Maurya, D., Kashyap, P. L., & Srivastava, A. K. (2012). Computational mining and genome wide distribution of microsatellites in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. Notulae Scientia Biologicae, 4, 127–131.
Kumar, S., Singh, R., Kashyap, P. L., & Srivastava, A. K. (2013). Rapid detection and quantification of Alternaria solani in tomato. Scientia Horticulturae, 151, 184–189.
Levinson, G., & Gutman, G. A. (1987). Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 4, 203–221.
Ma, L. J., van der Does, H. C., Borkovich, K. A., Colema, J. J., Daboussi, M. J., Di Pietro, A., et al. (2010). Comparative genomics reveals mobile pathogenicity chromosomes in Fusarium. Nature, 464, 367–373.
Mahfooz, S., Maurya, D. K., Srivastava, A. K., Kumar, S., & Arora, D. K. (2012). A comparative in-silico analysis on frequency and distribution of microsatellites in coding regions of three formae speciales of Fusarium oxysporum and development of EST-SSR markers for polymorphism studies. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 328, 54–60.
Mesapogu, S., Bakshi, A., Kishore Babu, B., Reddy, S. S., Saxena, S., & Arora, D. K. (2012). Genetic diversity and pathogenic variability among Indian isolates of Fusarium udum infecting pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.). International Research Journal of Agricultural Science and Soil Science, 2, 51–57.
Pashley, C. H., Ellis, J. R., McCauley, D. E., & Burke, J. M. (2006). EST databases as a source for molecular markers: lessons from Helianthus. Journal of Heredity, 97, 381–388.
Peakall, R., Gilmore, S., Keys, W., Morgante, M., & Rafalski, A. (1998). Cross-species amplification of soybean (Glycine max) simple sequence repeats (SSRs) within the genus and other legume genera: implications for the transferability of SSRs in plants. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 15, 1275–1287.
Raju, N. L., Gnanesh, B. N., Lekha, P., Jayashree, B., Pande, S., Hiremath, P. J., et al. (2010). The first set of EST resource for gene discovery and marker development in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.). BMC Plant Biology, 10, 45.
Rohlf, J. F. (1998). NTSYS-PC: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system Version 2.01. Setauket, NY, USA: Exetersoftware.
Rouxel, M., Papura, D., Nogueira, M., Machefer, V., Dezette, D., Richard-Cervera, S., et al. (2012). Microsatellite markers for characterization of native and introduced populations of Plasmopara viticola, the causal agent of grapevine downy mildew. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 78, 6337.
Varshney, R. K., Graner, A., & Sorrells, M. E. (2005). Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends in Biotechnology, 23, 48–55.
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial assistance under project ‘Outreach project on Phytophthora, Fusarium and Ralstonia Disease in Horticulture and Field Crops’ from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Rai, S., Maurya, D.K. et al. Cross-species transferability of microsatellite markers from Fusarium oxysporum for the assessment of genetic diversity in Fusarium udum . Phytoparasitica 41, 615–622 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-013-0324-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-013-0324-y