Abstract
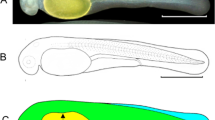
In order to establish the basement for developmental engineering in osmerid fishes, a dechorionation technique and developmental stages were described using rainbow smelt Osmerus eperlanus mordax. Eggs of rainbow smelt were fertilized with tap water. One minute after fertilization, dechorionation was performed by treatment with smelt’s Ringer solution: SRS (128 mM NaCl, 2.8 mM KCl, 2.7 mM CaCl2) containing 0.1 % trypsin and adjusted to pH 11.0 with 1 N NaOH. The chorion was digested completely within 5 h at 10 °C and the resulting denuded embryos developed normally under artificial culture conditions with SRS containing 1.6 % albumen before embryonic body formation, and then tap water. At the hatching stage, the average survival rate was 37.8 %. Embryos without the chorion were highly transparent and organogenesis was easily observed under a stereomicroscope. Embryos developed slowly to the embryonic body formation stage (66 hours postfertilization (hpf)) and hatching stage (22 day postfertilization (dpf)) at 10 °C. The embryonic development of rainbow smelt was similar to that of zebrafish Danio rerio and generally followed the basic developmental pattern of teleosts. These characteristics suggest that developmental engineering technology developed in model fishes can be applied to rainbow smelt.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson JS (2006) Family OSMERIDAE (172)–smelts. In: Nelson JS (ed) Fishes of the World, 4th edn. WILEY-Blackwell, New Jersey, pp 194–196
Nii H, Makiguchi Y, Fuji M, Ueda H (2010) Upriver spawning migration of shishamo smelt Spirinchus lanceolatus assessed by radio telemetry. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 76:855–869 (in Japanese with English abstract) doi:10.2331/suisan.76.855
Carscadden JE, Frank KT, Leggett WC (2001) Ecosystem changes and the effects on capelin (Mallotus villosus), a major forage species. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58:73–85. doi:10.1139/f00-185
Ohta H, Kusuda S, Kudo S (1995) Motility of testicular spermatozoa in the Shishamo smelt Spirinchus lanceolatus. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 61:7–12 (in Japanese with English abstract) doi:10.2331/suisan.61.7
Yamaha E, Saito T, Goto-Kazeto R, Arai K (2007) Developmental biotechnology for aquaculture, with special reference to surrogate production in teleost fishes. J Sea Res 58:8–22. doi:10.1016/j.seares.2007.02.003
Okutsu T, Yano A, Nagasawa K, Shikina S, Kobayashi T, Takeuchi Y, Yoshizaki G (2006) Manipulation of fish germ cell: visualization, cryopreservation and transplantation. J Reprod Dev 52:685–693. doi:10.1262/jrd.18096
Yasui GS, Fujimoto T, Sakao S, Yamaha E, Arai K (2011) Production of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) germ-line chimera using transplantation of primordial germ cells isolated from cryopreserved blastomeres. J Anim Sci 89:2380–2388. doi:10.2527/jas.2010-3633 (Epub 2011 Mar 11)
Saito T, Goto-Kazeto R, Fujimoto T, Kawakami Y, Arai K, Yamaha E (2010) Inter-species transplantation and migration of primordial germ cells in cyprinid fish. Int J Dev Biol 54:1481–1486. doi:10.1387/ijdb.103111ts
Saito T, Goto-Kazeto R, Kawakami Y, Nomura K, Tanaka H, Adachi S, Arai K, Yamaha E (2011) The mechanism for primordial germ-cell migration is conserved between japanese eel and zebrafish. PLoS One 6:e24460. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.002446
Saito T, Psˇenicˇka M, Goto R, Adachi S, Inoue K, Arai K, Yamaha E (2014) The Origin and Migration of Primordial Germ Cells in Sturgeons. PLoS ONE 9:e86861. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086861
Saito T, Goto-Kazeto R, Arai K, Yamaha E (2008) Xenogenesis in teleost fish through generation of germ-line chimeras by single primordial germ cell transplantation. Biol Reprod 78:159–166. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.107.060038
Inokuchi K, Nakatani T, Takatsu T, Takahashi T (1997) Gonadal maturation of female rainbow smelt Osmerus eperlanus mordax in Funka bay, Hokkaido. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 63:50–55 (in Japanese with English abstract) doi:10.2331/suisan.63.50
Yanagimachi R (1957) Studies of fertilization in Clupea pallasii-VI. Fertilization of the egg deprived of the membrane. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 6:41–47 (in Japanese) doi:10.11369/jji1950.7.61
Iwamatsu T (1983) A new technique for dechorionation and observation on the development of the naked eggs in Oryzias latipes. J Exp Zool 228:83–89. doi:10.1002/jez.1402280109
Ogawa N, Ooi Y (1968) The chorion and hatching enzyme of medaka Oryzias latipes. Zool. Mag. 77:151–156 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Sakai YT (1964) Method for removal of chorion and fertilization of the naked eggs in Oryzias latipes. Embryologia 5:357–368. doi:10.1111/j.1440-169X.1961.tb00101.x
Kanoh Y, Yamamoto TS (1957) Removal of the membrane of the dog salmon egg by means of proteolytic enzymes. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 23:166–172. doi:10.2331/suisan.23.166
Kawakami Y, Goto-Kazeto R, Saito T, Fujimoto T, Higaki S, Takahashi Y, Arai K, Yamaha E (2010) Generation of germ-line chimera zebrafish using primordial germ cells isolated from cultured blastomeres and cryopreserved embryoids. Int J Dev Biol 54:1493–1501. doi:10.1387/ijdb.093059yk
Yamaha E, Usui K, Onozato H, Hamada K (1986) A method for dechorionation in goldfish Cayassius auratus. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 52(11):1929–1934. doi:10.2331/suisan.52.1929
Ito Y, Sakai H, Kondo M, Yamamoto K, Takagi M (1999) Development of denuded eggs of common carp. Aquaculture Sci. 47(2):257–261 (in Japanese with English abstract) doi: 10.11233/aquaculturesci1953.47.257
Tachihara K, Kawaguchi K (2003) Morphological development of eggs, larvae and juveniles of laboratory-reared Ryukyu-ayu Plecoglossus altivelis ryukyuensis Fish. Sci. 69:323–330. doi:10.1046/j.1444-2906.2003.00624.x
Yamada J (1963) The normal developmental stage of the pond smelt, Hypomesus olidus (pallas). Bull Fac Fish Hokkaido Univ 14:121–126
Hikita T (1958) On the development of long-finned smelt, Spirinchus lanceolatus (Hikita). Scientific Reports of the Hokkaido Fish Hatchery 13:39–49 (in Japanese)
Yanagawa H (1978) Embryonic development and fry of the Kyuriuo, Osmerus eperlanus mordax (Mitchill). Bull Fac Fish Hokkaido Univ 29:195–198
Mizuno S, Sasaki Y, Omoto N, Imada K (2004) Elimination of adhesiveness in the eggs of shishamo smelt Spirinchus lanceolatus using kaolin treatment to achieve high hatching rate in an environment with a high iron concentration. Aquaculture 242:713–726. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.09.019
Hyafil F, Babinet C, Jacob F (1981) Cell-cell interactions in early embryogenesis: a molecular approach to the role of calcium. Cell 26:447–454. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(81)90214-2
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203:253–310. doi:10.1002/aja.100203030
Thai HY, Chang M, Liu SC, Abe G, Ota KG (2013) Embryonic development of goldfish (Carassius auratus) a model for the study of evolutionary change in developmental mechanisms by artificial selection. Dev Dyn 242:1262–1283. doi:10.1002/dvdy.24022
Fujimoto T, Kataoka T, Sakao S, Saito T, Etsuro Y, Arai K (2006) Developmental stage and germ cell lineage of the Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus). Zool Sci 23:977–989. doi:10.2108/zsj.23.977
Willemse MTHM, Denucé JM (1973) Hatching glands in the teleosts, Brachydanio rerio, Danio Malabaricus, Moenkhausia Oligolepis and Barbus schuberti. Dev. Growth Differ 15:169–177. doi:10.1111/j.1440-169X.1973.00169.x
Yanai T, Ouji M, Iga T (1956) Development of the Hatching Glands in the Teleost, Hypomesus olidus (Pallas). Annot Zool Jpn 29:202–206
Strecker R, Seiler TB, Hollert H, Braunbeck T (2010) Oxygen requirements of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos in embryo toxicity tests with environmental samples. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C: Toxicol Pharmacol 153:318–327. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.12.002
Kanamori A, Naruse K, Mitani H, Shima A, Hori H (2003) Genomic organization of ZP domain containing egg envelope genes in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Gene 305:35–45. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(02)01211-8
Papadopoulou P, Galanopoulos VK, Hamodrakas SJ (1996) Molecular and supramolecular architecture of the Salmo gairdneri proteinaceous eggshell during development. J Struct Biol 116:399–412. doi:10.1006/jsbi.1996.0057
Ha CR, Iuchi I (1997) Extraction and partial characterization of egg envelope (chorion) transglutaminase of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss: properties for Efficient Chorion Hardening. Comp Biochem Physiol 118:293–301. doi:10.1016/S0305-0491(97)00064-3
Yoshizaki G, Oshiro T, Takashima F (1991) Introduction of carp α-globin gene into rainbow trout. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57:819–824. doi:10.2331/suisan.57.819
Saito T, Fujimoto T, Maegawa S, Inoue K, Tanaka M, Arai K, Yamaha E (2006) Visualization of primordial germ cells in vivo using GFP- nos1 3′ UTR mRNA. Int J Dev Biol 50:691–700. doi:10.1387/ijdb.062143ts
Iwamatsu T (2004) Stages of normal development in the medaka Oryzias latipes. Mech Dev 121:605–618. doi:10.1016/j.mod.2004.03.012
Saito T, Arai K, Yamaha E (2004) The Embryonic Development of Shima-ukigori, Gymnogobius opperiens. Aquacult. Sci. 52:177–184. doi:10.11233/aquaculturesci1953.52.177
Kawakami T, Okouchi H, Aritaki M, Aoyama J, Tsukamoto K (2011) Embryonic development and morphology of eggs and newly hatched larvae of Pacific herring Clupea pallasii. Fish Sci 77:183–190. doi:10.1007/s12562-010-0317-4
Fujimoto T, Kataoka T, Otani S, Saito T, Aita T, Yamaha E, Arai K (2004) Embryonic stages from cleavage to gastrula in the loach Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. Zool Sci 21:747–755. doi:10.2108/zsj.21.747
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Fujimoto for assistance with this manuscript and to Dr. Shirakawa for statistical analysis. We also thank members of the Nanae Fresh-Water Station for assistance with obtaining experimental fish, conducting the experiments, and discussing the results. This study was supported by grants from the Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution (BRAIN) of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, E., Kawakami, Y., Arai, K. et al. Dechorionation of fertilized eggs and embryonic development in arctic rainbow smelt Osmerus eperlanus mordax . Fish Sci 82, 639–652 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-016-0995-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-016-0995-7