Abstract
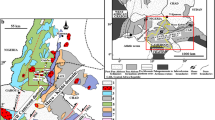
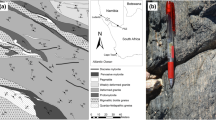
The Karakoram Shear Zone is a northwest-southeast trending dextral ductile shear zone, which has affected the granitic and granodioritic bodies of the southern Asian Plate margin in three distinct episodes. The ductile shearing of the granitic bodies at Tangste and Darbuk has resulted in the development of mylonites with mylonitic foliation and stretching lineation. More intense deformation is noted in the Tangste granite grading up to orthomylonite, as compared to the Darbuk granite. Kinematic indicators include S-C foliation, synthetic C′ and C″ antithetic shear bands, Type A s-mantled porphyroclasts, oblique quartz foliation, micro-shears with bookshelf gliding, mineral fishes including Group 2 mica fishes, and Type 1 and 2a pull-apart microstructures, and exhibit strong dextral sense of ductile shearing towards southeast. The textural features of the minerals, especially that of quartz and feldspar, indicate temperature of mylonitisation ranging between 300 and 500°C in the upper greenschist facies, and appear to have been evolved during exhumation as a consequence of oblique strike-slip movements along the Karakoram shear zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armijo, R., Tapponnier, P. and Tonglin, H. (1989) Late Cenozoic right-lateral strike slip faulting in southern Tibet. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.94, pp.2787–2838.
Avouac, J.-P. and Tapponnier, P. (1993) Kinematic model for active deformation in Central Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett., v.20, pp.895–898.
Berthe, D., Choukroune, P. and Jegouzo, P. (1979) Orthogneiss, mylonite and non-coaxial deformation of granites: the example of the South Armorican shear zone. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.1, pp.31–42.
Boullier, A.-M. (1980) A preliminary study on the behavior of brittle minerals in a ductile matrix: example of zircons and feldspars. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.2, pp.211–217.
Brown, E.T., Bendick, R., Bourles, D.L., Gaur, V., Molnar, P., Raisbeck, G.M. and Yiou, F. (2002) Slip rates of the Karakoram fault, Ladakh, India, determined using cosmic ray exposure dating of debris flows and morains. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.107(B9), pp.2192.
Dewey, J.F., Shackleton, R.M., Chang, C. and Sun, Y. (1988) The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. London, v.327, pp.379–413.
Hippertt, J.F.M. (1993) ’V’-pull-apart microstructures: a new shear sense indicator. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.15, pp.1392–1404.
Hodges, K.V. (2000) Tectonics of the Himalaya and southern Tibet from two decades perspectives. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.112, pp.324–350.
Honegger, K., Dietrich, V., Frank, W., Gansser, A., Thoni, M. and Trommsdorff, V. (1982) Magmatism and metamorphism in the Ladakh Himalaya (the Indus-Tsangpo suture zone). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.60, pp.253–292.
Jain, A.K. and Singh, S. (2008) Tectonics of the southern Asian Plate margin along the Karakoram Shear Zone: Constraints from field observations and U-Pb SHRIMP ages, Tectonophysics, v.451, pp.186–205.
Jain, A.K. and Singh, S. (2009) Geology and tectonics of southeast Ladakh and Karakoram. Geol. Soc. India, 181p.
Jain, A.K., Manickavasagam, R.M. and Singh, Sandeep (2002) Himalayan collision tectonics. Gondwana Res. Group Mem., v.7, 114p.
Jain, A.K., Singh, S. and Gupta, K.R. (2007) A late Cretaceous Karakoram Shear zone and its reactivation during the late Cenozoic. Gondwana Res. Group Mem., v.10, pp.77–88.
Jain, A.K., Singh, S., Manickavasagam, R.M., Joshi, M. and Verma, P.K. (2003) HIMPROBE Programme: integrated studies on geology, petrology, geochronology and geophysics of the trans-Himalaya and Karakoram. In: T.M. Mahadevan, B.R., Arora and K.R. Gupta, (Eds.), Indian Continental Lithosphere: Emerging Research Trends. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.53, pp.1–56.
Lacassin, R., Valli, F., Arnaud, N., Leloup, P.H., Paquette, J.L., Haibing, L., Tapponnier, P., Chevalier, M.-L., Guillot, S., Maheo, G. and Zhiqin, X. (2004) Large-scale geometry, offset and kinematic evolution of the Karakoram fault, Tibet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.219, pp.255–269.
Lister, G.S. and Snoke, A.W. (1984) C-S mylonites. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.6, pp.617–638.
Matte, Ph., Tapponnier, P., Arnaud, N., Bourjot, L., Avouac, J.-P., Vidal, Ph., Liu, Q., Pan, Y. and Wang, Y. (1996) Tectonics of Western Tibet, between the Tarim and Indus. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.142, pp.311–220.
Mukherjee, S. (2007). Geodynamics, deformation and mathematical analysis of Metamorphic Belts, NW Himalaya. Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee. India. Unpubl. Ph.D. Thesis. 267p.
Murphy, M.A., Yin, A., Kapp, P., Harrison, T.M., Ding, L. and Guo, J. (2000) Southward propagation of the Karakoram fault system, southwest Tibet: timing and magnitude of slip. Geology, v.28, pp.451–454.
Nyman, M.W., Law, R.D. and Smelik, E. (1992) Cataclastic deformation mechanism for the development of core-mantle structures in amphibole. Geology, v.20, pp.455–458.
Parrish, R.R. and Tirrul, R. (1989) U-Pb ages of the Baltoro granite, northwest Himalaya, and implication for zircon inheritance and monazite U-Pb systematics. Geology, v.17, pp.1076–1079.
Passchier, C.W. (1982) Mylonitic deformation in the Saint-Barthelemy Massif, French Pyrenees, with emphasis on the genetic relationship between ultramylonite and pseudotachylyte. GUA Pap Geol. Ser. 1, v.16, pp.1–173.
Passchier, C.W. and Simpson, C. (1986) Porphyroblast system as kinematic indicators. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.8, pp.831–844.
Passchier, C.W. and Trouw, R.A.J. (1996) Microtectonics, Springer-Verlag. 289 p.
Peltzer, G. and Tapponnier, P. (1988) Formation and evolution of strike-slip faults, rifts, and basins during India-Asia collision: an experimental approach. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.93, pp.15085–15117.
Phillips, R.J., Parrish, R.R. and Searle, M.P. (2004) Age constraints on ductile deformation and long-term slip rates along the Karakoram fault zone, Ladakh. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.26, pp.305–319.
Phillips, R.J and Searle, M.P. (2007) Macrostructural and microstructural architecture of the Karakoram Fault: Relationship between magmatism and strike-slip faulting. Tectonics, v.26, TC3017, doi:10.1029/2006TC001946.
Pryer, L.L. (1993) Microstructures in feldspar from a major crustal thrust zone: the Grenville front, Ontario, Canada. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.15, pp.21–36.
Rolland, Y. and Pecher, A. (2001) The Pangong granulites of the Karakoram Fault (Western Tibet): vertical extrusion within a lithospheric-scale fault. Comptes Rendus de l’Academy des Sciences, Paris, v.332, pp.363–370.
Rolland, Y., Pecher, A. and Picard, C. (2000) Middle Cretaceous back-arc formation and arc evolution along the Asian margin: the Shyok Suture Zone in northern Ladakh (NW Himalaya). Tectonophysics, v.325, pp.145–173.
Rolland, Y., Mahéo, G., Pêcher, A. and Villa, I.M. (2009) Synkinematic emplacement of the Pangong metamorphic and magmatic complex along the Karakorum Fault (N Ladakh). Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.34, pp.10–25.
Rutter, E.H., Faulkner, D.R, Brodie, K.H., Phillips R.J. and Searle, M.P. (2007) Rock deformation processes in the Karakoram fault zone, Eastern Karakoram, Ladakh, NW India. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.15, pp.1315–1326.
Samanta, S.K., Mandal, N. and Chakraborty, C. (2002) Development of different types of pull-apart microstructures in mylonites: an experimental investigation. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.24, pp.1345–1355.
Searle, M.P. (1996) Geological evidence against large-scale pre-Holocene offsets along the Karakoram Fault: implications for the limited extrusions of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics, v.15, pp.171–186.
Searle, M.P., Weinberg, R.F. and Dunlap, W.J. (1998) Transpressional tectonics along the Karakoram Fault Zone, northern Ladakh. In: R.E. Holdsworth, R.A. Strachan and J.E. Dewey (Eds.), Continental Transpressional and Transtensional Tectonics. Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., v.135, pp.307–326.
Sharma, K.K. and Gupta, K.R. (1978) Some observations on the geology of the Indus and Shyok valleys between Leh and Panamik, District Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir, India. Recent Res. in Geol., v.7, pp.133–143.
Sibson, R.H. (1977) Fault rocks and fault mechanisms. Jour. Geol. Soc. London, v.133, pp.191–213.
Simpson, C. (1985) Deformation of granitic rocks across the brittle-ductile transition. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.7, pp.503–511.
Singh, S., Kumar, R., Barley, M.E. and Jain, A.K. (2007) SHRIMP U-Pb ages and depth of emplacement of Ladakh Batholith, eastern Ladakh, India. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.30, pp.490–503.
Srikantia, S.V., Ganesan, T.M. and Wangdus, C. (1982) A note on the tectonic framework and geological set-up of the Pangong-Chushul sector, Ladakh Himalaya. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.23, pp.354–357.
Srimal, N. (1986) India-Asia collision: implications from the geology of the eastern Karakoram. Geology, v.14, pp.523–527.
Srimal, N., Basu, A.R. and Kyser, T.K. (1987) Tectonic inferences from oxygen isotopes in volcano-plutonic complexes of the India-Asia collision zone, NW India. Tectonics, v.6, pp.261–273.
Stipp, M., Stünitz, H., Heilbronner, R. and Schmid, S.M. (2002) The eastern Tonale fault zone: a “natural laboratory” for crystal plastic deformation of quartz over a temperature range from 250 to 700°C. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.24, pp.861–884.
Ten Grotenhuis, S.M., Trouw, R.A.J. and Passchier, C.W. (2003) Evolution of mica fish in mylonitic rocks. Tectonophysics, v.372, pp.1–21.
Thakur, V.C. (1993) Geology of the Western Himalaya. Pergmon Press, Oxford and New York, 355p.
Toy, V.G., Prior, D.J. and Norris, R.J. (2008) Quartz fabrics in the Alpine Fault mylonites: Influence of pre-existing preferred orientations on fabric development during progressive uplift. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.30, pp.602–621.
Weinberg, R.F. and Dunlap, J. (2000) Growth and deformation of the Ladakh Batholith, Northwest Himalayas: implications for timing of continental collision and origin of calc-alkaline batholiths. Jour. Geol., v.108, pp.303–320.
Weinberg, R.F. and Searle, M.P. (1998) The Pangong Injection Complex, Indian Karakoram: a case of pervasive granite flow through hot viscous crust. Jour. Geol. Soc. London, v.155, pp.883–891.
Weinberg, R.F., Dunlap, W.J. and Whitehouse, M. (2000) New field, structural and geochronological data from the Shyok and Nubra valleys, northern Ladakh: linking Kohistan to Tibet. In: M.A., Khan, P.J., Treloar, M.P. Searle and M.Q. Jan (Eds.), Tectonics of the Nanga Parbat Syntaxis and the Western Himalaya. Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., v.170, pp.253–275.
White, S. (1975) Tectonic deformation & recrystallisation of oligoclase. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.50, pp. 287–304.
White, S.H. (1977) Geological significance of recovery and recrystallization processes in quartz. Tectonophysics, v.39, pp.143–170.
Wise, D.V., Dunn, D.E., Engelder, J.T., Geiser, P.A., Hatcher, R.D., Kish, S.A., Odom S.A. and Schame, S. (1984) Fault related rocks: suggestions for terminology. Geology, v.12, pp.391–394.
Yin, A., Harrison, T.M., Murphy, M.A., Grove, M., Nie, S., Ryerson, F.J., Feng, Wang Xiao and Le, Chen Zheng (1999) Tertiary deformation history of southeastern and southwestern Tibet during the Indo-Asian collision. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.111, pp.1644–1664.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, P., Jain, A.K. & Singh, S. Microstructures of mylonites along the Karakoram Shear Zone, Tangste Valley, Pangong Mountains, Karakoram. J Geol Soc India 75, 679–694 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0065-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0065-1