Abstract
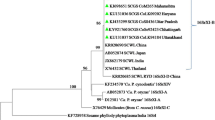
Sugarcane is an important cash crop in Vietnam and has been widely promoted at national and provincial level. In 2006, a new disease was discovered in sugarcane in the Nghean Tate&Lyle Sugar Mill in Nghean Province in north-central Vietnam. The key symptoms were the formation of green grassy shoots around the base of mature stools. We applied nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using P1/P7 and R16F2n/R16R2 for detection and characterization of phytoplasma from the symptomatic tissues. PCR products of the expected size (approx. 1200 bp) were obtained from the 16S rDNA of the phytoplasma. The restriction fragment length polymorphism profiles indicated that all samples were infected by the same phytoplasma. Phylogenetic analysis confirmed that the SCGS phytoplasma from Vietnam belong to the 16SrXI group, formerly Rice Yellow Dwarf group.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariyarathna, H. A. C. K., Everard, J. M. D. T., & Karunanayake, E. H. (2007). Diseased sugarcane in Sri Lanka is infected with sugarcane grassy shoot and/or sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma. Australian Plant Disease Notes, 2, 123–125.
Arocha, Y., Antesana, O., Montellano, E., Franco, P., Plata, G., & Jones, P. (2007). ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma lycopersici’, a phytoplasma associated with ‘hoja de perejil’ disease in Bolivia. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 57, 1704–1710.
Arocha, Y., López, M., Fernández, M., Piñol, B., Horta, D., Peralta, E. L., et al. (2005). Transmission of a sugarcane yellow leaf phytoplasma by the delphacid planthopper Saccharosydne saccharivora, a new vector of sugarcane yellow leaf syndrome. Plant Pathology, 54, 634–642.
Chandrasene, G., Brune, A. E., Rutherford, R. S., & Dharmawardena, N. (2003). Detection of phytoplasmas associated with grassy shoot and white leaf diseases of sugarcane in Sri Lanka using FTA TM Papers. Sugar Tech, 5, 237–241.
Chona, B. L. (1958). Some diseases of sugarcane reported from India in recent years. Indian Phytopathology, 11, 1–9.
Corbett, M. K., Misra, S. R., & Singh, K. (1971). Grassy shoot disease of sugarcane. IV. Association of mycoplasma-like bodies. Plant Science, 3, 80–82.
Deng, S., & Hiruki, C. (1991). Amplification of 16S rRNA genes from culturable and nonculturable mollicutes. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 14, 53–61.
Gundersen, D. E., & Lee, I.-M. (1996). Ultrasensitive detection of phytoplasmas by nested-PCR assays using two universal primer pairs. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 35, 144–151.
Gundersen, D. E., Lee, I.-M., Rehner, S. A., Davis, R. E., & Kingsbury, D. T. (1994). Phylogeny of mycoplasmalike organisms (phytoplasmas): A basis for their classification. Journal of Bacteriology, 176, 5244–5254.
Gundersen, D. E., Lee, I.-M., Schaff, D. A., Harrison, N. A., Chang, C. J., Davis, R. E., et al. (1996). Genomic diversity and differentiation among phytoplasma strains in 16S rRNA group I (aster yellows and related phytoplasmas) and III (X-disease and related phytoplasmas). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 46, 64–75.
Hanboonsong, Y., Choosai, C., Panyim, S., & Damak, S. (2002). Transovarial transmission of sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma in the insect vector Matsumuratettix hiroglyphicus (Matsumura). Insect Molecular Biology, 11, 97–103.
Hanboonsong, Y., Ritthison, W., Choosai, C., & Sirithorn, P. (2006). Transmission of sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma by Yamatotettix flavovittatus, a new leafhopper vector. Journal of Economic Entomology, 99, 1531–1537.
Hodgetts, J., Boonham, N., Mumford, R., Harrison, N., & Dickinson, M. (2008). Phytoplasma phylogenetics based on analysis of secA and 23S rRNA gene sequences for improved resolution of candidate species of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 58, 1826–1837.
Hodgetts, J., Boonham, N., Mumford, R., & Dickinson, M. (2009). A panel of real-time PCR assays for improved universal and group specific detection of phytoplasmas, based on the 23S rRNA gene. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 2945–2950.
Jung, H. Y., Sawayanagi, T., Wongkaew, P., Kakizawa, S., Nishigawa, H., Wei, W., et al. (2003). ‘Candidatus’ Phytoplasma oryzae’, a novel phytoplasma taxon associated with rice yellow dwarf disease. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53, 1925–1929.
Kumarasinghe, N. C., & Jones, P. (2001). Identification of white leaf disease of sugarcane in Sri Lanka. Sugar Tech, 3, 55–58.
Kunkel, L. O. (1926). Studies on aster yellows. American Journal of Botany, 23, 646–705.
Lee, I.-M., Hammond, R. W., Davis, R. E., & Gundersen, D. E. (1993). Universal amplification and analysis of pathogen 16S rDNA for classification and identification of mycoplasmalike organisms. Phytopathology, 83, 834–842.
Lee, I.-M., Klopmeyer, M., Bartoszyk, I. M., Gundersen-Rindal, D. E., Chou, T. S., Thomson, K. L., et al. (1997). Phytoplasma induced free-branching in commercial poinsettia cultivars. Nature Biotechnology, 15, 178–182.
Lee, I.-M., Gundersen-Rindal, D. E., Davis, R. E., & Bartoszyk, I. M. (1998). Revised classification scheme of phytoplasmas based on RFLP analyses of 16S rRNA and ribosomal protein gene sequences. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 48, 1153–1169.
Lee, I.-M., Davis, R. E., & Gundersen-Rindal, D. E. (2000). Phytoplasma: phytopathogenic mollicutes. Annual Review of Microbiology, 54, 221–255.
Ling, K. C. (1962). White leaf disease of sugarcane. Taiwan Sugar, 9, 1–5.
Man, V. T., Giao, N. K., Lien, N. T. M., Thuy, N. T., Diep, D. N., & Duong C. A. (2002). Study on sugarcane white leaf disease in Vietnam. The 1 st National Conference on Plant Pathology and Molecular Biology (pp. 23–25; Nong Lam University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam). (in Vietnamese)
Marcone, C. (2002). Phytoplasma diseases of sugarcane. Sugar Technology, 4, 79–85.
Marcone, C., Gibb, K. S., Streten, C., & Schneider, B. (2004). ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma spartii’, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma rhamni’ and ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma allocasuarinae’, respectively associated with spartium witches’-broom, buckthorn witches’-broom and allocasuarina yellows diseases. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54, 1025–1029.
Matsumoto, T., Lee, C. H., & Teng, W. S. (1968). Studies on white leaf disease of sugarcane – transmission by Epitettix hiroglyphicus Matsumura. Plant Protection Bulletin (Taiwan), 10, 3–9.
McCoy, R. E., Caudwell, A., Chang, C. J., Chen, T. A., Chiykowski, L. N., Cousin, M. T., et al. (1989). Plant diseases associated with mycoplasmalike organisms. In R. F. Whitcomb & J. G. Tully (Eds.), The Mycoplasmas (Vol. 5, pp. 545–560). New York, NY: Academic.
Nakashima, K., Chaleeprom, W., Wongkaew, P., & Sirithorn, P. (1994). Detection of mycoplasma-like organisms associated with white leaf disease of sugarcane in Thailand using DNA probes. Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences, 1, 57–67.
Nakashima, K., Hayashi, T., Chaleeprom, W., Wongkeaw, P., & Sirithorn, P. (1996). Complex phytoplasma flora in Northeast Thailand as revealed by 16S rDNA analysis. Annals of the Phytopathologicial Society of Japan, 62, 57–60.
Namba, S., Kato, S., Iwanami, S., Oyaizu, H., Shiozawa, H., & Tsuchizaki, T. (1993a). Detection and differentiation of plant-pathogenic mycoplasmalike organisms using polymerase chain reaction. Phytopathology, 83, 786–791.
Namba, S., Oyaizu, H., Kato, S., Iwanami, S., & Tsuchizaki, T. (1993b). Phylogenetic diversity of phytopathogenic mycoplasmalike organisms. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 43, 461–467.
Razin, S., Yogev, D., & Naot, Y. (1998). Molecular biology and pathogenicity of mycoplasmas. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 62, 1094–1156.
Rishi, N., & Chen, C. T. (1989). Grassy shoot and white leaf disease. In B. C. Ricaud & B. T. Egan (Eds.), The diseases of sugarcane: Major diseases (pp. 289–300). Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier Science Publisher.
Schneider, B., Seemuller, E., Smart, C. D., & Kikpatrick, B. C. (1995). Phylogenetic classification of plant pathogenic mycoplasma-like organisms or phytoplasmas. In S. Razin & J. G. Tully (Eds.), The molecular and diagnostic procedures in mycoplasmology (pp. 369–380). San Diego, CA, USA: Academic.
Sdoodee, R., Schneider, B., Padovan, A. C., & Gibb, K. S. (1999). Detection and genetic relatedness of phytoplasma associated with plant diseases in Thailand. The Journal of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics, 3, 133–140.
Seemüller, E., & Schneider, B. (2004). ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma mali’, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma pyri’ and ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma prunorum’, the causal agents of apple proliferation, pear decline and European stone fruit yellows, respectively. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54, 1217–1226.
Singh, V., Baitha, A., & Sinha, O. K. (2002). Transmission of grassy shoot disease of sugarcane by a leafhopper (Deltocephalus vulgaris Dash and Viraktamath). Indian Journal of Sugarcane Technology, 17, 60–63.
Srivastava, S., Singh, V., Gupta, P. S., Sinha, O. K., & Baitha, A. (2006). Nested PCR assay for detection of sugarcane grassy shoot phytoplasma in the leafhopper vector Deltocephalus vulgaris: a first report. Plant Pathology, 55, 25–28.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2011). MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 2731–2739.
Valiunas, D., Staniulis, J., & Davis, R. E. (2006). ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma fragariae’, a novel phytoplasma taxon discovered in yellows diseased strawberry, Fragaria ananassa. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 56, 277–281.
Viswanathan, R. (2001). Different aerated steam therapy (AST) regimes on the development of grassy shoot disease symptoms in sugarcane. Sugar Tech, 3, 83–91.
Viswanathan, R., Balamuralikrishnan, M., & Poongothai, M. (2005). Detection of phytoplasmas causing grassy shoot disease in sugarcane by PCR technique. Sugar Tech, 7, 71–73.
Wongkaew, P., & Fletcher, J. (2004). Sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma in tissue culture: long-term maintenance, transmission, and oxytetracycline remission. Plant Cell Reports, 23, 426–434.
Wongkaew, P., Hanboonsong, Y., & Sirithorn, P. (1997). Differentiation of phytoplasmas associated with sugarcane and gramineous weed white leaf disease and sugarcane grassy shoot by RFLP and sequencing. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 95, 660–663.
Acknowledgments
This work of T. X. Hoat was supported by the National Foundation for Science & Technology Development (NAFOSTED) (No. 106.15-2010.07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoat, T.X., Bon, N.G., Van Quan, M. et al. Detection and molecular characterization of sugarcane grassy shoot phytoplasma in Vietnam. Phytoparasitica 40, 351–359 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-012-0235-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-012-0235-3