Abstract
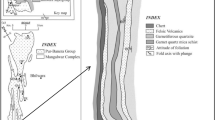
Detailed field and petrological studies in Vanambayi-Lingala-Lopatnutala section and old Kadiri Ghat-Pulivendela section in SW part of the Proterozoic Cuddapah basin of Eastern Dharwar craton brought to light the occurrence of hitherto unreported two significant phases of pyroclastic volcanic activity associated with the Vempalle Formation in Papaghni sub-basin. Occurrence of a significant pyroclastic agglomerate at the contact zone of Vempalle dolomite of Papaghni Group and Pulivendela quartzite of Chitravathi Group represents a significant event of the mafic phase of pyroclastic volcanic activity, while the finely laminated felsic tuff within the intercalated reddish siltstone, chert and dolomite sequence in the lower part of Vempalle Formation represents the felsic phase of pyroclastic activity. Studies indicate that the pyroclastic agglomerate zone in Vanambayi-Lingala-Lopatnutala section is a classical example of pyroclastic volcanism wherein the highly vesicular rock with rounded basalt clasts often exhibit embayed contact of welded nature with the matrix. The pyroclastic zone reported in the present paper particularly at the interface of Vempalle Formation and Pulivendela quartzite in Vanambayi-Lingala-Lopatnutala section represents a significant tectono-magmatic event of explosive volcanic activity that is contemporaneous with the culmination of the carbonate precipitation of Vempalle dolomite and marks the termination of sedimentation in Papaghni Group in southwestern part of Cuddapah basin during Paleoproterozoic times.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand, M., Gibson, S.A., Subba Rao, K.V., Kelley, S.P. and Dicken, A.P. (2003): Early Proterozoic melt generation process beneath the intracratonic Cuddapah basin, Southern India. Jour. Petrol., v.44(12), pp.2139–2171.
Ayres, L.D., van Wagoner, N.A. and Ferreira, W.S. 1991: Voluminous shallow water to emergent phreatomagmatic basaltic volcaniclastic rocks, Proterozoic (1886 Ma) Amisk Lake composite volcano, Flin Flon greenstone belt, Canada. In Sedimentation in Volcanic Settings. SEPM Spec. Publ., No. 47, pp.175–187.
Basei, M.A.S., Citroni, S.B. and Siga, Jr. O. (1998) Stratigraphy and age of Fini-Proterozoic basins of Paraná and Santa Catarina States, southern Brazil. Bol. IG-USP, Sér. Cient. Vol.29 São Paulo
Basu, A. and Bickford, M.E. (2013) Contributions of zircon UPb geochronology to understand the volcanic and sedimentary history of some Purana basins, India. Jour. Asian Earth Sci. online July 2013
Bhattacharji, J.C. and Singh, R.N. (1984) Thermo mechanical structure of the southern part of Indian sheild and its relevance to Precambrian basin evolution. Tectonophysic, v.105, pp.1103–1120.
Bickford, M.E. and Boardman, S.J. (1984) A Proterozoic Volcano-Plutonic Terrane, Gunnison and Salida Areas, Colorado. Jour. Geol., v.92(6), pp. 657–666.
Chalapathi Rao, N.V., Fu Yuan and Srinivas, M. (2012) Mesoproperozoic emplacement and enriched derivation of Racherla alkali syenite, Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Cuddapah basin, southern India: insights from in situ Sr-Nd isotope analyses of apatite. Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., v.365, pp.185–195.
Chatterjee, N. and Bhattacharji, S. (2001) Petrology, geochemistry and tectonic setting of the mafic dykes and sills associated the evolution of the Proterozoic Cuddapah basin, South India. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.) v.110(4), pp.433–453.
Chetty, T.R.K. (1999) Some observations on the tectonic framework of Southeastern Indian Shield. Gondwana Res., v.2, pp.651–653.
Dimarco, M.J. and Lowe, D.R. (1989) Stratigraphy and sedimentology of an early Archaean felsic volcanic sequence, eastern Pilbara Block, Western Australia, with special reference to the Duffer Formation and implications for crustal evolution. Precambrian Res., v.44(2), pp.147–169
Fisher, R.V. (1966) Classification of the pyroclastic rocks. Earth Sci. Rev., v.1, pp.287–298.
French, J.E., Heamen, L.M., Chacko, T. and Srivastava, R.K. (2008) 1891–1883 Ma Southern Bastar-Cuddapah mafic igneous events, India: a newly recognised large igneous province. Precambrian Res., v.160, pp.308–322.
Hildebrand, R.S. and Bowring, S.A. (1984) Continental intra-arc depressions: A nonextensional model for their origin, with a Proterozoic example from Wopmay orogen. Geology, v.12, No.2, pp.73–77.
Jhanwar, M.L., Rajurkar, S.T. and Phadtere, P.N. (1964) Stratigraphy of Vempalle Formation of Cuddapah basin. Jour. Indian Geoscience. Assoc., v.4, pp.43–62.
King, W. (1872) The Kadapa and Kurnul Formations in Madras. Mem.Geol. Surv. India No.8 (1), pp.1–320.
Lakshminarayana, G., Bhattacharjee, S. and Ramanaidu, K.V. (2001) Sedimentation and stratigraphic framework in the Cuddapah basin. Geol. Surv. India Spec. Publ. No. 55, pp.31–58.
Mazumder, R. (2005) Proterozoic sedimentation and volcanism in Singhbhum crustal province, India and their implications. Sedimentary Geol., v.176. pp.167–193.
Mueller, W.U., Garde, A.A. and Stendal, H. (2000) Shallow-water, eruption-fed, mafic pyroclastic deposits along a Paleoproterozoic coastline: Kangerluluk volcano-sedimentary sequence, southeast Greenland. Precambrian Research 101, pp.163–192
Murthy, N.G.K. (1964) The traps and dolerites in the Cuddapah basin. Jour. Indian Geoscience. Assoc., v.4, pp.79–88.
Nagaraja Rao, B.K., Ramalingaswamy, Rajurkar, S.T. and Ravindra Babu, B. (1987): Stratigraphy, structure and evolution of the Cuddapah basin. Purana basins of Peninsular India. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.6, pp.33–86.
Saha, D. and Tripathy, V. (2012): Tuff beds in Kurnool Sub basin, southern India and implications for felsic volcanism in Proterozoic intracratonic basins. Geoscience Frontiers, v.3(4), pp.429–444.
Sen, S.N. and Narasimha Rao, Ch. (1967) Igneous activity in Cuddapah basin and adjacent areas and suggestions on paleogeography of the basin. Symposium on Upper mantle project. GRB & NGRI, Publ. No.8, p.261–285
Sesha Sai, V.V. (2005) Petrographic and Petrochemical characterisation of Proterozoic granites in Northeastern fringes of Cuddapah basin, Andhra Pradesh. National Seminar on Proterozoic Systems of India. Evolution and Economic Potential, ISM, Dhanbad.
Sesha Sai, V.V. (2006) Igneous activity in Proterozoic Cuddapah basin. Vol. on Res. papers in DST sponsored field workshop “Cuddapah Basin” conducted by GSITI, Hyderabad, pp.53–62.
Sesha Sai, V.V. and Reddy, U.V.B. (2008) Occurrence of volcaniclastic conglomerate in Upper Part of Vempalle Formation in Lingala-Kuppalapalle section, Cuddapah district, Andhra Pradesh — Field evidence for first major phase of igneous activity in the Proterozoic Cuddapah basin. Abstract volume of 1st A.P Science Congress, Hyderabad, pp.42.
Sesha Sai, V.V. (2010) Petrology and Mineral Chemistry of Picrite Sill from Peddakudala-Velpula Area in Southwestern Part of the Proterozoic Cuddapah Basin, Andhra Pradesh, India. In: R.K. Srivastava (Ed.), Dyke Swarms: Keys for Geodynamic Interpretation, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp.115–124.
Srikantia, S.V. (1984). Kuppalapalle volcanic-a distinct Upper Papaghni volcanic activity in the Cuddapah Basin. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.25(12), pp.775–779.
Srivastava, R.K. and Gautam, G.C. (2009) Precambrian mafic magmatism in Bastar Craton, Central India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.73, pp. 52–72.
Tewari, H.C. and Rao, V.K. (1987) A high velocity intrusive body in the upper crust in the south western part of Cuddapah basin as delineated by Deep Seismic Sounding and gravity modeling. Purana basins of Peninsular India. Mem.Geol. Soc. India, no.6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sesha Sai, V.V. Pyroclastic volcanism in Papaghni sub-basin, Andhra Pradesh: Significant Paleoproterozoic tectonomagmatic event in SW part of the Cuddapah basin, Eastern Dharwar craton. J Geol Soc India 83, 355–362 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0052-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0052-z