Abstract
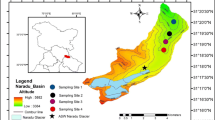
The river at its origin known as “Bhagirathi” attains the title “Ganga” after its confluence with Alaknanda, originates from the snout of Gangotri glacier. Water samples were collected from the selected sites from Gaumukh to Haridwar (2000–2001) for two seasons (pre-monsoon and post-monsoon) and analyzed for various physico-chemical characteristics. The pH, nitrate (NO3), conductance, chloride, alkalinity, total hardness, fluoride, sulphate and total dissolved solids were found to be in the ranges of 6.0–7.6, 0.225–10.6 mg/l, 73.0–978 μmhos, 5.0–70.0 mg/l, 15–90 mg/l, 10.0–250.0 mg/l, 0.23–1.60 mg/l, 12.0–150.0 mg/l and 37.0–190.6 mg/l respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, S. and Hasnain, S.I. (2001) Snow and stream water chemistry of the Ganga head water basin, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Hydrological sciences-Journal-des-Sciences Hydrologiques, v.46, pp.103–111.
Ahmad, S. and Hasnain, S.I. (2000) Meltwater characteristics of Garhwal Himalayan glaciers. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.56, pp.431–439.
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (1998) Standard methods for the analysis of water and waste water (20th edition). Am. Public Health Assoc., Washington DC, USA.
Bales, R.C. (1992) Snowmelt and the ionic pulse. In: Encyclopedia of Earth Science., Academic press, Ornaldo, Florida, USA, v.1, pp.199–207.
Bhatt, B.K. (1963). Preliminary studies of Bhagirathi basin between Uttarkashi and Gomukh. In: Proceedings of Symposium on Himalayan Glaciers. Geol. Surv. India. Misc. Publ., v.15, pp.1–8.
Hasnain, S.I. (1999) Runoff characteristics of a glacierized catchment, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Hydrological Sciences-Journal-des-Sciences Hydrologiques, v.44(6), pp.847–854.
Mukherjee, B.P. and Sangewar, C.V. (2001) Recession of the Gangotri glacier through 20th century. Nat. Symp. Role of Earth Sci. Integrated Development and Related Societal Issues. Geol. Surv. India Spec. Publ., No.65 (III), pp.1–3.
Naithani, A.K., Nainwal, H.C., Sati, K.K. and Prasad, C. (2001) Geomorphological Evidences of Retreat of the Gangotri glacier and its characteristics. Curr. Sci., v.80(1), pp.87–94.
Nijampurkar, V. N., Sarin, M.M. and Rao, D.K. (1993) Chemical composition of snow and ice from Chhota Shigri glacier, Central Himalaya. Jour. Hydrology, v.151, pp.19–34.
Pandey, S.K., Singh, A.K. and Hasnain, S.I. (2001) Hydrochemical characteristics of meltwater draining from Pindari glacier, Kumaon Himalaya. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.57, pp.519–527.
Puri, V.M.K. and Shukla, S.P. (1996) Tongue fluctuation studies on Gangotri glacier, Uttar Kashi dist., Uttar Pradesh. Proc. Symp. NW Himalaya and Foredeep. Geol. Surv. India Spec. Publ., no.21, pp.289–291.
Reuss, J.O. and Johanson, D.W. (1986) Acidic deposition and acidification of soil and surface waters. Ecological studies No. 59, Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
Sarin, M.M. and Krishnaswami, S. (1984) Major ion chemistry of the Ganga-Brahmaputra river systems, India. Nature, v.312, No.5994, pp.538–541.
Sarin, M.M., Krishnaswami, S., Trivedi, J.R. and Sharma, K.K. (1992) Major ion chemistry of the Ganga source waters: weathering in the high altitude Himalaya. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet., Sci.), v.101, No.1 pp. 89–98.
Singh, A.K. and Hasnain, S.I. (1998) Major ion chemistry and weathering control in a high altitude basin: Alaknanda River, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Hydrological Sciences-Journal-des-Sciences Hydrologiques., v.43(6), pp.825–843.
Singh, J. and Yadav, R.R. (2000) Tree ring indicators of recent glacier fluctuations in Gangotri, Western Himalaya, India. Curr. Sci., v.79(11), pp.1598–1601.
Singh, D.S. and Mishra, A. (2001) Gangotri glacier characteristics, retreat and processes of sedimentation in the Bhagirathi valley. Geol. Surv. India Spec. Publ. No.65 (III), pp.17–20.
Williamson, P. and Gribbin, J. (1991) How plankton change the climate. New Scientist, pp.48–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trivedi, S., Gopal, K. & Singh, J. Hydrogeochemical attributes of the meltwater emerging from Gangotri glacier, uttaranchal. J Geol Soc India 76, 105–110 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0087-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0087-8