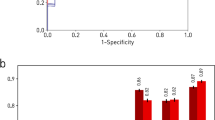
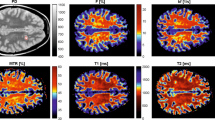
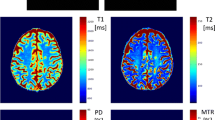
Abstract
Neurologists and radiologists often use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the management of subjects with multiple sclerosis (MS) because it is sensitive to inflammatory and demyelinative changes in the white matter of the brain and spinal cord. Two conventional modalities used for identifying lesions are T1-weighted (T1) and T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging, which are used clinically and in research studies. Magnetization transfer ratio (MTR), which is available only in research settings, is an advanced MRI modality that has been used extensively for measuring disease-related demyelination both in white-matter lesions as well across normal-appearing white matter. Acquiring MTR is not standard in clinical practice, due to the increased scan time and cost. Hence, prediction of MTR based on the modalities T1 and FLAIR could have great impact on the availability of these promising measures for improved patient management. We propose a spatio-temporal regression model for image response and image predictors that are acquired longitudinally, with images being co-registered within the subject but not across subjects. The model is additive, with the response at a voxel being dependent on the available covariates not only through the current voxel but also on the imaging information from the voxels within a neighboring spatial region as well as their temporal gradients. We propose a dynamic Bayesian estimation procedure that updates the parameters of the subject-specific regression model as data accumulate. To bypass the computational challenges associated with a Bayesian approach for high-dimensional imaging data, we propose an approximate Bayesian inference technique. We assess the model fitting and the prediction performance using longitudinally acquired MRI images from 46 MS patients.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry the methods. Neuroimage 11(6):805–821
Avants BB, Kandel BM, Duda JT, Cook PA, Tustison NJ, ANTsR SKL (2016) ANTs in R: quantification tools for biomedical images, R package version 0.3.3
Bilgel M, Prince JL, Wong DF, Resnick SM, Jedynak BM (2016) A multivariate nonlinear mixed effects model for longitudinal image analysis: application to amyloid imaging. Neuroimage 134:658–670
Brex PA, Ciccarelli O, O’Riordan JI, Sailer M, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2002) A longitudinal study of abnormalities on mri and disability from multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 346(3):158–164
Carass A, Wheeler MB, Cuzzocreo J, Bazin P-L, Bassett SS, Prince JL (2007) A joint registration and segmentation approach to skull stripping. In: Biomedical Imaging: from Nano to Macro, 2007. ISBI 2007. 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pp 656–659. IEEE
Casella G (1985) An introduction to empirical bayes data analysis. Am Stat 39(2):83–87
Catalaa I, Grossman RI, Kolson DL, Udupa JK, Nyul LG, Wei L, Zhang X, Polansky M, Mannon LJ, McGowan JC (2000) Multiple sclerosis: magnetization transfer histogram analysis of segmented normal-appearing white matter 1. Radiology 216(2):351–355
Chen Y, Wang X, Kong L, Zhu H (2016) Local region sparse learning for image-on-scalar regression. arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.08501
Dworkin J D, Sweeney E M, Schindler M K, Chahin S, Reich D S, Shinohara R T (2016) Prevail: predicting recovery through estimation and visualization of active and incident lesions. NeuroImage 12:293–299
Eidsvik J, Shaby BA, Reich BJ, Wheeler M, Niemi J (2014) Estimation and prediction in spatial models with block composite likelihoods. J Comput Graph Stat 23(2):295–315
Eloyan A, Shou H, Shinohara RT, Sweeney EM, Nebel MB, Cuzzocreo JL, Calabresi PA, Reich DS, Lindquist MA, Crainiceanu CM (2014) Health effects of lesion localization in multiple sclerosis: spatial registration and confounding adjustment. PLoS ONE 9(9):e107263
Fonov VS, Evans AC, McKinstry RC, Almli C, Collins D (2009) Unbiased nonlinear average age-appropriate brain templates from birth to adulthood. NeuroImage 47:S102
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline J-P, Frith CD, Frackowiak RS (1994) Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Human Brain Mapp 2(4):189–210
Gass A, Barker G, Kidd D, Thorpe J, MacManus D, Brennan A, Tofts P, Thompson A, McDonald W, Miller D (1994) Correlation of magnetization transfer ratio with clinical disability in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 36(1):62–67
Goldsmith J, Huang L, Crainiceanu CM (2014) Smooth scalar-on-image regression via spatial bayesian variable selection. J Comput Graph Stat 23(1):46–64
Griffin C, Parker GJ, Barker G, Thompson A, Miller D (2000) Mtr and t1 provide complementary information in ms nawm, but not in lesions. Mult Scler J 6(5):327–331
Grossman RI (1994) Magnetization transfer in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 36(S1):S97–S99
Hoff P (2011) Separable covariance arrays via the Tucker product, with applications to multivariate relational data. Bayesian Anal 6:179–196
Jog A, Carass A, Roy S, Pham DL, Prince JL (2015) Mr image synthesis by contrast learning on neighborhood ensembles. Med Image Anal 24(1):63–76
Jog A, Carass A, Roy S, Pham DL, Prince JL (2017) Random forest regression for magnetic resonance image synthesis. Med Image Anal 35:475–488
Kang J, Reich BJ, Staicu A-M (2016) Scalar-on-image regression via the soft-thresholded gaussian process. arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.03192
Kappos L, Moeri D, Radue EW, Schoetzau A, Schweikert K, Barkhof F, Miller D, Guttmann CR, Weiner HL, Gasperini C et al (1999) Predictive value of gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for relapse rate and changes in disability or impairment in multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis. Lancet 353(9157):964–969
Lai S-H, Fang M (1999) A new variational shape-from-orientation approach to correcting intensity inhomogeneities in magnetic resonance images. Med Image Anal 3(4):409–424
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung H-P, Lublin FD, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH, Reingold SC et al (2001) Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the international panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50(1):121–127
Mejia AF, Sweeney EM, Dewey B, Nair G, Sati P, Shea C, Reich DS, Shinohara RT (2016) Statistical estimation of t1 relaxation times using conventional magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 133:176–188
Moll NM, Rietsch AM, Thomas S, Ransohoff AJ, Lee J-C, Fox R, Chang A, Ransohoff RM, Fisher E (2011) Multiple sclerosis normal-appearing white matter: pathology-imaging correlations. Ann Neurol 70(5):764–773
Mori S, Wakana S, Van Zijl PC, Nagae-Poetscher L (2005) MRI atlas of human white matter. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Morris JS, Baladandayuthapani V, Herrick RC, Sanna P, Gutstein H (2011) Automated analysis of quantitative image data using isomorphic functional mixed models, with application to proteomics data. Ann Appl Stat 5(2A):894
Muschelli J, Extrantsr: Extra Functions to Build on the ANTsR Package. R package version 2.8
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan G, Filippi M, Hartung H-P, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Metz LM, McFarland HF, O’Connor PW et al (2005) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the mcdonald criteria. Ann Neurol 58(6):840–846
Pomann G-M, Staicu A-M, Lobaton EJ, Mejia AF, Dewey BE, Reich DS, Sweeney EM, Shinohara RT et al (2017) A lag functional linear model for prediction of magnetization transfer ratio in multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Appl Stat 10(4):2325–2348
Pomann G-M, Sweeney EM, Reich DS, Staicu A-M, Shinohara RT (2015) Scan-stratified case-control sampling for modeling blood-brain barrier integrity in multiple sclerosis. Stat Med 34(20):2872–2880
Ramsay JO (2006) Functional data analysis. Wiley, Hooken
Ramsay JO, Silverman BW (2006) Applied functional data analysis: methods and case studies, vol 77. Springer, New York
Reiss PT, Huo L, Zhao Y, Kelly C, Ogden RT et al (2015) Wavelet-domain regression and predictive inference in psychiatric neuroimaging. Ann Appl Stat 9(2):1076–1101
Roy S, Carass A, Prince JL (2013) Magnetic resonance image example-based contrast synthesis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 32(12):2348–2363
Schmierer K, Scaravilli F, Altmann DR, Barker GJ, Miller DH (2004) Magnetization transfer ratio and myelin in postmortem multiple sclerosis brain. Ann Neurol 56(3):407–415
Shi R, Kang J (2015) Thresholded multiscale gaussian processes with application to bayesian feature selection for massive neuroimaging data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1504.06074
Shiee N, Bazin P-L, Ozturk A, Reich DS, Calabresi PA, Pham DL (2010) A topology-preserving approach to the segmentation of brain images with multiple sclerosis lesions. NeuroImage 49(2):1524–1535
Shinohara RT, Crainiceanu CM, Caffo BS, Gaitán MI, Reich DS (2011) Population-wide principal component-based quantification of blood-brain-barrier dynamics in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage 57(4):1430–1446
Shinohara RT, Goldsmith J, Mateen F, Crainiceanu C, Reich DS (2012) Predicting breakdown of the blood-brain barrier in multiple sclerosis without contrast agents. Am J Neuroradiol 33(8):1586–1590
Shinohara R T, Sweeney E M, Goldsmith J, Shiee N, Mateen F J, Calabresi P A, Jarso S, Pham D L, Reich D S, Crainiceanu C M et al (2014) Statistical normalization techniques for magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 6:9–19
Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC (1997) A comparison of retrospective intensity non-uniformity correction methods for mri. In: Biennial International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging, pp 459–464. Springer
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, Watkins KE, Ciccarelli O, Cader MZ, Matthews PM et al (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31(4):1487–1505
Stein M (1999) Statistical interpolation of spatial data. Springer, New York
Suttner L H, Mejia A, Dewey B, Sati P, Reich D S, Shinohara R T (2016) Statistical estimation of white matter microstructure from conventional mri. NeuroImage 12:615–623
Sweeney E, Shinohara R, Shea C, Reich D, Crainiceanu C (2013) Automatic lesion incidence estimation and detection in multiple sclerosis using multisequence longitudinal mri. Am J Neuroradiol 34(1):68–73
Sweeney E M, Shinohara R T, Dewey B E, Schindler M K, Muschelli J , Reich D S, Crainiceanu C M, Eloyan A (2016) Relating multi-sequence longitudinal intensity profiles and clinical covariates in incident multiple sclerosis lesions. NeuroImage 10:1–17
Symms M, Jäger H, Schmierer K, Yousry T (2004) A review of structural magnetic resonance neuroimaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(9):1235–1244
Zhu H, Fan J, Kong L (2014) Spatially varying coefficient model for neuroimaging data with jump discontinuities. J Am Stat Assoc 109(507):1084–1098
Acknowledgements
The project described was supported in part by RO1NS085211, R21NS093349, and RO1MH 086633 from the National Institutes of Health. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies. This research was partially supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. The authors would like to acknowledge useful suggestions of Joseph Guinness and two anonymous reviewers which helped to improve the paper in several ways.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hazra, A., Reich, B.J., Reich, D.S. et al. A Spatio-Temporal Model for Longitudinal Image-on-Image Regression. Stat Biosci 11, 22–46 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12561-017-9206-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12561-017-9206-z