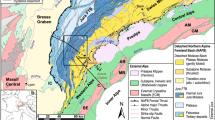
Abstract
The eastern Sichuan-western Hunan and Hubei belt (ESWHHB) is an important fold-thrust belt in the Middle-Upper Yangtze region of China, and it is also an important area for petroleum and gas prospect in China. The influence of mechanical stratigraphy on the deformation evolution of the ESWHHB is a hot problem that has received widespread attention. However, due to the complexity of geological conditions, this issue has not been sufficiently addressed. Previews geological exploration studies show that the deformation evolution of the belt is closely related to the mechanical stratigraphy. Physical simulation has proven to be effective for studying the deformation evolution of fold-and-thrust belt. Based on the geological conditions of the ESWHHB, six groups of physical models were designed to analyze the influences of the ductile layer and overlap configuration on the structural deformation of the ESWHHB. The results show that the mechanical stratigraphy has significant control on the deformation evolution of the fold-thrust belt. The ESWHHB evolution is related to the lower viscosity of the ductile layer and the larger thickness of the ductile layer, while only gradual propagated fold-and-thrust belt can be resulted from the higher viscosity of the ductile layer and the smaller thickness of the ductile layer. Additionally, the overlap between the stratigraphy at various structural belts leads to significant differences in their mechanical properties, and it critically influences the structural patterns of the ESWHHB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Bonini, M., 2001. Passive Roof Thrusting and Forelandward Fold Propagation in Scaled Brittle-Ductile Physical Models of Thrust Wedges. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 106(B2): 2291–2311. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000jb900310
Bonini, M., 2007. Deformation Patterns and Structural Vergence in Brittle-Ductile Thrust Wedges: An Additional Analogue Modelling Perspective. Journal of Structural Geology, 29(1): 141–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2006.06.012
Bonini, M., Sani, F., Antonielli, B., 2012. Basin Inversion and Contractional Reactivation of Inherited Normal Faults: A Review Based on Previous and New Experimental Models. Tectonophysics, 522/523: 55–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2011.11.014
Burchfiel, B. C., Royden, L. H., van der Hilst, R. D., et al., 2008. A Geological and Geophysical Context for the Wenchuan Earthquake of 12 May 2008, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China. GSA Today, 18(7): 4. https://doi.org/10.1130/gsatg18a.1
Costa, E., Vendeville, B. C., 2002. Experimental Insights on the Geometry and Kinematics of Fold-and-Thrust Belts above Weak, Viscous Evaporitic Décollement. Journal of Structural Geology, 24(11): 1729–1739. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0191-8141(01)00169-9
Costa, E., Vendeville, B. C., 2004. Experimental Insights on the Geometry and Kinematics of Fold-and-Thrust Belts above Weak. Journal of Structural Geology, 26: 2141–2143
Cruz, L., Malinski, J., Hernandez, M., et al., 2011. Erosional Control of the Kinematics of the Aconcagua Fold-and-Thrust Belt from Numerical Simulations and Physical Experiments. Geology, 39(5): 439–442. https://doi.org/10.1130/g31675.1
Dahlen, F. A., Suppe, J., Davis, D., 1984. Mechanics of Fold-and-Thrust Belts and Accretionary Wedges: Cohesive Coulomb Theory. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 89(B12): 10087–10101. https://doi.org/10.1029/jb089ib12p10087
Davis, D., Suppe, J., Dahlen, F. A., 1983. Mechanics of Fold-and-Thrust Belts and Accretionary Wedges. Journal of Geophysical Research, 88(B2): 1153. https://doi.org/10.1029/jb088ib02p01153
Graveleau, F., Malavieille, J., Dominguez, S., 2012. Experimental Modelling of Orogenic Wedges: A Review. Tectonophysics, 538–540: 1–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2012.01.027
Guo, T. L., Zhang, H. R., 2014. Formation and Enrichment Mode of Jiaoshiba Shale Gas Field, Sichuan Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(1): 31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1876-3804(14)60003-3
Gutscher, M. A., Klaeschen, D., Flueh, E., et al., 2001. Non-Coulomb Wedges, Wrong-Way Thrusting, and Natural Hazards in Cascadia. Geology, 29(5): 379. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0379:ncwwwt>2.0.co;2
He, W. G., Zhou, J. X., Yuan, K., 2018. Deformation Evolution of Eastern Sichuan-Xuefeng Fold-Thrust Belt in South China: Insights from Analogue Modelling. Journal of Structural Geology, 109: 74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2018.01.002
Hu, S., Zhu, L., Liu, S., et al., 2009. The Folding Time of the Eastern Sichuan Jura-Type Fold Belt: Evidence from Unconformity. Geological Review, 55: 32–42 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Hubbert, M. K., 1937. Theory of Scale Models as Applied to the Study of Geologic Structures. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 48(10): 1459–1520. https://doi.org/10.1130/gsab-48-1459
Jin, Z., Long, S., Zhou, Y., et al., 2006. A Study on the Distribution of Saline-Deposit in Southern China. Oil and Gas Geology, 27: 571–583 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, C. X., He, D. F., Sun, Y. P., et al., 2015. Structural Characteristic and Origin of Intra-Continental Fold Belt in the Eastern Sichuan Basin, South China Block. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 111: 206–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.07.027
Liu, C., Zhou, J., Lang, J., 2013. Study on Restrictive Factor of Thrust-and-Fold Belt Formation with Multiple Decollements: Taking Eastern Sichuan-Xuefeng Structural Belt as an Example. Journal. Earth Science. Environment, 2: 45–55 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, S. F., Qian, T., Li, W. P., et al., 2015. Oblique Closure of the Northeastern Paleo-Tethys in Central China. Tectonics, 34(3): 413–434. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014tc003784
Liu, S. G., Deng, B., Jansa, L., et al., 2018. Multi-Stage Basin Development and Hydrocarbon Accumulations: A Review of the Sichuan Basin at Eastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Earth Science, 29(2): 307–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0904-8
Liu, S., 1995. My Opinions of Structural Pattern of Thin-Skinned Structure in Eastern Sichuan. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 15: 264–267 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, S., Wang, P., Hu, M., et al., 2010. Evolution and Geodynamic Mechanism of Basin-Mountain Systems in the Northern Margin of the Middle-Upper Yangtze. Earth Science Frontiers, 3: 14–26 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Lu, G., Zhao, L., Zheng, T. Y., et al., 2014. Strong Intracontinental Lithospheric Deformation in South China: Implications from Seismic Observations and Geodynamic Modeling. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 86: 106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.08.020
Luo, M., Gong, Y. M., Shi, G. R., et al., 2018. Palaeoecological Analysis of Trace Fossil Sinusichnus Sinuosus from the Middle Triassic Guanling Formationin Southwestern China. Journal of Earth Science, 29(4): 854–863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-018-0794-4
Luo, Z., 1998. New Recognition of Basement in Sichuan Basin. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 25: 191–200 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ma, Y., Cai, X., Li, G., 2005. Basic Characteristics and Concentration of the Puguang Gas Field in the Sichuan Basin. Acta Geologica Sincia, 79: 858–865 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Marques, F. O., Cobbold, P. R., 2002. Topography as a Major Factor in the Development of Arcuate Thrust Belts: Insights from Sandbox Experiments. Tectonophysics, 348(4): 247–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-1951(02)00077-x
Marques, F. O., Cobbold, P. R., 2006. Effects of Topography on the Curvature of Fold-and-Thrust Belts during Shortening of a 2-Layer Model of Continental Lithosphere. Tectonophysics, 415(1/2/3/4): 65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2005.12.001
Mei, L., Liu, S., Tang, J., et al., 2010. Mesozoic Intra-Continental Progressive Deformation in Western Hunan-Hubei-Eastern Sichuan Provinces of China: Evidence from Apatite Fission Track and Balanced Cross-Section. Earth Science—.Journal of China University of Geosciences, 35(2): 161–174 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ni, X., Chen, H., Wei, D., et al., 2009. Superimposing and Rebuilding of the Middle-Upper Yangtze Basins and Its Prospects of Oil and Gas in Marine Strata. Acta Geologica Sinica, 4: 468–477 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Qiu, Y., Zhang, Y., Ma, W., 1998. Structurals and Geological Evolution of Xuefeng Intra-Continental Orogene, South China. Geological Journal of China Universities, 4: 432–443 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Rossetti, F., Faccenna, C., Ranalli, G., 2002. The Influence of Backstop Dip and Convergence Velocity in the Growth of Viscous Doubly-Vergent Orogenic Wedges: Insights from Thermomechanical Laboratory Experiments. Journal of Structural Geology, 24(5): 953–962. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0191-8141(01)00127-4
Rossetti, F., Faccenna, C., Ranalli, G., et al., 2000. Convergence Rate-Dependent Growth of Experimental Viscous Orogenic Wedges. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 178(3/4): 367–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(00)00082-0
Santolaria, P., Vendeville, B. C., Graveleau, F., et al., 2015. Double Evaporitic Décollements: Influence of Pinch-Out Overlapping in Experimental Thrust Wedges. Journal of Structural Geology, 76: 35–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2015.04.002
Sherkati, S., Letouzey, J., Frizon de Lamotte, D., 2006. Central Zagros Fold-Thrust Belt (Iran): New Insights from Seismic Data, Field Observation, and Sandbox Modeling. Tectonics, 25(4): 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004tc001766
Tang, L., Guo, T., Yu, Y., et al., 2007. Salt-Related Structures in the Foreland Thrust-and-Fold Belt of the Northeastern Sichuan Basin, South China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81: 1048–1056 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, F., Zhang, S. X., Li, M. K., 2018. Crustal Structure of Yunnan Province of China from Teleseismic Receiver Functions: Implications for Regional Crust Evolution. Journal of Earth Science, 29(6): 1419–1430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0822-9
Weijermars, R., Schmeling, H., 1986. Scaling of Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid Dynamics without Inertia for Quantitative Modelling of Rock Flow Due to Gravity (Including the Concept of Rheological Similarity). Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 43(4): 316–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9201(86)90021-x
Xie, G., Jia, D., Zhang, Q., et al., 2013. Physical Modeling of the Jura-Type Folds in Eastern Sichuan. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87: 773–788 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yan, D. P., Zhou, M. F., Song, H. L., et al., 2003. Origin and Tectonic Significance of a Mesozoic Multi-Layer Over-Thrust System within the Yangtze Block (South China). Tectonophysics, 361(3/4): 239–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-1951(02)00646-7
Zhang, G. W., Guo, A. L., Wang, Y. J., et al., 2013. Tectonics of South China Continent and Its Implications. Science China Earth Sciences
Zhou, J. X., Zhang, B., Xu, Q., 2016. Effects of Lateral Friction on the Structural Evolution of Fold-and-Thrust Belts: Insights from Sandbox Experiments with Implications for the Origin of Landward-Vergent Thrust Wedges in Cascadia. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 128(3/4): 669–683. https://doi.org/10.1130/b31320.1
Zhou, W. D., Xie, S. Y., Bao, Z. Y., et al., 2019. Chemical Compositions and Distribution Characteristics of Cements in Longmaxi Formation Shales, Southwest China. Journal of Earth Science, 30(5): 879–892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-019-1013-7
Zou, C., Dong, D., Wang, Y., et al., 2015. Shale Gas in China: Characteristics, Challenges and Prospects. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 42: 689–701 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Project of the State Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resource and Prospecting, China University of Petroleum, Beijing (No. PRP/Open-1903), and the Zunyi Normal University Project (No. BS[2018]04). I thank Prof. Jianxun Zhou, associate Prof. Graveleau and two anonymous reviewers for their helpful reviews and suggestions. The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1281-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, W. Influence of Mechanical Stratigraphy on the Deformation Evolution of Fold-Thrust Belts: Insights from the Analogue Modeling of Eastern Sichuan-Western Hunan and Hubei, South China. J. Earth Sci. 31, 795–807 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1281-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1281-2