Abstract
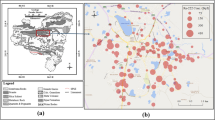
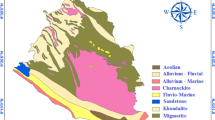
Parts of the coastal tracts of southern Kerala, India are among the well-known High Background Radiation Areas (HBRA) of the world, attributed to the presence of radionuclides in the monaziterich beach sand deposits. A comparative study of the radon concentrations in groundwater in the high and normal background radiation areas in the coastal tract has been taken up using analytical data of 24 ground water samples collected from tube wells of ranging in depth from 6.0 to 300.0 m. The radon concentration in the samples ranged from 0.88 to 25.80 Bq.L−1. The mean radon concentration in the study area, including those from the HBRA are within the maximum contamination levels of 300 pCi.L−1 (11.10 Bq.L−1) recommended by the United States Environmental Protection Agency except for a sample collected from Chavara. Groundwater from the high background radiation areas has significantly higher concentrations of radon ranging from 2.84 — 25.80 Bq.L−1 when compared to the normal background areas where the concentrations range from 0.86 — 7.46 Bq.L−1. Radon concentration does not show significant correlation with depth of sampled wells. The mean annual effective doses of ingestion and inhalation from water-borne radon, though comparatively higher in HBRA, are well below the average doses reported from all natural sources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliyu, A.S. and Ramli, A.T. (2015) The world’s high background natural radiation areas (HBNRAs) revisited: A broad overview of the dosimetric, epidemiological and radiobiological issues. Radiation Measurements, v.73, pp. 51–59.
Central Ground Water Board (2012) Aquifer Systems of Kerala. Unpub. Report of CGWB, Kerala Region, Thiruvananthapuram.
Cheriyan, V.D., Kurien, C.J., Das, B., Ramachandran, E.N., Karuppasamy, C.V., et al. (1999) Genetic monitoring of the human population from high level natural radiation areas of Kerala on the south-west coast of India; II. Incidence of numerical structural and chromosomal aberrations in the lymphocytes of newborns. Jour. Radiat. Res., v.152, pp. 154–158.
Chougaonkar, M.P., Eappen, K.P., Ramachandran, T.V., Shetty, G.P., Mayya, Y.S., Sadasivan, S., Venkat Raj, V. (2004) Profiles of doses to the population living in the high background radiation areas in Kerala, India. Jour. Environ. Radioactivity, v.71(3), pp.275–297
Christa, E.P., John, J.P., Vaidyan, V.K., Anilkumar, S., Eappen, K.P. (2011) Radiation dose in the high background radiation area in Kerala, India. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, v. 148(4), pp482–486
Das, B. (2010) Genetic studies on human population residing in High Level Natural Radiation Areas of Kerala coast. BARC Newsletter, no.313, pp.28–37
Das, B., Karuppasamy, C. (2009) Spontaneous frequency of micronuclei among the newborns from high level natural radiation areas of Kerala in the southwest coast of India. Int. Jour. Radiat. Biol., v.85, pp. 272–280.
D’Cunha, Primal., Narayana, Y., Karunakara, N., Yashodhara, I., and Kumara, S. (2011) Concentration of 222Rn in drinking water along coastal Kerala and evaluation of ingestion doses. Radiation Protection and Environment, v.34, pp. 197–200.
Derin, M.T., Vijayagopal., P, Venkatraman, B., Chaubey, R.C., Gopinathan, A. (2012). Radionuclides and Radiation Indices of High Background Radiation Area in Chavara-Neendakara Placer Deposits (Kerala, India). PLoS ONE, v.7(11): e50468. doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050468.
Divya P.V., Prakash, V. (2018) Seasonal variation of radon concentration in water and assessment of whole-body dose to the public along South-west coast of Kerala, India. Radiat. Prot. Environ., v.41, pp. 84–87.
Duggal, Vikas., Asha Rani., and Mehra, Rohit. (2012) In situ measurements of radon levels in groundwater in Northern Rajasthan, India. Adv. Appld. Sci. Res., v.3(6), pp. 3825–3830.
Dytham, Calvin. (2011) Choosing and Using Statistics: A Biologist’s Guide — 3rd Ed. Chichester, West Sussex, UK. Wiley-Blackwell.
EPA. (2012). User’s guide: Radionuclide carcinogenicity. Radiation protection. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. http://www.epa.gov/rpdweb00/heast/userguid.html. May 16, 2012; Accessed 25.06.2015.
George, K.P., Sundaram, K., Mistry, K.B., Ayengar, A.R.G. (1976) Investigations on human populations residing in high background radiation areas of Kerala and adjoining regions. Reprint from “Biological and environmental effects of low level radiation”. Vol. II, IAEA, Vienna, SM — 202/703, pp. 325–329.
Gopal Krishan., Rao, M.S., Kumar, C.P., Semwal, P. (2015) Radon concentration in groundwater of east coast of West Bengal, India. Jour. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., v.303, pp. 2221–2225.
Helsel, D.R., and Hirsch, R.M., (2002). Statistical Methods in Water Resources — Techniques of Water Resources Investigations. Book 4, chapter A3. U.S. Geological Survey.
Lee, J.M., Kim, G. (2006). A simple and rapid method for analysing radon in coastal and groundwaters using a radon-in-air monitor. Jour. Environ. Radioact., v.89, pp. 219–228.
Loveson, V.J., Chandrasekar, N., Sinha, A. (Ed.) (2005) Proceedings of the National Seminar on National Planning of Coastal Placer Minerals (PLACER- 2005). Allied Publishers Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.
Lyle, Shane (2007) The geology of radon in Kansas. Kansas Geological Survey Public Information Circular 26. Web version March 2007. http://www.kgs.ku.edu/Publications/PIC/pic25.html; Accessed 26.05.2015.
Mallik, T.K., Vasudevan, V., Aby Verghese, P. and Machado, T., (1987) The black sand placer deposits of Kerala beach, southwest India. Mar. Geol., v.77, pp. 129–150.
Nair, M.K., Nambi, K.S., Amma, N.S., Gangadharan, P., Jayalekshmi, P., Jayadevan, S., Cherian, V., Reghuram, K.N. (1999). Population study in the high natural background radiation area in Kerala, India. Radiat. Res., v.152 (6 Suppl), pp.S145–8.
Nair, R.R., Rajan, B., Akiba, S., Jayalekshmi, P., Nair, M. K., Gangadharan, P., Koga, T., Morishima, H., Nakamura, S., Sugahara, T. (2009) Background radiation and cancer incidence in Kerala, India-Karanagappally cohort study. Health Phys., v.96(1), pp. 55–66.
Nandakumaran, P., Vinayachandran, N., Anitha Shyam, T.S., Jose, Bijimol., Sarangan, S.M.S., Subramani, M.S. (2015) Radon in groundwater in parts of the coastal tracts of southern Kerala, India. Jour. Radioanl Nucl Chem. DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4272-5.
Paul, A.C., Pillai, P.M.B., Haridasan, P.P., Radhakrishnan, S., Krishnamony, S. (1998) Population exposure to airborne thorium at the high natural radiation areas in India. Jour. Environ. Radioact., v.40, pp. 251–259.
Rajan, T.N and Anil Kumar, P.S. (2005) Geology and Mineral Resources of the States of India PART IX — KERALA. Geological Survey of India, Miscellaneous Publication No. 30.
Ramachandra, T.V., Karthik, B., Boominathan, M., Sameer Ali and Avinash, K.G (2013) Waterscape of Kerala: Characterization of Surface, Well and Tap Water in All Districts, CES Technical Report 133, August 2013, Energy &Wetlands Research Group, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India.
Ravikumar, K.; Somasekhar, R.K. (2014) Determination of the radiation dose due to radon ingestion and inhalation. Int. Jour. Environ. Sci. Technol., v.11, pp.493–508
Roberts, L. E. J. (1984) Nuclear power and public responsibility. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge (UK), 143p.
Singh, P., Singh, P., Singh, S., Sahoo, B.K., Sapra B.K; Sapra, B.S. (2015). A study of indoor radon, thoron and their progeny measurement in Tosham region, Haryana, India. Jour. Radiation Res. Appld. Sci., v.8, pp. 226–233.
Sunta, C.M. (1993) A review of the studies of high background radiation areas of the S-W coast of India. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on High levels of Natural Radiation Areas. Ramsar, Iran. IAEA Publication Series, IAEA, Vienna, pp. 71–86.
Sunta, C.M., David, M., Abani, M.C., Basu, A.S., Nambi, K.S.V. (1982) Analysis of dosimetry data of high natural radioactivity areas of southwest coast of India. In: The Natural Radiation Environment, Wiley Eastern Limited, India, pp. 35–42.
Tayyeb, Z.A., Kinsara, A.R., Farid, S.M. (1998) A study on the radon concentrations in water in Jeddah (Saudi Arabia) and the associated health effects. Jour. Environ. Radioact., v.38(1), pp. 97–104.
Thampi, M.V., Cheriyan, V.D., Kurien, C.J., Ramachandran, E.N., Karuppasamy, C.V. (2002) Cytogenetic studies in the high level natural radiation areas of Kerala. Int. Congr. Ser., v.1225, pp. 207–211.
UNSCEAR. (1988) Sources, Effects and Risks of Ionizing Radiation. Report to the General Assembly, United Nations, New York.
UNSCEAR. (1993) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation., United Nations, New York.
UNSCEAR. (2000) Sources and effects and risks of ionizing radiation; Report to General Assembly with annexes. United Nations sales Publications E.94.IX.2. United Nations, New York.
Virk, H.S., Walia, V., Bajwa, B.S. (2001) Radon monitoring in underground water of Gurdaspur and Bathinda districts of Punjab, India. Indian Jour. Pure Appld. Physics, v.39, pp. 746–749.
WHO (World Health Organization). (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality; Radiological Aspects. 4th ed., WHO, Geneva, Switzerland.
Wu, Yun-Yun., Ma, Yong-Zhong., Cui, Hong-Xing., Liu, Jian-Xiang., Sun, Ya-Ru., Shang, Bing., Su, Xu. (2014) Radon Concentrations in Drinking Water in Beijing City, China and Contribution to Radiation Dose. Int. Jour. Environ. Res. Public Health, v.11, pp. 11121–11131.
Yu, K.N., Guan, Z.J., Stokes, M.J., Young, E.C.M. (1994) A preliminary study on the radon concentrations in water in Hong Kong and the associated health effects. Appl. Radiat. Isot., v.45, pp. 809–810.
Acknowledgements
The sampling and analysis of groundwater was carried out under a study taken up by the Central Ground Water Board, Kerala Region, Thiruvananthapuram during 2013–14. The authors are thankful to the Chairmen, Shri Sushil Gupta, Chairman (Retd.) and Shri. K B Biswas for granting permission to conduct the study and for publication of the paper. Thanks are also due to Dr. R C Jain, Member (SAM) and Shri K Md. Najeeb, Member (TT & WQ), Central Ground Water Board for their encouragement, as also to the Regional Director, CGWB, Bengaluru for making RAD 7 instrument available for work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandakumaran, P., Vinayachandran, N. A Preliminary Appraisal of Radon Concentration in Groundwater from the High Background Radiation Area (HBRA) of Coastal Kerala. J Geol Soc India 95, 491–496 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1466-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1466-4