Abstract
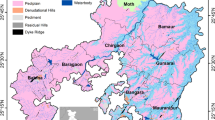
Groundwater demand in northwestern districts of Bangladesh is increasing rapidly with the growth of population and the expansion of irrigated agriculture. Development and management of groundwater resources are essential to supply the growing population with sufficient water for economic development as well as for the sustainable environment of the region. In the present study, groundwater recharge-abstraction balance method has been used for the spatial assessment of groundwater development potential. The abstraction of groundwater is estimated from irrigation and domestic water demands in the study area. The net recharge calculated from groundwater table fluctuation data, whereas the abstraction of groundwater is estimated from irrigation and domestic water demands in the study area. The study shows that out of twenty-six sub-districts, groundwater exploitation has reached to a critical condition in fourteen subdistricts. Development of surface water resources and water conservation are essential to reduce the stress on groundwater exploitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R.G., Pereira, L.S., Raes, D. and Smith, M. (1998) Crop evapotranspiration: Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56, FAO, Rome, Italy.
Asad-Uz-Zaman, M. and Rushton, K.R. (2006) Improved yield from aquifers of limited saturated thickness using inverted wells. Jour. Hydrol., v.326, pp.311–324.
Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (2011) Agricultural statistics yearbook-2011. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS), Dhaka.
Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (2012) Report of Bangladesh population and household census 2011. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS), Dhaka.
Banglapedia (2003) National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh. Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, Dhaka.
Begum, S.F., Bashar, K. and Hossain, M.S. (1997) An evaluation of hydraulic parameters of the aquifer and wells of the western part of the Barind area, Bangladesh. Bangladesh Geosci. Jour., v.3, pp.49–64.
Bhatti, M.A. (2002) Groundwater Management in South Asia:A Regional Initiative, Assemblée générale 2002- Québec, Province de Québec, ANADA. http://www.inbo-news.org/ag2002/GroundWaterAsia.htm. Accessed 25 January 2009
British Geological Survey And Department Of Public Health Engineering (2001) Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh. BGS Technical Report, WC/00/19, London.
Brouwer, C. and Heibloem, M. (1986) Irrigation Water Management: Irrigation Water Needs. Food and Agriculture Organization. FAO, Rome. http://www.fao.org/docrep/ S2022E/ S2022E00.htm#Contents. Accessed 25 January 2009.
Crosbie, R., Binning, P. and Kalma, J. (2005) A time series approach to inferring groundwater recharge using the water table fluctuation method. Wat. Resour. Res., v.41(1), pp.1–9.
Delin, G., Healy, R., Lorenz, D. and Nimmo, J. (2007) Comparison of local- to regional-scale estimates of ground-water recharge in Minnesota, USA. Jour. Hydrol., v.334(1-2), pp.231–249.
Faisal, I.M., Parveen, S. and Kabir, M.R. (2005) Sustainable Development through Groundwater Management: A Case Study on the Barind Tract. Wat. Resour. Dev., v.21, pp.425–435.
Haque, M.N., Keramat, M. and Rahman, A.M.A. (2000) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in the western Barind Tract of Bangladesh. Jour. Bangladesh National Geographical Assoc., v.21-26, pp.13–20.
Institute Of Water Research (1996).Overlay Methods, Institute of Water Research, Michigan State University. http:// www.iwr.msu.edu/edmodule/gis/foverpn.html. Accessed 25 January 2009.
Isaaks HE, Srivastava RM (1989) An Introduction to Applied Geostatisitics. Oxford University Press, New York.
Islam, M.M. and Kanumgoe, P. (2005) Natural recharge to sustainable yield from the Barind aquifer: A tool in preparing effective management plan of groundwater resources. Wat. Sc. and Tech., v.52, pp.251–258.
Jahan, C.S. and Ahmed, M. (1997) Flow of groundwater in the Barind area, Bangladesh: Implication of structural framework. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.50, pp.743–752.
Jahan, C.S., Mazumder, Q.H., Ghose, S.K. and Asaduzzaman, M, (1994) Specific yield evaluation: Barind area, Bangladesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.44, pp.283–290.
Johnson, A.I. (1967) Specific yield–Compilation of specific yields for various materials, USGS Water-Supply Paper, 1662-A.
Kasenow, M. (1997) Applied Groundwater Hydrology and Well Hydraulics. Water Resources Publications, LLC., Highlands Ranch, CO.
Komuscu, A.U., Erkan, A. and Oz, S. (1998) Possible impacts of climate change on soil moisture availability in the southeast Anatolia development project region (GAP): an analysis from an agricultural drought perspective. Climatic Change, v.40, pp.519–545.
Koo, M. and Lee, D. (2002) A numerical analysis on the applicability of the water level fluctuation method for quantifying groundwater recharge. American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2002, abstract #H52B-0867
Mahmood, R. (1997) Impacts of air temperature variations on the boro rice phenology in Bangladesh: implications for irrigation requirements. Agricultural and Forest Meteor., v.84(3), pp.233–247.
Master Planning Organization (1987) National Water Management Plan. Water Development and Flood Control, Government of Bangladesh, Dhaka.
Master Planning Organization (1991) National Water Management Plan (Update). Water Development and Flood Control, Government of Bangladesh, Dhaka.
Rasmussen, W.C. and Andreasen, G.E. (1959) Hydrologic budget of the Beaverdam Creek Basin. Maryland. USGS Water-Supply Paper 1472.
Risser, D., Gburek, W. and Folmar, G. (2005) Comparison of methods for estimating ground-water recharge and base flow at a small watershed underlain by fractured bedrock in the eastern United States. USGS Scientific Investigations Report 2005–5038.
Shahid, S. (2008) Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Droughts in the Western Part of Bangladesh. Hydrol. Proces., v.22(13), pp.2235–2247.
Shahid, S. (2010) Rainfall variability and the trends of wet and dry periods in Bangladesh, Internat. Jour. Climatology, v.30(15), pp.2299–2313.
Shahid, S. (2011) Impacts of Climate Change on Irrigation Water Demand in Northwestern Bangladesh. Climatic Change, v.105(3–4), pp.433–453
Shahid, S. and Behrawan, H. (2008) Drought Risk Assessment in the Western Part of Bangladesh. Natural Hazards, v.46(3), pp.391–413.
Shahid, S. and Hazarika, M.K. (2010) Groundwater Droughts in the Northwestern Districts of Bangladesh. Water Resources Management, v.24(10), pp.1989–2006
Shahid, S. and Khairulmaini, O.S. (2009) Spatio-Temporal variability of Rainfall over Bangladesh during the time period 1969–2003, Asia-Pacific Jour. Atmos. Sci., v.45(3), pp.375–389.
Shwets, V.M., Danilov, V.V. and Jahan, C.S. (1995) Seasonal effect on regional groundwater flow: Barind area, Bangladesh. Proc. Internat. Symp., 14–16 August, 1995, San Antonio, Texas.
Sinha, B.P.C. (1988) Natural ground water recharge estimation methodologies in India. In: I. Simmers (Eds.), Estimation of Natural Groundwater Recharge. D. Reidel Publishing Company, New York.
United Nations Development Program (2006) Human Development Report 2006, Beyond scarcity: Power, poverty and the global water crisis. United Nations Development Program, New York.
Water Resources Planning Organization (2004) National Water Management Plan. Water Resources Planning Organization (WAPRO), Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahid, S., Wang, XJ., Moshiur Rahman, M. et al. Spatial assessment of groundwater over-exploitation in northwestern districts of Bangladesh. J Geol Soc India 85, 463–470 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0238-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0238-z