Abstract
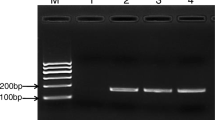
Major fish bacterial diseases in Korea are edwardsiellosis, streptococcosis, and vibriosis. Among vibrionaceae, Listonella anguillarum, Vibrio harveyi, V. ichthyoenteri, and Photobacterium damselae were identified as causative organisms of vibriosis in flounder. In this study, we developed a multiplex PCR method using the RNA polymerase β subunit (rpoB) gene, known as a housekeeping gene for identification of Vibrio spp. causing vibriosis in flounder. Three pairs of PCR primers were designed based on the rpoB sequence of three species, V. harveyi, V. ichthyoenteri, and P. damselae. The PCR assay, using a mixture of six primers, yielded amplicons of 601, 434, and 533 bp in V. harveyi, V. ichthyoenteri, and P. damselae. None of the untargeted species yielded an amplicon. The detection limits for pure culture in kidney were 2.5 × 104 cfu/g kidney for V. harveyi, 2.5 × 105 cfu/g kidney for V. ichthyoenteri, and 2.5 × 106 cfu/g kidney for P. damselae. From the colonies on TCBS agar plates of different samples, 632 Vibrio spp. isolated from aquacultured flounder between 2004 and 2010 were identified by the multiplex PCR method. As a result, 265 strains (41.9 %) were V. ichthyoenteri; 115 strains (18.2 %) were V. harveyi and 72 strains (11.4 %) were P. damselae.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim JW, Jung SH, Park MA, Do JW, Choi DL, Jee BY, Cho MY, Kim MS, Choi HS, Kim YC, Lee JS, Lee CH, Bang JD, Park MS, Seo JS (2006) Monitoring of pathogens in cultured fish of Korea for the summer period from 2000 to 2006. Kor J Fish Pathol 19:207–214
Edward JN (1996) Fish diseases: diagnosis and treatment. Iowa state university Press, USA
Kim DH, Han HJ, Kim SM, Lee DC, Park SI (2004) Bacterial enteritis and the development of the larval digestive tract in olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Kor J Fish Pathol 27:497–505
Won KM, Choi JH, Park SI (2006) Characteristics of the extracellular products (ECPs) of Vibrio harveyi grown under various conditions. Kor J Fish Pathol 19:119–126
Sunaryanto A, Mariam A (1986) Occurrence of pathogenic bacteria causing luminescence in penaeid larvae in Indonesian hatcheries. Bull Brackishwater Aqua Dev Cent 8:105–112
Lavilla-Pitogo CR, Baticados MCL, Cruz-Lacierda ER, Pena LD (1990) Occurrence of luminous bacterial disease of Penaeus monodon larvae in the Philippines. Aquaculture 91:1–13
Won KM, Park SI (2008) Pathogenicity of Vibrio harveyi to cultured marine fishes in Korea. Aquaculture 285:8–13
Fukuda Y, Matsuoka S, Mizuno Y, Narita K (1996) Pasteurella piscicida infection in cultured juvenile Japanese flounder. Fish Pathol 31:33–38
Kwon MG, Cho BY, Park SI (2009) Comparative study of Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae and Vibrios on pathogenicity in vivo. Kor J Fish Pathol 22:115–124
Gomez-Gil B, Soto-Rodrı′guez S, Garcı′a-Gasca A, Roque A, Vazquez-Juarez R, Thompson FL, Swings J (2004) Molecular identification of Vibrio harveyi-related isolates associated with diseased aquatic organisms. Microbiology 150:1769–1777
Moon YG, Heo MS (2005) Use of 16S–23S rRNA intergenic spacer region for species-specific primer developed of Vibrio Ichthyoenteri. Kor J Microbiol 41:117–124
Osorio CR, Toranzo AE, Romalde JL, Barja JL (2000) Multiplex PCR assay for ureC and 16s rRNA genes clearly discriminates between both subspecies of Photobacterium damselae. Dis Aquat Organ 40:177–183
Bauer Røvik LM (2007) A novel multiplex PCR for the identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus. Lett Appl Microbiol 45:371–375
Nhung PH, Ohkusu K, Miyasaka J, Sun XS, Ezaki T (2007) Rapid and specific identification of 5 human pathogenic Vibrio species by multiplex polymerase chain reaction targeted to dnaJ gene. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 59:271–275
Martens M, Dawyndt P, Coopman R, Gillis M, de Vos P, Wilems A (2008) Advantages of multilocus sequence analysis for taxonomic studies: a case study using 10 housekeeping genes in the genus Ensifer (including former Sinorhizobium). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:200–214
Klenk HP, Zillig W (1994) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase subunit B as a tool for phylogenetic reconstructions: branching topology of the archaeal domain. J Mol Evol 38:420–432
Tarr CL, Patel JS, Puhr ND, Sowers EG, Bopp CA, Strockbine NA (2007) Identification of Vibrio isolates by a multiplex PCR assay and rpoB sequence determination. J Clin Microbiol 45:134–140
Clarridge JE III (2004) Impact of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis for identification of bacteria on clinical microbiology and infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:840–862
Urakawa H, Kita-Tsukamoto K, Ohwada K (1997) 16S rDNA genotyping using PCR/RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) analysis among the family Vibrionaceae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 152:125–132
Kwok S, Kellogg DE, McKinney N, Spasic D, Goda L, Levenson C, Sninsky JJ (1990) Effects of primer-template mismatches on the polymerase chain reaction: human immunodeficiency virus type 1 model studies. Nucleic Acids Res 18(4):999–1005
Kutyavin IV, Afonina IA, Mills A, Gorn VV, Lukhtanov EA, Belousov ES, Singer MJ, Walburger DK, Lokhov SG, Gall AA, Dempcy R, Reed MW, Meyer RB, Hedgpeth J (2000) 3′-Minor groove binder-DNA probes increase sequence specificity at PCR extension temperatures. Nucleic Acids Res 28(2):655–661
Roux KH (2009) Optimization and troubleshooting in PCR. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 4:1–6
Fukui Y, Sawabe T (2007) Improved one-step colony PCR detection of Vibrio harveyi. Microbes Environ 22:1–10
Gonzalez SF, Osorio CR, Santos Y (2003) Development of a PCR-based method for the detection of Listonella anguillarum in fish tissues and blood samples. Dis Aquat Organ 55:109–115
Kwon MG, Park SU, Bang JD, Park SI (2005) Isolation of pathogenic Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae from olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Kor J Fish Pathol 18:205–214
Kim JY, Yang DK, Kim H, Kim CL, Choi JG, Kim YH, Jang H, Son SW (2010) Pathogenicity and isolation of Vibrio species from cultured olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus farms in Korea. Kor J Vet Public Health 34:89–94
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the funds of NFRDI in Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.S., Cho, J.Y. & Choi, H.S. Identification of Vibrio harveyi, Vibrio ichthyoenteri, and Photobacterium damselae isolated from olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in Korea by multiplex PCR developed using the rpoB gene. Fish Sci 80, 333–339 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-014-0702-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-014-0702-5