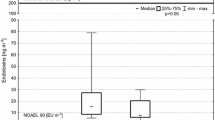
Abstract
Exposure to bioaerosols associated with wastewater treatment processes may represent an occupational health risk for workers at wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). A high frequency of acute symptoms in the gastrointestinal tract among the wastewater workers at a Danish WWTP has been reported. The objective of the study was therefore to examine the exposure of the workers to aerosolised microorganisms. Sampling of inhalable endotoxin, bacteria, moulds and viruses was performed on one occasion using personal samplers. Noroviruses (NoVs) and endotoxin were detected at concentrations that could pose an occupational health risk and possibly contribute to the increased frequency of gastrointestinal illness among the workers and should therefore be investigated further. In addition, positive correlations between exposure to endotoxin, bacteria, moulds and NoVs were found and indicate that the exposure to bioaerosols may be related to work tasks. This is the first study directly showing an occupational exposure to airborne NoVs by its detection in airborne dust.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizenberg, V., Grinshpun, S. A., Willeke, K., Smith, J., & Baron, P. A. (2000). Performance characteristics of the button personal inhalable aerosol sampler. AIHAJ, 61, 398–404.
Boon, N., De Windt, W., Verstraete, W., & Top, E. M. (2002). Evaluation of nested PCR-DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) with group-specific 16S rRNA primers for the analysis of bacterial communities from different wastewater treatment plants. FEMS Microbiology and Ecology, 39, 101–112.
Bünger, J., Antlauf-Lammers, M., Schulz, T. G., Westphal, G. A., Müller, M. M., Ruhnau, P., et al. (2000). Health complaints and immunological markers of exposure to bioaerosols among biowaste collectors and compost workers. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 57, 458–464.
Cheesbrough, J. S., Green, J., Gallimore, C. I., Wright, P. A., & Brown, D. W. G. (2000). Widespread environmental contamination with Norwalk-like viruses (NLV) detected in a prolonged hotel outbreak of gastroenteritis. Epidemiology and Infection, 125, 93–98.
Clark, C. S. (1987). Potential and actual biological related health risks of wastewater industry employment. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation, 59, 999–1008.
Clark, C. S., Linnemann, J., & Gartside, P. S. (1985). Serologic survey of rotavirus, Norwalk agent and prototheca wickerhamii in wastewater workers. American Journal of Public Health, 75, 83–85.
Clark, C. S., Rylander, R., & Larsson, L. (1983). Levels of gram-negative bacteria, Aspergillus fumigatus, dust, and endotoxin at compost plants. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 45, 1501–1505.
Comelli, H. L., Rimstad, E., Larsen, S., & Myrmel, M. (2008). Detection of norovirus genotype I.3b and II.4 in bioaccumulated blue mussels using different virus recovery methods. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 127, 53–59.
Costafreda, M. I., Bosch, A., & Rosa, M. (2006). Development, evaluation, and standardization of a real-time TaqMan reverse transcription-PCR assay for quantification of hepatitis A virus in clinical and shellfish samples. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 3846–3855.
Da Silva, A. K., Le Saux, J. C., Parnaudeau, S., Pommepuy, M., Elimelech, M., & Le Guyader, F. (2007). Evaluation of removal of noroviruses during wastewater treatment, using real-time reverse transcription-PCR: Different behaviors of genogroups I and II. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 7891–7897.
Donham, K. J., Cumro, D., Reynolds, S. J., & Merchant, J. A. (2000). Dose-response relationships between occupational aerosol exposures and cross-shift declines of lung function in poultry workers: Recommendations for exposure limits. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 42, 260–269.
Douwes, J., Mannetje, A., & Heederik, D. (2001). Work-related symptoms in sewage treatment workers. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, 8, 39–45.
Eduard, W. (2009). Fungal spores: A critical review of the toxicological and epidemiological evidence as a basis for occupational exposure limit setting. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 39, 799–864.
Gentry, J., Vinjé, J., & Lipp, E. K. (2009). A rapid and efficient method for quantitation of genogroups I and II norovirus from oysters and application in other complex environmental samples. Journal of Virological Methods, 156, 59–65.
Grisoli, P., Rodolfi, M., Villani, S., Grignani, E., Cottica, D., Berri, A., et al. (2009). Assessment of airborne microorganism contamination in an industrial area characterized by an open composting facility and a wastewater treatment plant. Environmental Research, 109, 135–142.
Haas, D., Unteregger, M., Habib, J., Galler, H., Marth, E., & Reinthaler, F. F. (2010). Exposure to Bioaerosol from sewage systems. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 207, 49–56.
Haramoto, E., Katayama, H., Oguma, K., Ohgaki, S., Yamashita, H., Tajima, A., et al. (2006). Seasonal profiles of human noroviruses and indicator bacteria in a wastewater treatment plant in Tokyo, Japan. Water Science and Technology, 54, 301–308.
Heinonen-Tanski, H., Reponen, T., & Koivunen, J. (2009). Airborne enteric coliphages and bacteria in sewage treatment plants. Water Research, 43, 2558–2566.
Ivens, U. I., Breum, N. O., Ebbehoj, N., Nielsen, B. H., Poulsen, O. M., & Wurtz, H. (1999). Exposure-response relationship between gastrointestinal problems among waste collectors and bioaerosol exposure. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment and Health, 25, 238–245.
Jones, A. M., & Harrison, R. M. (2004). The effects of meteorological factors on atmospheric bioaerosol concentrations—A review. Science of the Total Environment, 326, 151–180.
Jothikumar, N., Cromeans, T. L., Hill, V. R., Lu, X., Sobsey, M. D., & Erdman, D. D. (2005). Quantitative real-time PCR assays for detection of human adenoviruses and identification of serotypes 40 and 41. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 3131–3136.
Kageyama, T., Kojima, S., Shinohara, M., Uchida, K., Fukushi, S., Hoshino, F. B., et al. (2003). Broadly reactive and highly sensitive assay for Norwalk-like viruses based on real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41, 1548.
Katayama, H., Haramoto, E., Oguma, K., Yamashita, H., Tajima, A., Nakajima, H., et al. (2008). One-year monthly quantitative survey of noroviruses, enteroviruses, and adenoviruses in wastewater collected from six plants in Japan. Water Research, 42, 1441–1448.
Kenny, L. C., Aitken, R. J., Baldwin, P. E. J., Beaumont, G. C., & Maynard, A. D. (1999). The sampling efficiency of personal inhalable aerosol samplers in low air movement environments. Journal of Aerosol Science, 30, 627–638.
Kenny, L. C., Aitken, R., Chalmers, C., Fabriès, J. F., Gonzalez-Fernandez, E., Kromhout, H., et al. (1997). A collaborative European study of personal inhalable aerosol sampler performance. Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 41, 135–153.
Kerr, S. M., Muranko, H. J., & Vincent, J. H. (2002). Personal sampling for inhalable aerosol exposures of carbon black manufacturing industry workers. Applied Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, 17, 681–692.
Khuder, S. A., Arthur, T., Bisesi, M. S., & Schaub, E. A. (1998). Prevalence of infectious diseases and associated symptoms in wastewater treatment workers. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 33, 571–577.
Laitinen, S., Nevalainen, A., Kotimaa, M., Liesivuori, J., & Martikainen, P. J. (1992). Relationship between bacterial counts and endotoxin concentrations in the air of wastewater treatment plants. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58, 3774–3776.
Le Guyader, F., Parnaudeau, S., Schaeffer, J., Bosch, A., Loisy, F., Pommepuy, M., et al. (2009). Detection and quantification of noroviruses in shellfish. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 618–624.
Loisy, F., Atmar, R. L., Guillon, P., Le Cann, P., Pommepuy, M., & Le Guyader, F. S. (2005). Real-time RT-PCR for norovirus screening in shellfish. Journal of Virological Methods, 123, 1–7.
Lopman, B., Zambon, M., & Brown, D. W. (2008). The evolution of Norovirus, “the Gastric Flu”. PloS Medicine, 5, 187–189.
Lundholm, M., & Rylander, R. (1983). Work related symptoms among sewage workers. British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 40, 325–329.
Madsen, A. M. (2006a). Airborne endotoxin in different background environments and seasons. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, 13, 81–86.
Madsen, A. M. (2006b). Exposure to airborne microbial components in autumn and spring during work at Danish biofuel plants. Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 50, 821–831.
Madsen, A. M., & Sharma, A. K. (2008). Sampling of high amounts of bioaerosols using a high-volume electrostatic field sampler. Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 52, 167–176.
Marks, P. J., Vipond, I. B., Carlisle, D., Deakin, D., Fey, R. E., & Caul, E. O. (2000). Evidence for airborne transmission of norwalk-like virus (NLV) in a hotel restaurant. Epidemiology and Infection, 124, 481–487.
Marks, P. J., Vipond, I. B., Regan, F. M., Wedgwood, K., Fey, R. E., & Caul, E. O. (2003). A school outbreak of Norwalk-like virus: Evidence for airborne transmission. Epidemiology and Infection, 131, 727–736.
Melbostad, E., Eduard, W., Skogstad, A., Sandven, P., Lassen, J., Sostrand, P., et al. (1994). Exposure to bacterial aerosols and work-related symptoms in sewage workers. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 25, 59–63.
Nielsen, E. M., Breum, N. O., Nielsen, B. H., Würtz, H., Poulsen, O. M., & Midtgaard, U. (1997). Bioaerosol exposure in waste collection: A comparative study on the significance of collection equipment, type of waste and seasonal variation. Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 41, 325–344.
Nordgren, J., Matussek, A., Mattsson, A., Svensson, L., & Lindgren, P. E. (2009). Prevalence of norovirus and factors influencing virus concentrations during one year in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. Water Research, 43, 1117–1125.
Oppliger, A., Duc, T. V., & Hilfiker, S. (2005). Influence of seasons and sampling strategy on assessment of bioaerosols in sewage treatment plants in Switzerland. Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 49, 393–400.
Palmgren, U., Ström, G., Blomquist, G., & Malmberg, P. (1986). Collection of airborne microorganisms on nucleopore filters, estimation and analysis-CAMNEA method. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 61, 401–406.
Pepys, J., Jenkins, P. A., Festenstein, G. N., Gregory, P. H., Lacey, M. E., & Skinner, F. A. (1963). Farmer’s lung. Thermophilic actinomycetes as a source of “Farmer’s Lung Hay” antigen. Lancet, 2, 607–611.
Rylander, R. (1999). Health effects among workers in sewage treatment plants. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 56, 354–357.
Sanchez-Monedero, M. A., Aguilar, M. I., Fenoll, R., & Roig, A. (2008). Effect of the aeration system on the levels of airborne microorganisms generated at wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 42, 3739–3744.
Schultz, A. C., Perelle, S., Di Pasquale, S., Kovac, K., De Medici, D., Fach, P., et al. (2011). Collaborative validation of a rapid method for efficient virus concentration in bottled water. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 145, 158–166.
Smit, L. A. M., Spaan, S., & Heederik, D. (2005). Endotoxin exposure and symptoms in wastewater treatment workers. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 48, 30–39.
Svraka, S., Duizer, E., Vennema, H., Bruin, E. D., Veer, B. V. D., Dorresteijn, B., et al. (2007). Etiological role of viruses in outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis in the Netherlands from 1994 through 2005. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 45, 1389–1394.
Teunis, P. F. M., Moe, C. L., Liu, P., Miller, S. E., Lindesmith, L., Baric, R. S., et al. (2008). Norwalk virus: How infectious is it? Journal of Medical Virology, 80, 1468–1476.
Thorn, J., Beijer, L., & Rylander, R. (2002). Work related symptoms among sewage workers: A nationwide survey in Sweden. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 59, 562–566.
Uhrbrand, K., Myrmel, M., Maunula, L., Vainio, K., Trebbien, R., Nørrung, B., et al. (2010). Evaluation of a rapid method for recovery of norovirus and hepatitis A virus from oysters and blue mussels. Journal of Virological Methods, 169, 70–78.
Van Hooste, W., Charlier, A. M., Rotsaert, P., Bulterys, S., Moens, G., van Sprundel, M., et al. (2010). Work-related Helicobacter pylori infection among sewage workers in municipal wastewater treatment plants in Belgium. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 67, 91–97.
Vinjé, J. (2010). A Norovirus vaccine on the horizon? Journal of Infectious Diseases, 202, 1623–1625.
Acknowledgments
The work was partially supported by grant NKJ-130 from the Nordic Joint Committee for Agricultural Research. We highly acknowledged Thora Brendstrup and Birgitte Zwicky-Hauschild at Occupational Health Consultancy, City of Copenhagen, as well as Albert Dam for initiating this study. We thank Margit W. Frederiksen for skilful technical assistance and the WWTP workers for their participation in the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uhrbrand, K., Schultz, A.C. & Madsen, A.M. Exposure to Airborne Noroviruses and Other Bioaerosol Components at a Wastewater Treatment Plant in Denmark. Food Environ Virol 3, 130–137 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-011-9068-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-011-9068-3