Abstract
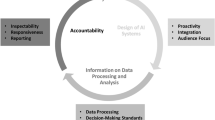
Collaborative business intelligence (BI) is widely embraced by enterprises as a way of making the most of their business processes. However, decision makers usually work in isolation without the knowledge or the time needed to obtain and analyze all the available information for making decisions. Unfortunately, collaborative BI is currently based on exchanging e-mails and documents between participants. As a result, information may be lost, participants may become disoriented, and the decision-making task may not yield the needed results. The authors propose a modeling language aimed at modeling and eliciting the goals and information needs of participants of collaborative BI systems. This approach is based on innovative methods to elicit and model collaborative systems and BI requirements. A controlled experiment was performed to validate this language, assessing its understandability, scalability, efficiency, and user satisfaction by analyzing two collaborative BI systems. By using the framework proposed in this work, clear guideless can be provided regarding: (1) collaborative tasks, (2) their participants, and (3) the information to be shared among them. By using the approach to design collaborative BI systems, practitioners may easily trace every element needed in the decision processes, avoiding the loss of information and facilitating the collaboration of the stakeholders of such processes.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asur S, Huberman BA (2010) Predicting the future with social media. In: 2010 IEEE/WIC/ACM international conference on web intelligence and intelligent agent technology. IEEE, Toronto, pp 492–499
Basili VR, Caldiera G, Rombach HD (1994) The goal question metric approach. In: Marciniak J (ed) Encyclopedia of software engineering. Wiley, New York, pp 528–532
Berthold H, Rösch P, Zöller S et al (2010) An architecture for ad-hoc and collaborative business intelligence. In: 1st International workshop on data semantics (DataSem’10). ACM Press, Lausanne, pp 13:1–13:6
Dalpiaz F, Franch X, Horkoff J (2016) iStar 2.0 language guide. Cornell University. http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.07767
Dayal U, Vennelakanti R, Sharma R et al (2008) Collaborative business intelligence: enabling collaborative decision making in enterprises. In: Meersman R, Tari Z (eds) On the move to meaningful internet systems: OTM 2008. Springer, Berlin, pp 8–25
de Moor A (1999) Empowering communities: a method for the legitimate user-driven specification of network information systems. Tilburg University, Tilburg
Devlin B (2012) Collaborative business intelligence: socializing team-based decision making. Bus Intell J 17:9–17
Embley DW, Liddle SW (2013) Big data – conceptual modeling to the rescue. In: Ng W, Storey VC, Trujillo JC (eds) ER 2013: conceptual modeling. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–8
Figueroa-Martinez J, López-Jaquero V, Gutiérrez Vela FL, González P (2013) Enriching UsiXML language to support awareness requirements. Sci Comput Program 78:2259–2267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scico.2012.09.020
Giorgini P, Mylopoulos J, Nicchiarelli E, Sebastiani R (2003) Formal reasoning techniques for goal models. J Data Semant I 2800(2003):1–20
Giorgini P, Mylopoulos J, Sebastiani R (2005) Goal-oriented requirements analysis and reasoning in the tropos methodology. Eng Appl Artif Intell 18:159–171
Giorgini P, Rizzi S, Garzetti M (2008) GRAnD: a goal-oriented approach to requirement analysis in data warehouses. Decis Support Syst 45:4–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2006.12.001
Golfarelli M, Mandreoli F, Penzo W et al (2012) BIN: business intelligence networks. In: Zorrilla ME, Mazón J-N, Ferrández Ó et al (eds) Business intelligence applications and the web: models, systems and technologies. IGI Global, Hershey, pp 244–265
Gross T (2013) Supporting effortless coordination: 25 years of awareness research. Comput Support Coop Work 22:425–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10606-013-9190-x
Gutwin C, Greenberg S (2002) A descriptive framework of workspace awareness for real-time groupware. Comput Support Coop Work 11:411–446. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021271517844
Horkoff J, Yu E (2010) Finding solutions in goal models: an interactive backward reasoning approach. In: International conference on conceptual modeling. Springer, Aachen, Germany, pp 59–75
Horkoff J, Yu ES-K (2012) Comparison and evaluation of goal-oriented satisfaction analysis techniques. Requir Eng 18:199–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00766-011-0143-y
Höst M, Regnell B, Wohlin C (2000) Using students as subjects – a comparative study of students and professionals in lead-time impact assessment. Empir Softw Eng 5:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026586415054
ISO/IEC 9126 (1991) Software engineering – product quality. ISO/IEC. https://www.iso.org/standard/22749.html. Accessed 27 July 2018
Kaufmann J, Chamoni P (2014) Structuring collaborative business intelligence: a literature review. In: 2014 47th Hawaii international conference on system sciences. IEEE, Waikoloa, pp 3738–3747
Kelly J, Jones P, Barta F et al (2004) Successful transport decision-making: a project management and stakeholder engagement handbook. European Commission, Brussels
Lakomaa E, Kallberg J (2013) Open data as a foundation for innovation: the enabling effect of free public sector information for entrepreneurs. IEEE Access 1:558–563. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2013.2279164
Limbourg Q, Vanderdonckt J, Michotte B et al (2004) USIXML: a language supporting multi-path development of user interfaces. In: Bastide R, Palanque P, Roth J (eds) Engineering human computer interaction and interactive systems. Springer, Berlin, pp 200–220
Lindman J, Rossi M, Tuunainen VK (2013) Open data services: research agenda. In: 2013 46th Hawaii international conference on system sciences. IEEE, Wailea, pp 1239–1246
Liu L, Daniels H (2012) Towards a value model for collaborative, business intelligence-supported risk assessment. In: 6th International workshop on value modeling and business ontology (VMBO’12). Vienna, pp 1–5
Martínez-Carreras MA, Muñoz A, Botía J (2013) Building and evaluating context-aware collaborative working environments. Inf Sci (NY) 235:224–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2013.02.009
Maté A, Trujillo J, Franch X (2011) A modularization proposal for goal-oriented: analysis of data warehouses using I-star. In: 30th International conference on conceptual modeling (ER’11), pp 421–428
Mazón J-N, Pardillo J, Trujillo J (2007) A model-driven goal-oriented requirement engineering approach for data warehouses. In: Hainaut J-L, Rundensteiner EA, Kirchberg M et al (eds) Advances in conceptual modeling - foundations and applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 255–264
Mettler T, Raber D (2011) Developing a collaborative business intelligence system for improving delivery reliability in business networks. In: 2011 17th International conference on concurrent enterprising, Aachen, pp 1–7
Moody DL (2009) The “Physics” of notations: toward a scientific basis for constructing visual notations in software engineering. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 35:756–779. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSE.2009.67
Oh O, Agrawal M, Rao HR (2013) Community intelligence and social media services: a rumor theoretic analysis of tweets during social crises. MIS Q 37:407–426
Pohl K (2010) Requirements engineering: fundamentals, principles, and techniques. Springer, Berlin
Pressman RS (2009) Software engineering: a practitioners approach, 7th edn. McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math, New York
Rizzi S (2012) Collaborative business intelligence. In: Aufaure M-A, Zimányi E (eds) Business intelligence. Springer, Berlin, pp 186–205
Schmidt K, Bannon L (1992) Taking CSCW seriously. Comput Support Coop Work 1:7–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00752449
Teruel MA (2013) CSRML Tool 2013. https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=MiguelATeruel.CSRMLTool2013. Accessed 23 June 2017
Teruel MA (2017) CSRML4BI Tool. http://bit.ly/2nrfqOC. Accessed 23 June 2017
Teruel MA, Navarro E, López-Jaquero V et al (2011a) CSRML: a goal-oriented approach to model requirements for collaborative systems. In: Jeusfeld M, Delcambre L, Ling T-W (eds) Conceptual modeling – ER 2011. Springer, Berlin, pp 33–46
Teruel MA, Navarro E, López-Jaquero V et al (2011b) A comparative of goal-oriented approaches to modelling requirements for collaborative systems. In: 6th International conference on evaluation of novel software approaches to software engineering (ENASE’11). SciTePress, Beijing, pp 131–142
Teruel MA, Navarro E, López-Jaquero V et al (2012) Analyzing the understandability of requirements engineering languages for CSCW systems: a family of experiments. Inf Softw Technol 54:1215–1228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2012.06.001
Teruel MA, Navarro E, López-Jaquero V et al (2014) A CSCW requirements engineering CASE tool: development and usability evaluation. Inf Softw Technol 56:922–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2014.02.009
Teruel MA, Navarro E, González P et al (2016) Applying thematic analysis to define an awareness interpretation for collaborative computer games. Inf Softw Technol 74:17–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2016.01.009
Teruel MA, Maté A, Navarro E et al (2018) The new era of business intelligence applications: building from a collaborative point of view – experimental material. Technical report no. DIAB-18-04-2. Computing systems department, University of Castilla–La Mancha
Vitali M, Pernici B, O’Reilly U-M (2015) Learning a goal-oriented model for energy efficient adaptive applications in data centers. Inf Sci (NY) 319:152–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2015.01.023
Winer BJ, Brown DR, Michels KM (1991) Statistical principles in experimental design, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill Humanities/Social Sciences/Languages, New York
Wohlin C, Runeson P, Höst M et al (2012) Experimentation in software engineering. Springer, Berlin
Yu ESK (1997) Towards modelling and reasoning support for early-phase requirements engineering. In: 3rd IEEE international symposium on requirements engineering (ISRE’97). IEEE Computer Society Press, Annapolis, pp 226–235
Zhu M-X, Luo X-X, Chen X-H, Wu DD (2012) A non-functional requirements tradeoff model in trustworthy software. Inf Sci (NY) 191:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2011.07.046
Zikopoulos PC, Eaton C, de Roos D et al (2011) Understanding big data: analytics for enterprise class hadoop and streaming data. McGraw-Hill Osborne, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Accepted after two revisions by Jelena Zdravkovic.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teruel, M.A., Maté, A., Navarro, E. et al. The New Era of Business Intelligence Applications: Building from a Collaborative Point of View. Bus Inf Syst Eng 61, 615–634 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12599-019-00578-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12599-019-00578-3