Abstract
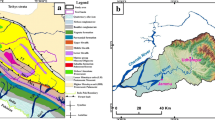
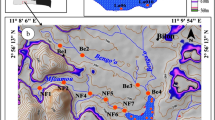
Holocene palaeoweathering conditions and environmental changes of Loulan (楼兰) Stupa Section were reconstructed by major elements analysis results and optical stimulated luminescence dating results. Major element results show source rock change little, with the composition equivalent to granodiorite. The low R value and high CIA (chemical index of alteration) value indicating the section at primary weathering phases. The muddy silt and silty clay have low R value and high CIA value and total iron content. In contrast, the sandy clay silt and sandy silt have high R value and low CIA and total iron value. Deglaciation time climate was relatively humid. In comparison to previous and posterior hiatus, the Middle-Holocene climate was relatively wet but still displayed high-frequency and high-amplitude fluctuations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Buylaert, J. P., Murray, A. S., Thomsen, K. J., et al., 2009. Testing the Potential of an Elevated Temperature IRSL Signal from K-Feldspar. Radiation Measurements, 44(5–6): 560–565
Cao, G. C., Ma, H. Z., Zhang, P., et al., 2009. Geochemical Composition of Sediment in Gahai Lake since 11.5 ka BP and Its Environmental Implication. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 27(2): 360–366 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Condie, K. C., 1993. Chemical Composition and Evolution of the Upper Continental Crust: Contrasting Results from Surface Samples and Shales. Chemical Geology, 104(1–4): 1–37, doi:10.1016/0009-2541(93)90140-E
Davison, W., 1993. Iron and Manganese in Lakes. Earth-Science Review, 34(2): 119–163
Fedo, C. M., Nesbitt, H. W., Young, G. M., 1995. Unraveling the Effects of Potassium Metasomatism in Sedimentary Rocks and Paleosols, with Implications for Paleowearhering Conditions and Provenance. Geology, 23: 921–924
Fedo, C. M., Young, G. M., Nesbitt, H. W., 1997. Paleoclimatic Control on the Composition of the Paleoproterozoic Serpent Formation, Huronian Supergroup, Canada: A Greenhouse to Icehouse Transition. Precambrian Research, 86(3): 201–223
Jia, H. J., Liu, J. Q., Qin, X. G., 2011. Early Holocene Climatic Changes and Agricultural Activities Inferred from Spore-pollen of Lop Nur. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 41(Suppl. 1): 181–186 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Lerman, A., 1978. Lakes: Chemistry, Geology, Physics. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. 226
Luo, C., Peng, Z. C., Yang, D., et al., 2008. Paleoclimate of Lop Nur and the Response to Global Change by Geochemical Elements Multi-Analysis. Geochimica, 37(2): 139–148 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Luo, C., Peng, Z. C., Yang, D., et al., 2009. A Lacustrine Record from Lop Nur, Xinjiang, China: Implications for Paleoclimate Change during Late Pleistocene. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34(1): 38–45
Ma, C. M., Wang, F. B., Cao, Q. Y., et al., 2008. Climate and Environment Reconstruction during the Medieval Warm Period in Lop Nur of Xinjiang, China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(19): 3016–3027 (in Chinese)
Middleburg, J. J., van der Weijden, C. H., Woittiez, J. R. W., 1988. Chemical Processes Affecting the Mobility of Major, Minor and Trace Element during Weathering of Granitic Rocks. Chemical Geology, 68(3–4): 253–273, doi:10.1016/0009-2541(88)90025-3
Nesbitt, H. W., Young, G. M., 1982. Early Proterozoic Climates and Plate Motions Inferred from Major Element Chemistry of Lutites. Nature, 299: 715–717, doi:10.1038/299715a0
Nesbitt, H. W., Young, G. M., 1984. Predietion of Some Weathering Trends of Plutonic and Volcanic Rocks Based on Thermodynamic and Kinetic Considerations. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48(7): 1523–1534, doi:10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3
Nesbitt, H. W., Young, G. M., 1989. Formation and Diagenesis of Weathering Profiles. Journal of Geology, 97(2): 129–147
Panahi, A., Young, G. M., Rainbird, R. H., 2000. Behavior of Major and Trace Elements (including REE) during Paleoproterozoic Pedogenesis and Diagenetic Alteration of an Archean Granite near Ville Marie, Québec, Canada. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(13): 2199–2220, doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00420-2
Rudnick, R. L., Gao, S., 2003. Composition of the Continental Crust. Treatise on Geochemistry, 3: 1–64
Ruxton, B. P., 1968. Measures of the Degree of Chemical Weathering of Rocks. Journal of Geology, 76(5): 518–527
Tardy, Y., Bocquier, G., Paquet, H., et al., 1973. Formation of Clay from Granite and Its Distribution in Relation to Climate and Topography. Geoderma, 10: 271–284
von Eynatten, H., 2004. Statistical Modelling of Compositional Trends in Sediments. Sedimentary Geollogy, 171(1–4): 79–89
Wang, F. B., Ma, C. M., Xia, X. C., et al., 2008. Environmental Evolution in Lop Nur since Late Pleistocene and Its Response to the Global Changes. Quaternary Science, 28(1): 150–153 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xia, X. C., 1987. Lop Nur Scientific Expedition and Research. Science Press, Beijing. 28, 51 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was supported by the Key Consultation Project (No. 2008-ZD-05) of Chinese Academy of Engineering, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 40472094, 40772212), and National Project (No. NP2010-033).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, H., Qin, X. & Liu, J. Environmental changes recorded by major elements in Loulan Stupa Section during Early-Middle Holocene. J. Earth Sci. 23, 155–160 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-012-0240-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-012-0240-y