Abstract
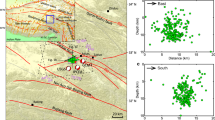
On May 22, 2021, a Mw 7.3 earthquake occurred in Maduo County, Qinghai Province with the epicenter of 34.59°N, 98.34°E. The distribution of aftershocks and surface ruptures suggested that the seismogenic structure might be the Jiangcuo fault (JF), <70 km south of East Kunlun fault (EKLF). Due to the high altitude and sparse human habitats, there are very few researches on the Jiangcuo fault, which makes us know little about the deformation features and even the geometry of Jiangcuo fault. In this study, we used the high-resolution pre-earthquake satellite images to interpret the spatial distribution and geometry of the Jiangcuo fault. Our results show that the Jiangcuo fault strikes nearly east, extending 180-km-long from Eling Lake to east of Changmahe Town. Based on the geometric features, the Jiangcuo fault could be divided into three segments characterized as the linear structures, fault valleys, scarps and systematic offset of channels. The boundary between Bayan Har Block and Qaidam Block is presented as a wide deformation zone named of Kunlun belt that is composed of East Kunlun fault and several branch faults around Anemaqen Mountain. Geometric analysis and deep lithosphere structure around Maduo County suggest that the Jiangcuo fault should be one of branch of East Kunlun fault at south, where the Kunlun fault developed as a giant flower structure. In addition, the seismic hazards potential of Jiangcuo fault should be given enough attention in the future, because west of the Jiangcuo fault, there is a rupture gap between the co-seismic surface ruptures of the 2001 Kunlun, 2021 Maduo and 1937 Huashixia Earthquakes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Bai, M. K., Chevalier, M. L., Pan, J. W., et al., 2018. Southeastward Increase of the Late Quaternary Slip-Rate of the Xianshuihe Fault, Eastern Tibet: Geodynamic and Seismic Hazard Implications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 485: 19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2017.12.045
Bai, S. H., 1992. Geological Map of the Republic of China (1: 200 000 Hegesi Sheet). Geological Brigade of Regional Geological Survey in Qinghai Province, Xining (in Chinese)
Chen, J., Chen, Y. K., Ding, G. Y., et al., 2003. Surface Rupture Zones of the 2001 Earthquake Ms 8.1 West of Kunlun Pass, Northern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Quaternary Sciences, 23(6): 629–639 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Chevalier, M. L., Leloup, P. H., Replumaz, A., et al., 2018. Temporally Constant Slip Rate along the Ganzi Fault, NW Xianshuihe Fault System, Eastern Tibet. GSA Bulletin, 130(3/4): 396–410. https://doi.org/10.1130/b31691.1
Cunningham, W. D., Mann, P., 2007. Tectonics of Strike-Slip Restraining and Releasing Bends. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 290(1): 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1144/sp290.1
Deng, Q. D., Gao, X., Chen, G. H., et al., 2010. Recent Tectonic Activity of Bayankala Fault-Block and the Kunlun-Wenchuan Earthquake Series of the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(5): 163–178 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Deng, Q. D., Ran, Y. K., Yang, X. P., et al., 2007. Active Tectonic Map of China. Seismological Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Deng, Q. D., Zhang, P. Z., Ran, Y. K., et al., 2003. Active Tectonics and Earthquake Activities in China. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(S1): 66–73 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Department of Earthquake Disaster Prevention of State Seismological Bureau, 1995. The Catalogue of Historical Strong Earthquakes in China. Seismological Press, Beijing. 1–514 (in Chinese)
Guo, J. M., Lin, A. M., Sun, G. Q., et al., 2007. Surface Ruptures Associated with the 1937 M 7.5 Tuosuo Lake and the 1963 M 7.0 Alake Lake Earthquakes and the Paleoseismicity along the Tuosuo Lake Segment of the Kunlun Fault, Northern Tibet. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 97(2): 474–496. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120050103
Karplus, M. S., Zhao, W., Klemperer, S. L., et al., 2011. Injection of Tibetan Crust beneath the South Qaidam Basin: Evidence from INDEPTH IV Wide-Angle Seismic Data. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 116(B7): B07301. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010jb007911
Kilb, D., Gomberg, J., Bodin, P., 2002. Aftershock Triggering by Complete Coulomb Stress Changes. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 107(B4): ESE2–1. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001jb000202
Kirby, E., Harkins, N., Wang, E. Q., et al., 2007. Slip Rate Gradients along the Eastern Kunlun Fault. Tectonics, 26(2): TC2010. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006TC002033
Li, C. F., He, Q. L., Zhao, G. G., 2004. Holocene Slip Rate along the Eastern Segment of the Kunlun Fault. Seismology and Geology, 26(4): 122–133 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, C. X., Xu, X. W., Wen, X. Z., et al., 2011. Rupture Segmentation and Slip Partitioning of the Mid-Eastern Part of the Kunlun Fault, North Tibetan Plateau. Science China Earth Sciences, 41(9): 12–13 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, C. X., Yuan, D. Y., Yang, H., et al., 2016. The Tectonic Activity Characteristics of Awancang Fault in the Late Quaternary, the Sub-Strand of the Eastern Kunlun Fault. Seismology and Geology, 38(1): 44–64 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, H. B., Pan, J. W., Sun, Z. M., et al., 2021. Continental Tectonic Deformation and Seismic Activity: A Case Study from the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(1): 194–213 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, H. B., van der Woerd, J., Tapponnier, P., et al., 2005. Slip Rate on the Kunlun Fault at Hongshui Gou, and Recurrence Time of Great Events Comparable to the 14/11/2001, Mw ∼ 7.9 Kokoxili Earthquake. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 237(1/2): 285–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.05.041
Li, Z. M., Xu, Y. R., Li, T., et al., 2021. Preliminary Investigation on Seismogenic Structure and Surface Rupture of Maduo Ms7.4 Earthquake on May 22, 2021, Qinghai Province. Seismology and Geology. Accepted (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liang, M. J., Yang, Y., Du, F., et al., 2020. Late Quaternary Activity of the Central Segment of the Dari Fault and Restudy of the Surface Rupture Zone of the 1947 M7 3/4 Dari Earthquake, Qinghai Province. Seismology and Geology, 42(3): 703–714 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liang, M. J., Zhao, R. J., Yan, L., et al., 2013. Study on the Late Quaternary Activity Characteristics and Its Tectonic Geomorphology Response of the Middle Segment of Dari Fault in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(z1): 403–405 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Lin, A. M., Nishikawa, M., 2011. Riedel Shear Structures in the Co-Seismic Surface Rupture Zone Produced by the 2001 Mw 7.8 Kunlun Earthquake, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Structural Geology, 33(9): 1302–1311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2011.07.003
Liu, L., Li, Y. J., Zhu, L. Y., et al., 2021. Influence of the 1947 Dari Ms7.7 Earthquake on Stress Evolution along the Boundary Fault of the Bayan Har Block: Insights from Numerical Simulation. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(7): 2221–2231 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ma, S. L, Chen, S. Y., Liu, P. X., et al., 2008. Experimental Study on the Effect of Fault Step on Sliding Behavior. Science China Earth Sciences, 38(7): 842–851 (in Chinese)
Mo X. X., 2020. Growth and Evolution of Crust of Tibetan Plateau from Perspective of Magmatic Rocks. Earth Science, 45(7): 2245–2257. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2020.160 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Molnar, P., Chen, W. P., 1983. Focal Depths and Fault Plane Solutions of Earthquakes under the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 88(B2): 1180–1196. https://doi.org/10.1029/jb088ib02p01180
Molnar, P., Stock, J. M., 2009. Slowing of India’s Convergence with Eurasia since 20 Ma and Its Implications for Tibetan Mantle Dynamics. Tectonics, 28(3): TC3001. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008tc002271
Pan, J. W., Bai, M. K., Li, C., et al., 2021. Coseismic Surface Rupture and Seismogenic Structure of the 2021-05-22 Maduo (Qinghai) Ms7.4 Earthquake. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(6): 1655–1670 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ren, J. J., Xu, X. W., Yeats, R. S., et al., 2013. Millennial Slip Rates of the Tazang Fault, the Eastern Termination of Kunlun Fault: Implications for Strain Partitioning in Eastern Tibet. Tectonophysics, 608: 1180–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2013.06.026
Ren, Z. K., Zhang, Z. Q., 2019. Structural Analysis of the 1997 Mw 7.5 Manyi Earthquake and the Kinematics of the Manyi Fault, Central Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 179: 149–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.05.003
Seismological Bureau of Qinghai Province, Institute of Crustal Dynamics of China Earthquake Administration, 1999. Eastern Kunlun Active Fault Zone. Seismological Press, Beijing. 1–227 (in Chinese)
Stein, R. S., 1999. The Role of Stress Transfer in Earthquake Occurrence. Nature, 402(6762): 605–609. https://doi.org/10.1038/45144
Stein, R. S., Barka, A. A., Dieterich, J. H., 1997. Progressive Failure on the North Anatolian Fault since 1939 by Earthquake Stress Triggering. Geophysical Journal International, 128(3): 594–604. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246x.1997.tb05321.x
Tapponnier, P., Ryerson, F. J., van der Woerd, J., et al., 2001. Long-Term Slip Rates and Characteristic Slip: Keys to Active Fault Behaviour and Earthquake Hazard. Comptes Rendus De l’Académie Des Sciences-Series IIA-Earth and Planetary Science, 333(9): 483–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1251-8050(01)01668-8
Toda, S., Stein, R. S., Sagiya, T., 2002. Evidence from the AD 2000 Izu Islands Earthquake Swarm that Stressing Rate Governs Seismicity. Nature, 419(6902): 58–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00997
van der Woerd, J., Tapponnier, P., Ryerson, F. J., et al., 2002. Uniform Postglacial Slip-Rate along the Central 600 km of the Kunlun Fault (Tibet), from 26Al, 10Be, and 14C Dating of Riser Offsets, and Climatic Origin of the Regional Morphology. Geophysical Journal International, 148(3): 356–388. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246x.2002.01556.x
Vergne, J., Wittlinger, G., Hui, Q., et al., 2002. Seismic Evidence for Stepwise Thickening of the Crust across the NE Tibetan Plateau. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 203(1): 25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821x(02)00853-1
Wang, C. S., Gao, R., Yin, A., et al., 2011. A Mid-Crustal Strain-Transfer Model for Continental Deformation: A New Perspective from High-Resolution Deep Seismic-Reflection Profiling across NE Tibet. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 306(3/4): 279–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.04.010
Wang, S. Y., Zhou, R. J., Liang, M. J., et al., 2021. Co-Seismic Surface Rupture and Recurrence Interval of Large Earthquakes along Damaoyaba-Litang Segment of the Litang Fault on the Eastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau in China. Journal of Earth Science, 32(5): 1139–1151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1425-z
Wang, W. L., Fang, L. H., Wu, J. P., et al., 2021. Aftershock Sequence Relocation of the 2021 Ms7.4 Maduo Earthquake, Qinghai, China. Science China Earth Sciences, 51(7): 1193–1202 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wen, X. Z., 2018. The 2008 Wenchuan, 2013 Lushan and 2017 Jiuzhaigou Earthquakes, Sichuan, in the Last More than One Thousand Years of Rupture History of the Eastern Margin of the Bayan Har Block. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 40(3): 255–267 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wu, W. Y., Xu, C., Wang, X. Q., et al., 2020. Landslides Triggered by the 3 August 2014 Ludian (China) Mw 6.2 Earthquake: An Updated Inventory and Analysis of Their Spatial Distribution. Journal of Earth Science, 31(4): 853–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1297-7
Wu, Z. H., Zhou, C. J., Ma, X. X., et al., 2018. Distribution Map of Active Faults in China and Its Adjacent Sea Area. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Xiong, R. W., Ren, J. W., Zhang, J. L., et al., 2010. Late Quaternary Active Characteristics of the Gande Segment in the Maduo-Gande Fault Zone. Earthquake, 30(4): 65–73 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xiong, W., Tan, K., Liu, G., et al., 2015. Coseismic and Postseismic Coulomb Stress Changes on Surrounding Major Faults Caused by the 2015 Nepal Mw7.9 Earthquake. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58 (11): 4305–4316 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xu, J., Shao, Z. G., Liu, J., et al., 2017. Analysis of Interaction between Great Earthquakes in the Eastern Bayan Har Block Based on Changes of Coulomb Stress. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 60: 4056–4068 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xu, X. W., Chen, W. B., Yu, G. H., et al., 2002. Characteristic Features of the Hoh Sai Hu (Kunlunshan) Earthquake (Ms8.1), Northern Tibetan Plateau, China. Seismology and Geology, 24(1): 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.01.001 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xu, X. W., Han, Z. J., Yang, X. P., et al. 2016. Seismotectonic Map of China and Adjacent Areas. China Cartographic Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Xu, X. W., Wen, X. Z., Chen, G. H., et al., 2008. Discovery of the Longriba Fault Zone in Eastern Bayan Har Block, China and Its Tectonic Implication. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 51(9): 1209–1223 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yan, B., Toda, S., Lin, A. M., 2018. Coulomb Stress Evolution History as Implication on the Pattern of Strong Earthquakes along the Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang Fault System, China. Journal of Earth Science, 29(2): 427–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-018-0840-2
Yu, M. Y., Yu, C. Q., Qu, C., et al., 2021. Deep Structural Characteristics of Pengguan Complex in Longmenshan Fault Zone Derived from Seismic Reflective Profile. Earth Science, 46(5): 1737–1748. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2020.020 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhan, Y., Liang, M. J., Sun, X. Y., et al., 2021. Deep Structure and Seismogenic Pattern of the 2021.5.22 Madoi (Qinghai) Ms7.4 Earthquake. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(7): 2232–2252 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, P. Z., Shen, Z. K., Wang, M., et al., 2004. Continuous Deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from Global Positioning System Data. Geology, 32(9): 809. https://doi.org/10.1130/g20554.1
Zhang, P. Z., Xu, X. W., Wen, X. Z., et al., 2008. Slip Rates and Recurrence Intervals of the Longmen Shan Active Fault Zone, and Tectonic Implications for the Mechanism of the May 12 Wenchuan Earthquake, 2008, Sichuan, China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(4): 1066–1073 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, Y. M., Li, M. F., Meng, Y. Q., et al., 1996. Research on Fault Activities and Their Seismogeological Implication in Bayankala Mountain Area. Research on Active Faults, 5: 154–171 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhou, R. J., Ma, S. H., Cai, C. X., 1996. Late Quaternary Active Features of the Ganzi-Yushu Fault Zone. Earthquake Research in China, 12(3): 250–260 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhou, R. J., Wen, X. Z., Cai, C. X., et al., 1997. Recent Earthquakes and Assessment of Seismic Tendency on the Ganzi Yushu Fault Zone. Seismology and Geology, 19(2): 20–29 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Nonprofit Fundamental Research Grant of China, Institute of Geology, China, Earthquake Administration (Nos. IGCEA1803; IGCEA2110) and the Seismic Hazard Prevention Project from Ministry of Finance (No. JH-21-10). The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1556-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, G., Liu, J., Ren, Z. et al. The Interpretation of Seismogenic Fault of the Maduo Mw 7.3 Earthquake, Qinghai Based on Remote Sensing Images—A Branch of the East Kunlun Fault System. J. Earth Sci. 33, 857–868 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1556-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1556-2