Abstract
Understanding the change in elastic properties of peripheral arteries in heart failure patients is of particular importance, especially when compared with normal subjects. To investigate factors associated with their difference, 40 normal subjects and 60 heart failure patients were studied. Electrocardiograms, carotid pulses and radial pulses were simultaneously recorded to determine carotid-radial pulse transit time (carotid-radial PTT), arm pulse wave velocity (PWV), and arterial volume distensibility. In comparison with normal subjects, carotid-radial PTT was lower by 8 ms in heart failure patients, arm PWV higher by 1.4 m/s, and peripheral arterial distensibility lower by 0.04 % per mmHg (all significant, P < 0.01). Peripheral arterial distensibility was significantly related to systolic blood pressure (SBP) and to left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) for heart failure patients (both P < 0.001), but the relationship for the normal group was not statistically significant (both 0.05 < P<0.1). Ageing had a significant inverse relationship with arterial distensibility in normal subjects (P < 0.05), but not in heart failure patients (P = 0.59). No subject in the normal group had an arterial distensibility lower than 0.1 % per mmHg, in comparison with 28 % (17/60) in the heart failure group. Peripheral arterial distensibility has been shown to be significantly lower in heart failure patients in comparison with normal subjects. High SBP and low LVEF were the main factors associated with low arterial distensibility in heart failure patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Chronic heart failure is a major global health problem, affecting about 7 million Europeans and 5 million North Americans each year [1, 2]. The peripheral circulation plays a fundamental role in the pathophysiology of heart failure. A better understanding of the changing elastic properties of arteries in heart failure patients is of particular importance, because modest changes in left ventricular function can have profound hemodynamic and clinical effects [3–5]. Experimental evidence suggests that heart failure patients have abnormal ventricular–vascular coupling and impaired endothelial dysfunction [6–9]. Measurement of arterial properties in heart failure patients is therefore clinically important.
The elastic properties of arteries can be quantitatively and indirectly assessed by various non-invasive techniques. The most commonly used technique measures pulse wave velocity (PWV) over two superficial artery sites. However, the majority of these published studies mainly focused on the relatively large arteries by measuring the carotid-femoral PWV, and their conclusions were clinically different, with higher [9], lower [10] ,and no change [11] of carotid-femoral PWV reported. Some studies assessed the change of elastic properties of peripheral arteries in heart failure patients by measuring the brachial-radial and carotid-radial PWV. Increased brachial-radial PWV [12] and decreased [10] or no change [11] of carotid-radial PWV have also been reported. By investigating the whole artery from the heart to the fingertip, Wagner et al. reported that pulse transit time (PTT) measured from the electrocardiogram (ECG) to the finger photoplethysmogram was mildly elevated in heart failure patients, indicating impaired ventricular-arterial coupling [13], but the PTT used in their study included the left ventricular pre-ejection time, and cannot precisely represent the elastic properties of peripheral arm arteries. These conflicting results may be partly due to the different segments of arteries used for investigation, and also due to the methodological difference. Further investigation is therefore worthwhile as the results so far are still inconclusive.
Arterial volume distensibility is also commonly used to directly quantify the elastic and hence structural properties of the arterial wall [14, 15]. However, published results on the changes of peripheral arterial distensibility in heart failure patients are also clinically controversial: some showed impaired arterial distensibility [16, 17] and others showed no impairment [4, 18]. Ultrasound techniques were commonly used in these studies, but they are operator-dependent. Recently, Zheng and Murray [15] reported a simple measurement technique to measure the peripheral arterial volume distensibility. Because of its simplicity, its application to heart failure patients is worth further investigation.
The aim of this study was to quantify the elastic properties of peripheral arteries in heart failure patients by measuring their arterial volume distensibility, and to compare with measurements from normal subjects. The factors influencing the elastic properties of peripheral arteries in heart failure patients were also investigated.
Methods
Subjects
Totals of 40 normal subjects and 60 heart failure patients were studied. They were matched by age and sex, and aged between 30 and 75 years. The study obtained full approval of the Clinical Ethics Committee of the Qilu Hospitals of Shandong University. The investigation conformed with the principles in the Declaration of Helsinki. All subjects gave their written informed consent to participate in the study, and confirmed that they had not have participated in any other clinical trials within the previous 3 months.
The heart failure patients were in classes II–III of the New York Heart Association (NYHA) with functional classification confirmed by an ultrasonic cardiogram (UCG). Left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) from three cardiac cycles were measured by a cardiologist, and their average value was used as the reference LVEF for that subject. The LVEF from the heart failure patients was less than 50 % in this study. The normal subjects had normal UCG and ECG and normal LVEF in the range of 50–70 %. The subject demographic information is given in Table 1.
Experimental procedure
All measurements were undertaken in a quiet, temperature-controlled clinical measurement room (25 ± 3 °C) at Qilu Hospital of Shandong University. Before the formal signal recording, each subject lay supine on a measurement bed for a 10-min rest period to allow cardiovascular stabilization. ECG electrodes were attached to the right wrist and the right and left ankles to acquire a standard limb lead-II ECG. Two piezoresistive sensors were attached to the neck and left wrist to acquire carotid artery pressure waveforms (CAPW) and radial artery pressure waveforms (RAPW), respectively. Subjects were told to breathe regularly and gently during the measurement.
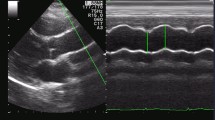
For each subject, the ECG, CAPW, and RAPW signals were synchronously recorded at a sample rate of 1,000 Hz for 5 min. Figure 1 gives typical examples of these signals. Manual auscultatory systolic and diastolic blood pressures (SBP and DBP) were recorded from the right upper arm at the beginning and end of the signal recording, and no significant differences were found (both P > 0.05). The average SBP and DBP from the two measurements were used as reference BPs for that subject. The mean arterial pressure (MAP) and pulse pressure (PP) were calculated using the classic formulas: MAP = DBP + (SBP − DBP)/3 and PP = SBP − DBP. The overall mean and standard deviation (SD) of SBP, DBP, MAP and PP are given in Table 1.
Simultaneously measured ECG, carotid and radial arterial pulse waveforms (CAPW and RAPW). The detected R-wave peaks are indicated by closed circle, and the starting points of CAPW and RAPW signals are indicated by "upward triangles and downward triangles", respectively. The heart-carotid pulse transit time (PTT) is the interval from the R-wave peak to the starting point of the CAPW signal; the heart-radial PTT is from the R-wave peak to the starting point of RAPW signal; the carotid-radial PTT is between the starting points of CAPW and RAPW signals
Finally, the difference in propagation distance to the carotid and radial arteries, referred to as arm length below, was obtained by the length difference, using the radial-suprasternal notch distance minus the carotid-suprasternal notch distance. The arm length is also included in Table 1.
Peripheral arterial volume distensibility calculation
Off-line analysis was performed by a custom-designed computer program using the MATLAB software (v.R2009a; MathWorks, USA). The ECG, CAPW, and RAPW signals were first pre-processed to remove the slow varying components (0–0.05 Hz). Ectopic beats in the ECGs were excluded using our previously developed method [19].
The heart to carotid artery pulse transit time (heart-carotid PTT) and heart to radial artery pulse transit time (heart-radial PTT) were then measured from the R-wave peak of the QRS complex to the corresponding pulse foot of the CAPW and RAPW signals from all acceptable beats over the first 2 min. A manual check was also performed to ensure the algorithm detected the correct pulse feet. To isolate the effect of the ventricular electrical mechanical delay time, which is common to all simultaneous PTTs, heart-carotid PTTs were subtracted from the heart-radial PTTs to obtain the propagation time along the major section of the arm (carotid-radial PTT) [15, 20]. The average arm PWV was then calculated from the arm length and carotid-radial PTT using the following equation:
From the definition of arterial volume distensibility (\( {\text{Dv}} = (\Updelta V/V)/\Updelta P \), where \( \Updelta V \), \( \Updelta P \) are the changes in blood volume and arterial transmural pressure) and the Bramwell and Hill equation (\( {\text{PWV}} = \sqrt {\frac{V \times \Updelta P}{\rho \times \Updelta V}} \), where \( \rho \) is blood density = 1,025 kg m−3) [21], peripheral arterial volume distensibility (\( {\text{Dv}} \)) was then derived as follows [15]:
Data and statistical analysis
The mean PTTs from all beats over the first 2 min of signals were calculated for each subject. The overall means and SDs of PTTs, arm PWV, and arterial volume distensibility were then obtained, separately for normal subjects and heart failure patients. Next, the differences between the two groups were calculated and compared. A non-parametric Mann–Whitney U Test was performed using the SPSS 19.0 software package (SPSS). A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Finally, regression analysis was performed to determine the effect of resting arterial pressures (SBP, DBP, MAP, and PP), sex, weight, heart rate, LVEF, and age on peripheral arterial volume distensibility, with the correlation coefficient R values and P values obtained.
Results
Physiological characteristic information
As expected, there was a significant difference in LVEF between the heart failure patients and normal subjects (P < 0.001). In terms of gender, age, height, weight, heart rate, arm length, and resting BPs, there were no significant differences between the two groups (all P > 0.05) (see Table 1).
Differences of pulse transit times, arm pulse wave velocity and arterial volume distensibility between the two groups
Table 2 gives the overall means and SDs of PTTs (heart-carotid PTT, heart-radial PTT, and carotid-radial PTT), arm PWV ,and arterial volume distensibility from the two groups. Statistical analysis showed that all the parameters had significant differences between the two groups (all P < 0.05, except for the heart-carotid PTT). For the heart failure patients, heart-radial PTT was significantly lower by 7 ms (118 ± 16 vs. 125 ± 13 ms, P < 0.01), carotid-radial PTT was significantly lower by 8 ms (56 ± 11 vs. 64 ± 10 ms, P < 0.01), arm PWV significantly higher by 1.4 m/s (10.4 ± 2.4 vs. 9.0 ± 1.1 m/s, P < 0.01), and peripheral arterial volume distensibility significantly lower by 0.04 % per mmHg (0.13 ± 0.05 vs. 0.17 ± 0.04 % per mmHg, P = 0.001).
Effect of resting arterial pressures, left ventricular ejection fraction and ageing on peripheral arterial volume distensibility
Multiple regression analysis showed that peripheral arterial volume distensibility was significantly related to SBP and LVEF for the heart failure group (both P < 0.001), but the relationship for the normal group was not statistically significant (both 0.05 < P < 0.1). Arterial volume distensibility had a significant inverse relationship with ageing in the normal group (P < 0.05) but not in the heart failure group (P = 0.59). Arterial volume distensibility had no relationship with other physiological characteristics (DBP, MAP, PP, sex, weight, and heart rate). Figure 2 shows the raw data of arterial volume distensibility as a function of resting SBP, LVEF, and age for both the normal and heart failure groups.
Factors associated with low arterial volume distensibility in heart failure patients
Figure 3 shows the histograms of arterial volume distensibility in normal and heart failure groups. No subject in the normal group had an arterial distensibility lower than 0.1 % per mmHg, in comparison with 28 % (17/60) in the heart failure group. The association between heart failure patients and low distensibility was highly significant (Chi-square test; P < 0.001).
As summarized in Table 3, for those heart failure patients with low distensibility (≤0.1 % per mmHg), their SBP was significantly higher and LVEF significantly lower than those from the heart failure patients with high distensibility (>0.1 % per mmHg) (both P < 0.01), indicating that high SBP and low LVEF were the main factors associated with low arterial volume distensibility in heart failure patients.
Discussion
This study has demonstrated that peripheral arterial volume distensibility was significantly lower in heart failure patients. Assessing arterial elastic properties using a simple measurement technique is clinically important. There are several non-invasive techniques, but most of them assess factors influenced by arterial properties rather than the properties themselves. The ultrasound technique has been used to directly measure arterial distensibility of medium-sized arteries [22, 23]. However, the ultrasound technique is operator-dependent. The non-invasive method employed in this study to obtain peripheral arterial volume distensibility is much simpler, and we have shown that it can measure the differences in elastic properties of arteries between normal subjects and heart failure patients.
The lower arterial volume distensibility in heart failure patients in comparison with normal subjects agreed with Giannattasio et al.’s work [16, 17], where they reported that the reduction of arterial distensibility was related to the severity of heart failure. However, these results were not consistent with the work of Khder et al. [4] or Kaiser et al. [18], where no impairment of arterial distensibility was concluded in heart failure patients. Ramsey et al. [24] also found no difference in brachial artery distensibility in heart failure patients. One reason for the controversial results is partly due to the different measurement methods used in those studies.
The effect of ageing on arterial volume distensibility is of great clinical interest. It is generally accepted that ageing increases arterial diameter, arterial thickness, and sympathetic vascular smooth muscle tone under physiological pressures [25–27], all of which cause a decrease of arterial distensibility. A decrease in distensibility with ageing for normal subjects has been reported [15, 28, 29]. However, the ageing effect on arterial volume distensibility in heart failure patients has not been well investigated. We have shown in a human population study that ageing has little effect on arterial volume distensibility in heart failure patients.
In addition, we have shown that in this study only heart failure patients had an arterial distensibility lower than 0.1 % per mmHg. The influencing factors of the low arterial volume distensibility are also of great clinical importance. Our results indicated that SBP and LVEF were important factors associated with low arterial volume distensibility in heart failure patients. We speculate that persistent high SBP and low LVEF cause irreversible changes in arterial elastic properties. Using ultrasound imaging, Kaiser et al. [4] found a reduced brachial artery lumen size and an increased wall-to-lumen ratio in heart failure patients, which could result in reduced arterial distensibility. Other mechanisms may also contribute to vascular remodeling in heart failure patients, including significantly increased endothelin levels [30], changes in the amounts of collagen and elastin or their ratio, changes in collagen type, or alterations in the mechanical arrangement of wall components [4]. Nevertheless, further investigation is still required to better understand the underlying mechanism for the changes of arterial elastic properties in heart failure patients.
Limitation
Possible limitations in the methodology should be emphasized. The traditional time-reference point measurement is very important for the PTTs calculation. If the reflection wave moves forward, it will mix with the incident wave and will cause the peak of the whole waveform to become obtuse [3, 9, 10, 13]. Then, the measurement of the pulse foot of the CAPW and RAPW signals will not be sufficiently accurate; so a manual check was also used to ensure that the algorithm detected the correct pulse feet.
Conclusion
The current study demonstrated that heart failure patients had lower peripheral arterial volume distensibility in comparison with normal subjects. We have also demonstrated that, in the heart failure group, ageing was not related to low arterial volume distensibility, and that low LVEF and high SBP are the main factors associated with low arterial volume distensibility. These findings are clinically important, and the simple measurement technique used here has been demonstrated to be useful in assessing heart failure patients and monitoring the disease progression.
References
Stewart S (2005) Financial aspects of heart failure programs of care. Eur J Heart Fail 7:423–428
Wu JR, Corley DG, Lennie TA, Moser DK (2012) Effect of a medication-taking behavior feedback theory-based intervention on outcomes in patients with heart failure. J Card Fail 18:1–9
Simon AC, O’Rourke M, Levenson J (1991) Arterial distensibility and its effect on wave reflection and cardiac loading in cardiovascular disease. Coron Artery Dis 2:1111–1120
Kaiser DR, Mullen K, Bank AJ (2001) Brachial artery elastic mechanics in patients with heart failure. Hypertension 38:1440–1445
Gharacholou SM, Scott CG, Borlaug BA, Kane GC, McCully RB, Oh JK, Pellikka PA (2012) Relationship between diastolic function and heart rate recovery after symptom-limited exercise. J Card Fail 18:34–40
Mathier MA, Rose GA, Fifer MA, Miyamoto MI, Dinsmore RE, Castano HH, Dec GW, Palacios IF, Semigran MJ (1998) Coronary endothelial dysfunction in patients with acute-onset idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:216–224
Bank AJ, Lee PC, Kubo SH (2000) Endothelial dysfunction in patients with heart failure: relationship to disease severity. J Card Fail 6:29–36
Fischer D, Rossa S, Landmesser U, Spiekermann S, Engberding N, Hornig B, Drexler H (2005) Endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic heart failure is independently associated with increased incidence of hospitalization, cardiac transplantation, or death. Eur J Heart Fail 26(1):65–69
Balmain S, Padmanabhan N, Ferrell WR, Morton JJ, McMurray JJ (2007) Differences in arterial compliance, microvascular function and venous capacitance between patients with heart failure and either preserved or reduced left ventricular systolic function. Eur J Heart Fail 9:865–871
Tartiere JM, Logeart D, Safar ME, Cohen-Solal A (2006) Interaction between pulse wave velocity, augmentation index, pulse pressure and left ventricular function in chronic heart failure. J Hum Hypertens 20:213–219
Mitchell GF, Tardif JC, Arnold JM, Marchiori G, O’Brien TX, Dunlap ME, Pfeffer MA (2001) Pulsatile hemodynamics in congestive heart failure. Hypertension 38:1433–1439
Arnold JM, Marchiori GE, Imrie JR, Burton GL, Pflugfelder PW, Kostuk WJ (1991) Large artery function in patients with chronic heart failure. Studies of brachial artery diameter and hemodynamics. Circulation 84:2418–2425
Wagner D, Roesch N, Harpes P, Körtke H, Plumer P, Saberin A, Chakoutio V, Oundjede D, Delagardelle C, Beissel J, Gilson G, Kindermann I, Böhm M (2010) Relationship between pulse transit time and blood pressure is impaired in patients with chronic heart failure. Clin Res Cardiol 99:657–664
McVeigh GE, Hamilton PK, Morgan DR (2002) Evaluation of mechanical arterial properties: clinical, experimental and therapeutic aspects. Clin Sci 102:51–67
Zheng DC, Murray A (2011) Peripheral arterial volume distensibility: significant differences with age and blood pressure measured using an applied external pressure. Physiol Meas 32:499–512
Giannattasio C, Failla M, Stella ML, Mangoni AA, Turrini D, Carugo S, Pozzi M, Grassi G, Mancia G (1995) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and radial artery compliance in patients with congestive heart failure. Hypertension 26:491–496
Giannattasio C, Achilli F, Failla M, Capra A, Vincenzi A, Valagussa F, Mancia G (2002) Radial, carotid and aortic distensibility in congestive heart failure: effects of high-dose angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or low-dose association with angiotensin type 1 receptor blockade. J Am Coll Cardiol 39:1275–1282
Khder Y, El Ghawi R, Boscs LB, Aliot E, Zannad F (1996) Investigations of the peripheral vascular mechanisms implicated in congestive heart failure by the non-invasive evaluation of radial artery compliance and reactivity. Int J Cardiol 56:149–158
Liu CY, Li LP, Zhao LN, Zheng DC, Li P, Liu CC (2012) A combination method of improved impulse rejection filter and template matching for identification of anomalous intervals in electrocardiographic RR sequences. J Med Biol Eng 32:245–250
Zheng DC, Allen J, Murray A (2007) Non-invasive in vivo assessment of changes in peripheral arterial properties with estimation of arterial volume compliance. Physiol Meas 28:1317–1327
Nichols WW, O’Rourke MF (2005) McDonald’s blood flow in arteries. Hodder Arnold, London
Girerd X, Mourad JJ, Acar C, Heudes D, Chiche S, Bruneval P, Mignot JP, Billaud E, Safar M, Laurent S (1994) Noninvasive measurement of medium-sized artery intima-media thickness in humans: in vitro validation. J Vasc Res 31:114–120
MacWilliams BA, Hoffman AH, Savilonis BJ (1998) Variation of arterial compliance within the cardiac pressure pulse. J Biomech 31:867–871
Ramsey MW, Goodfellow J, Jones CJ, Luddington LA, Lewis MJ, Henderson AH (1995) Endothelial control of arterial distensibility is impaired in chronic heart failure. Circulation 92:3212–3219
Bjarnegård N, Länne T (2010) Arterial properties along the upper arm in humans: age-related effects and the consequence of anatomical location. J Appl Physiol 108:34–38
Van Der Heijden-Spek JJ, Staessen JA, Fagard RH, Hoeks AP, Boudier HA, Van Bortel LM (2000) Effect of age on brachial artery wall properties differs from the aorta and is gender dependent: a population study. Hypertension 35:637–642
Dinenno FA, Jones PP, Seals DR, Tanaka H (2000) Age-associated arterial wall thickening is related to elevations in sympathetic activity in healthy humans. Am J Physiol Heart C 278:H1205–H1210
Bortolotto LA, Hanon O, Franconi G, Boutouyrie P, Legrain S, Girerd X (1999) The aging process modifies the distensibility of elastic but not muscular arteries. Hypertension 34:889–892
Mitchell GF (2008) Effects of central arterial aging on the structure and function of the peripheral vasculature: implications for end-organ damage. J Appl Physiol 105:1652–1660
Li JS, Lariviere R, Schiffrin EL (1994) Effect of a nonselective endothelin antagonist on vascular remodeling in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats: evidence for a role of endothelin in vascular hypertrophy. Hypertension 24:183–188
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61201049), the Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (No. 2009AA02Z408) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 20110491593).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chengyu Liu and Dingchang Zheng are joint first authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Zheng, D., Zhao, L. et al. Elastic properties of peripheral arteries in heart failure patients in comparison with normal subjects. J Physiol Sci 63, 195–201 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-013-0254-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-013-0254-y