Abstract
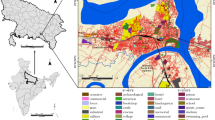
Land use land cover (LULC) classification of Churu district of Rajasthan state in India was done through hybrid classification technique. Landsat imageries of 1998, 2008 and 2018 were used to ascertain the rate and nature of spatio-temporal LULC changes. Major focus was given on vegetative cover change detection of the study area. On the basis of field survey and standard classification classes, the land use classes of the study area were divided into eleven classes. A detailed vegetative classification has been done while categorizing the classes. This classification method employed maximum likelihood and ISODATA clustering. The decision tree approach was used to create the multi-temporal hybrid LULC classification. The accuracy assessment results have shown excellent results at 91% overall accuracy with a kappa of 0.92. The results indicated that agriculture, crop land dominated the land use of Churu district while natural vegetation (forest areas) had the least share in land cover during the entire study period from 1998 to 2018. Shannon’s entropy index was used to determine the changes in spatial distributional pattern of built up during the period 1998 to 2018 for the study area in general and also for each of the eight sub-administrative regions (tehsils). The increase in the built up area in the study area during the period of 1998 to 2018 was quite paltry with a general dispersed type of built up. The increase varied from moderate to nominal with the entropy value decreasing from 0.84 to 0.71 for the study area in general.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J.R., Hardy, E.E., Roach, J.T. and Witmer, R.E. (1976) A land use and land cover classification system for use with remote sensor data. USGS Prof. Paper, No. 964. USGS, Washington, D.C.
Alexakis, D.D., Gryllakis, M.G., Koutroulis, A.G., Agapiou, A., Themistocleous, K., Tsanis, I.K., Michaelides, S., Pashiardis, S., Demetriou, C., Aristeidou, K., Retalis, A., Tymvios, F., Hadjim D.G., (2014). GIS and remote sensing techniques for the assessment of land use changes impact on flood hydrology: the case study of Yialias Basin in Cyprus. Nat. Hazard Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss., v.14, pp.413–426.
Alphan, H. (2003). Land-use change and urbanization of Adana, Turkey. Land Degradation & Development, v.14, pp.575–586.
Al-Mashagbah, A., Al-Adamat, R. and Al-Amoush, H. (2012) GIS and Remote Sensing to Investigate Urban Growth in Mafraq City/Jordan between 1987 and 2010. Jour. Geographic Information System, v.4, pp.377–382.
Balak Ram and Kolarkar A.S. (1993) Remote Sensing application in monitoring land use changes in arid Rajasthan. Int. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.14(17), pp.3191–3200.
Belal, A.A. and Moghanm, F.S. (2011), Detecting Urban Growth Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques in Al Gharbiya Governorate, Egypt. Egyptian Jour. Remote Sensing and Space Science, v.14, pp.73–79. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2011.09.001.
Butt, A., Shabbir, R., Ahmad, S.S., Aziz, N., Nawaz, M., Shah, M.T.A. (2015) Land cover classification and change detection analysis of Rawal watershed using remote sensing data. Jour. Biol. Environ. Sci., v.6(1), pp.236–248.
Burnett, C., and T. Blaschke. (2003) A multi-scale segmentation/object relationship modeling methodology for landscape analysis. Ecological Modeling, v.16(8), pp.233–249.
Clarke, K.C. and Gaydos, L.J. (1998) Loose-coupling a cellular automaton model and GIS: long-term urban growth prediction for San Francisco and Washington/Baltimore. Internat. Jour. Geograph. Inform. Sci., v.12 (7), pp.699–714.
Congalton, R.G. (1991) A review of assessing the accuracy of classification of remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing of Environment, v.37, pp.35–46.
Dadras, M., Shafri, H.Z., Ahmad, N., Pradhan, B., Safarpour, S., (2015), Spatiotemporal analysis of urban growth from remote sensing data in Bandar Abbas city, Iran. Egypt. Jour. Remote Sens. Space Sci., v.18(1), pp.35–52.
Deep, S. and Saklani, A. (2014) Urban sprawl modeling using cellular automata. Egyptian Jour. Remote Sens. Space Sci., v.17(2), pp.179–187.
Dewan, A.M. and Yamaguchi, Y., (2009) Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Appl. Geography., v.29(3), pp.390–401.
Doxani, G., Siachalou, S., Tsakiri-Strat, M. (2008) An Object-Oriented Approach to Urban Land Cover Change Detection. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, v.37(7), pp.245–251.
El Nasser, H., and Overberg, P. (2001) A comprehensive look at sprawl in America, USA Today, p.1
Epstein, J., Payne, K. and Kramer, E. (2002) Techniques for mapping suburban sprawl. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, v.63, pp.913–918.
Ewing, R. (1997) Is Los Angeles-style sprawl desirable? Jour. Amer. Planning Assoc., v.63(1), pp.107–126.
Ewing, R., Pendall, R., Chen, D. (2003) Measuring sprawl and its transportaion impacts. Transportation Research Record, v.1831, pp.175–183.
Foody, G. (1992) On the Compensation for Chance Agreement in Image Classification Accuracy Assessment. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, v.58(10), pp.1459–1460.
Friedl, M.A., Brodley, C.E. (1997) Decision tree classification of land cover from remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ., v.61, pp.399–409. DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(97)00049-7.
Galster, G., Hanson, R., Ratcliffe, M.R., Wolman, H., Coleman, S., Freihage, J. (2001) Wrestling sprawl to the ground: defining and measuring an elusive concept. Housing Policy Debate, v.12(4), pp.681–717.
Government of Rajasthan WR (2019) Water Resource department, Government of Rajasthan, viewed on 5th April, 2019, <http://water.rajasthan.gov.in/wrd>.
Haack, B.N., Rafter, A. (2006) Urban growth analysis and modeling in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Habit. Int., v.30(4), pp.1056–1065.
Hardin, P.J., Jackson, M.W., Oerstrom, S.M. (2007) Mapping, measuring, and modeling urban growth. In Geo-Spatial Technologies in Urban Environments: Policy, Practice, and Pixels, pp.141–17.
Hasse, J.E. and Lathrop, R.G. (2003) Land resource impact indicators of urban sprawl. Appl. Geograph., v.23(2), pp.159–175.
Iqbal, M.F. and Khan, I.A. (2014) Spatiotemporal land use land cover change analysis and erosion risk mapping of Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan Egypt. Jour. Remote Sens. Space Sci., v.17, pp.209–229.
Jat, M.K., Garg, P.K. and Khare, D. (2008) Modeling of urban growth using spatial analysis techniques: a case study of Ajmer city (India). Internat. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.29(2), pp.543–567.
Jenks, M. and Dempsey, N. (Eds.) (2005) Future Forms and Design for Sustainable Cities, Architectural Press, Oxford.
Jensen, J.R. (2005) Introductory digital image processing: a remote sensing perspective, third ed., Pearson Education Inc., Upper Saddle River. NJ.
Ji, W., Ma, J., Twibell, R.W., Underhill, K. (2006) Characterizing urban sprawl using multi-stage remote sensing images and landscape metrics. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst., v.30(6), pp.861–879.
Joshi, P.K., Lele, N. and Agarwal, S.P. (2006) Entropy as an indicator of fragmented landscape. Curr. Sci., v.91, pp.276–278.
Kantakumar, L.N. and Neelamsetti, P. (2015) Multi-temporal land use classification using hybrid approach Egypt. Jour. Remote Sens. Space Sci., v.18, pp.289–295.
Konecny, G., (2003) Geoinformation: Remote Sensing, Photogrammetry and Geographic Information Systems. Taylor & Francis.
Kundu, A., Dutta, D., Patel, N.R., Saha, S.K., Siddiqui, A.R., 2014a. Identifying the process of environmental changes of Churu district, Rajasthan (India) using remote sensing indices. Asian Jour. Geoinf., v.14, pp.14–22.
Kushner, J.A. (2002) Smart growth, new urbanism and diversity: progressive planning movements in America and their impact on poor and minority ethnic populations. UCLA. Jour. Envtl. L. Policy, v.21, pp.45.
Lillesand, T.M., Kiefer, R.W., Chipman, J.W. (2004) Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation(5th_edn.), John Wiley and sons, Inc.: Hoboken, New Jersey. Detection. http://www.isprs.org/proceedings/XXXVII/congress/7_pdf/10_ThS-18/22.pdf.
Lal, A.M. and Anouncia, S.M. (2015) Detection of boundaries by fusing the topographic sheets and multi-spectral images for geographic landscapes. Int. Jour. Ecol., v.30(3), pp.11–25.
Lata, K.M., Sankar, R.C.H., Krishna, P.V., Badrinath, K.V.S. and Raghavaswamy (2001) Measuring urban sprawl: a case study of Hyderabad. GIS Development, v.5, pp.8–13.
Li, X. and Yeh, A. G. O. (1998). Principal component analysis of stacked multi temporal images for the monitoring of rapid urban expansion in the Pearl River delta. Internat. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.19, pp.1501–18.
Lin, Z., Stamnes, S., Jin, Z., Laszlo, I., Tsay, S.-C., Wiscombe, W.J. and Stamnes, K. (2015) Improved discrete ordinate solutions in the presence of an anisotropically reflecting lower boundary: Upgrades of the DISORT computational tool. Jour. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer, v.157, pp.119–134.
Liu, T., Yang, X., (2015) Monitoring land changes in an urban area using satellite imagery, GIS and landscape metrics. Appl. Geograph., v.56, pp.42–54.
López, J.L., Mederos, C.M., Torres, Y., Leyva, L., (2001) Digestive indices and balance of nutrients in diets for growing pigs fed graded levels of ensiled Clitoria ternatea L.. Revista Computadorizada de Producción Porcina, v.8(2), pp.50–60.
Lucy Chepkosgei Chepkochei (2011) Object-Oriented Image classification of Individual trees using ERDAS Imagine objective: Case study of Wanjohi area, Lake Naivasha Basin, Kenya. Proceedings, Kenya Geothermal Conference.
Masser, I. (2001) Managing our urban future: the role of remote sensing and geographic information systems. Habit. Int., v.25(4), pp.503–512.
McCoy, Roger M. (2005) Field methods in Remote Sensing. New York: The Guilford Press.
Muñiz, I. and Galindo, A. (2005) Urban Form and the Ecological Footprint of Commuting. The Case of Barcelona. Ecolog. Econ., v.55, pp.499–514.
Parka, S., Jeon, S., Kim, S. and Choi, C. (2011) Prediction and Comparison of Urban Growth by Land Suitability Index Mapping Using GIS and RS in South Korea. Landscape and Urban Planning, v.99, pp.104–114.
Purkis, S.J., Klemas, V.V., (2011) Remote Sensing and Global Environmental Change. John Wiley & Sons.
Rawat, J.S., Biswas, V., Kumar, M., (2013) Changes in land use/cover using geospatial techniques: a case study of Ramnagar town area, district Nainital, Uttarakhand, India. Egypt. Jour. Remote Sens. Space Sci., v.16(1), pp.111–117
Rosenfield, G. and Fitzpat Rick-Lins, K. (1986) A Coefficient of agreement as a Measure of Thematic Classification Accuracy. Photogrammetric Engineering& Remote Sensing, v.52(2), pp.223–227.
Sharma, K.P. (2016) Regional Disparities in Socio Economic Development in Thar Desert. IJRG, v.2(3), pp.1–10.
Shaw, J.S. (2000) Sprawl and smart growth. Jour. Environ. Law, v.21, pp.43–74.
Sudhira, H.S., Ramachandra, T.V. and Jagadish, K.S. (2004) Urban sprawl: metrics, dynamics and modeling using GIS. Internat. Jour. Appld. Earth Observation and Geoinformation, v.5, pp.29–39.
Tewolde, M.G., Cabral, P., (2011) Urban sprawl analysis and modeling in Asmara, Eritrea. Remote Sens., v.3(10), pp.2148–2165.
The National Map Accuracy Standards (October 9, 1998) Minnesota Governor’s Council on Geographic Information, Spatial Data Accuracy Handbook.
Thomas, N., Hendrix, C., Congalton, R.G. (2003) A Comparison of Urban Mapping Methods using High-resolution Digital Imagery. Photogram. Engg. Remote Sens., v.69(9), pp.963–972.
Xu, H., Wang, X. and Xiao, G. (2000) A Remote Sensing and GIS Integrated Study on Urbanization with Its Impact on Arable Lands: Fuqing City, Fujian Province, China. Land Degradation & Development, v.11, pp.301–314. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-145X(200007/08)
Yeh, A.G.O. and Li, X. (1997). An integrated remote sensing and GIS approach in the monitoring and evaluation of rapid urban growth for sustainable development in the Pearl River Delta, China. Int. Plan. Stud., v.2(2), pp.193–210.
Yeh, A.G.O. and Li, X. (2001) Measurement and Monitoring of Urban Sprawl in a Rapidly Growing Region Using Entropy. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, v.67, pp.83–90.
Zubair, A.O. (2006) Change Detection in Land Use and Land Cover Using Remote Sensing Data and GIS: A Case Study of Ilorin and its Environs in Kwara State. <www.geospatialworld.net/uploads/thesis>.
Acknowledgement
The authors are indebted to ICSSR for financial assistance through MRP entitled “Application of Geo-Informatics for Sustainable Development of Environmental Resources in a Semi-Arid Region of India”. The authors also wish to acknowledge the editors of the journal for their timely and resourceful insights.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, J., Biswas, B. & Walker, S. Multi-temporal LULC Classification using Hybrid Approach and Monitoring Built-up Growth with Shannon’s Entropy for a Semi-arid Region of Rajasthan, India. J Geol Soc India 95, 626–635 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1489-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1489-x