Abstract
Background
In this study, we aimed to compare low-dose dobutamine stress echocardiography (DSE) and iodine 123-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scintigraphy for predicting the response to beta-blocker therapy in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).
Methods
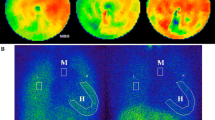
MIBG imaging was performed in 10 patients with DCM (mean EF 28 ± 8%), who were subsequently treated with beta-blocker therapy. The heart-to-mediastinum (H/M) MIBG uptake ratio was evaluated in initial and delayed images, and the percent washout ratio of myocardial MIBG was determined. DSE was also performed in all patients to measure left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at rest and during dobutamine infusion (10 μg/kg/min). LVEF at rest was also assessed by echocardiography before and after 6 months of beta-blocker therapy.
Results
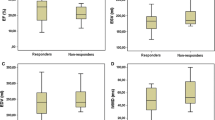
LVEF was significantly improved after beta-blocker therapy (28 ± 8 to 41 ± 11%, p < 0.001). The relative change in LVEF after beta-blocker therapy was significantly correlated with the relative change in LVEF during DSE (r = 0.68, p < 0.03). The H/M MIBG uptake ratio in both early and delayed imaging was not significantly correlated with the relative change in LVEF in response to beta-blockade therapy.
Conclusions
The relative change in LVEF during DSE, but not MIBG imaging predicted the relative change in LVEF in response to beta-blockade therapy in a limited number of DCM patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waagstein F, Hjalmarson A, Swedeberg K, Wallentin I. Beta-blockers in dilated cardiomyopathies. Eur Heart J. 1983;4(Suppl A):173–8.
Fowler MB, Bristow MR. Rational for beta-adrenergic blocking drugs in cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 1985;55:120D–4D.
Waagstein F, Bristow MR, Swedberg K, Camerini F, Fowler MB, Silver MA, et al. Beneficial effects of metoprolol in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Metoprolol in dilated cardiomyopathy (MDC) trial study group. Lancet. 1993;342:1441–6.
Kline RC, Swanson DP, Wieland DM, Thrall JH, Gross MD, Pitt B, et al. Myocardial imaging in man with I-123 meta-iodobenzylguanidine. J Nucl Med. 1981;22:129–32.
Henderson EB, Kahn JK, Corbett JR, Jansen DE, Pippin JJ, Kulkarni P, et al. Abnormal I-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial washout and distribution may reflect myocardial adrenergic derangement in patients with congestive cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1988;78:1192–9.
Suwa M, Otake Y, Moriguchi A, Ito T, Hirota Y, Kawamura K, et al. Iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial scintigraphy for prediction of response to beta-blocker therapy in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Am Heart J. 1997;133:353–8.
Fukuoka S, Hayashida K, Hirose Y, Shimotsu Y, Ishida Y, Kakuchi H, et al. Use of iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial imaging to predict the effectiveness of beta-blocker therapy in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J Nucl Med. 1997;24:523–9.
Yamazaki J, Muto H, Kabano T, Yamashina S, Nanjo S, Inoue A. Evaluation of beta-blocker therapy in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy—clinical meaning of iodine 123-metaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial single-photon emission computed tomography. Am Heart J. 2001;141:645–52.
Jourdain P, Funck F, Fulla Y, Hagege A, Bellorini M, Guillard N, et al. Myocardial contractile reserve under low doses of dobutamine and improvement of left ventricular ejection fraction with treatment by carvedilol. Eur J Heart Fail. 2002;4:269–76.
Kitaoka H, Takata J, Yabe T, Hitomi N, Furuno T, Doi YL. Low dose dobutamine stress echocardiography predicts the improvement of left ventricular systolic function in dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart. 1999;81:523–7.
Nihoyannopoulos P. Stress echocardiography. J Echocardiogr. 2008;6:91–9.
Naruse H, Arii T, Kondo T, Ohnishi M, Sakaki T, Takahashi K, et al. Relation between myocardial response to dobutamine stress and sympathetic nerve activation in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy: a comparison of 123I-MIBG scintigraphic and echocardiographic data. Ann Nucl Med. 2000;14:427–32.
Scrutinio D, Napoli V, Passantino A, Ricci A, Lagioia R, Rizzon P. Low-dose dobutamine responsiveness in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy: relation to exercise capacity and clinical outcome. Eur Heart J. 2000;21:927–34.
Hara Y, Hamada M, Ohtsuka T, Ogimoto A, Saeki H, Suzuki J, et al. Use of thallium-201 myocardial scintigraphy for the prediction of the response to β-blocker therapy in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ J. 2002;66:1139–43.
Kasama S, Toyama T, Hatori T, Sumino H, Kumakura H, Takayama Y, et al. Evaluation of cardiac sympathetic nerve activity and left ventricular remodelling in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy on the treatment containing carvedilol. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:989–95.
Yamada T, Fukunami M, Ohmori M, Iwakura K, Kumagai K, Kondoh N, et al. Which subgroup of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy would benefit from long-term beta-blocker therapy? A histologic viewpoint. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;21:628–33.
Hasegawa T, Nakatani S, Maruo T, Tanaka N, Kim J, Hanatani A, et al. Quantitative assessment of wall motion using myocardial strain. J Echocardiogr. 2003;1:23–8.
Merlet P, Benvenuti C, Moyse D, Pouillart F, Dubois-Rande JL, Duval AM, et al. Prognostic value of MIBG imaging in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:917–23.
Yamada T, Shimonagata T, Fukunami M, Kumagai K, Ogita H, Hirata A, et al. Comparison of the prognostic value of cardiac iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging and heart rate variability in patients with chronic heart failure: a prospective study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41:231–8.
Anastasiou-Nana MI, Terrovitis JV, Athanasoulis T, Karaloizos L, Geramoutsos A, Pappa L, et al. Prognostic value of iodine-123-metaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial uptake and heart rate variability in chronic congestive heart failure secondary to ischemic or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96:427–31.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors received any financial support for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K., Daimon, M., Kuwabara, Y. et al. Prediction of the response to beta-blocker therapy in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy: comparison of 123I-MIBG scintigraphy and low-dose dobutamine stress echocardiography. J Echocardiogr 7, 74–79 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12574-009-0022-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12574-009-0022-4